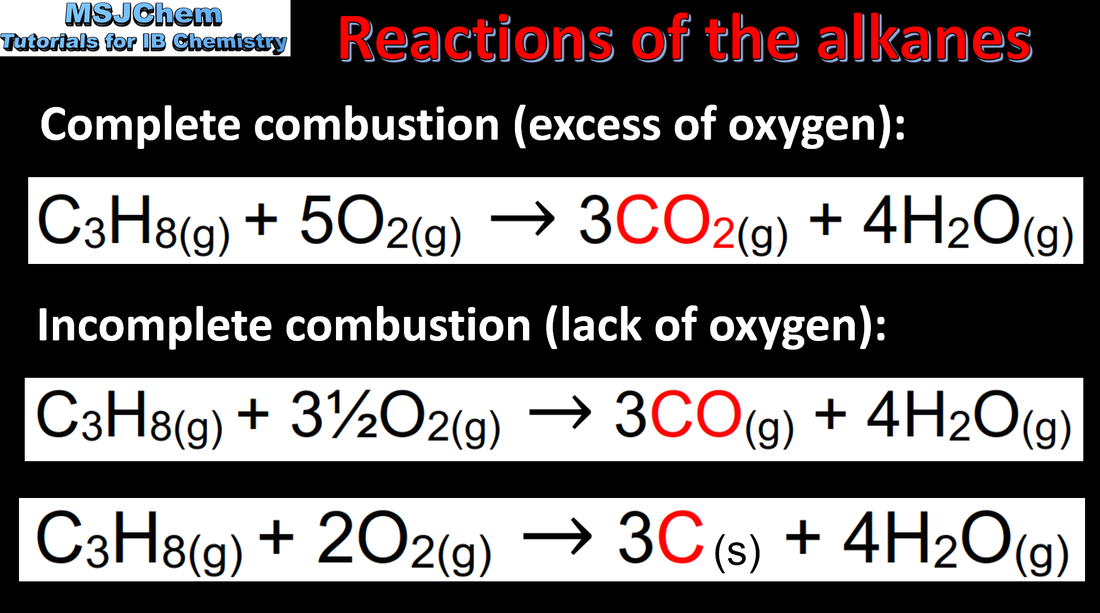Reactivity 1.3 Energy from fuels
Reactivity 1.3.1 and 1.3.2
Understandings:
Understandings:
- Reactive metals, non-metals and organic compounds undergo combustion reactions when heated in oxygen (1.3.1).
- Incomplete combustion of organic compounds, especially hydrocarbons, leads to the production of carbon monoxide and carbon (1.3.2).
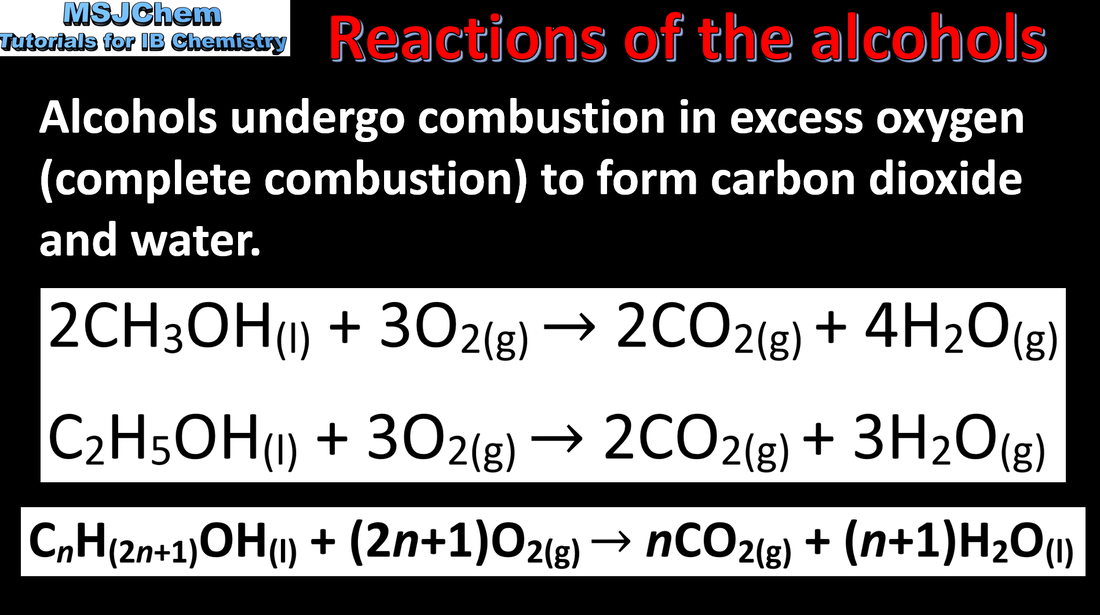
- Deduce equations for reactions of combustion, including hydrocarbons and alcohols (1.3.1).
- Deduce equations for the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons and alcohols (1.3.2).
- Reactivity 2.2 Why is high activation energy often considered to be a useful property of a fuel?
- Reactivity 3.2 Which species are the oxidizing and reducing agents in a combustion reaction?
- Reactivity 2.1 How does limiting the supply of oxygen in combustion affect the products and increase health risks?
Reactivity 1.3.3
Understandings:
Understandings:
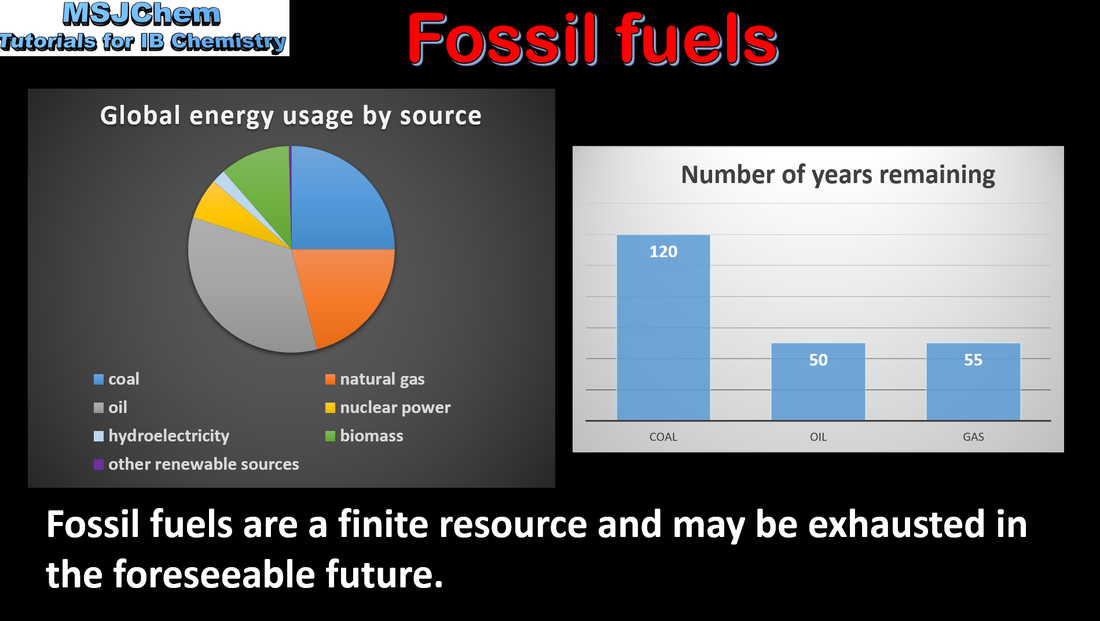
- Fossil fuels include coal, crude oil and natural gas, which have different advantages and disadvantages.
- Evaluate the amount of carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere when different fuels burn.
- Understand the link between carbon dioxide levels and the greenhouse effect.
- The tendency for incomplete combustion and energy released per unit mass should be covered.
- Structure 3.2 Why do larger hydrocarbons have a greater tendency to undergo incomplete combustion?
- Structure 3.2 (HL) Why is carbon dioxide described as a greenhouse gas?
Reactivity 1.3.4
Understandings:
Understandings:
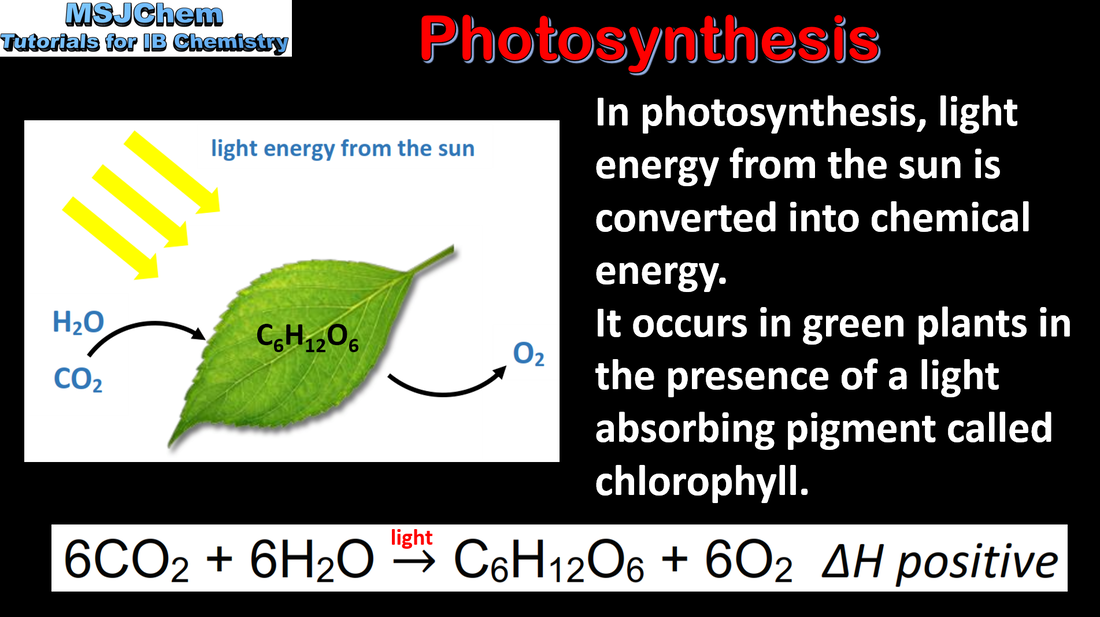
- Biofuels are produced from the biological fixation of carbon over a short period of time through photosynthesis.
- Understand the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources.
Consider the advantages and disadvantages of biofuels.
- The reactants and products of photosynthesis should be known.
Reactivity 1.3.5
Understandings:
Understandings:
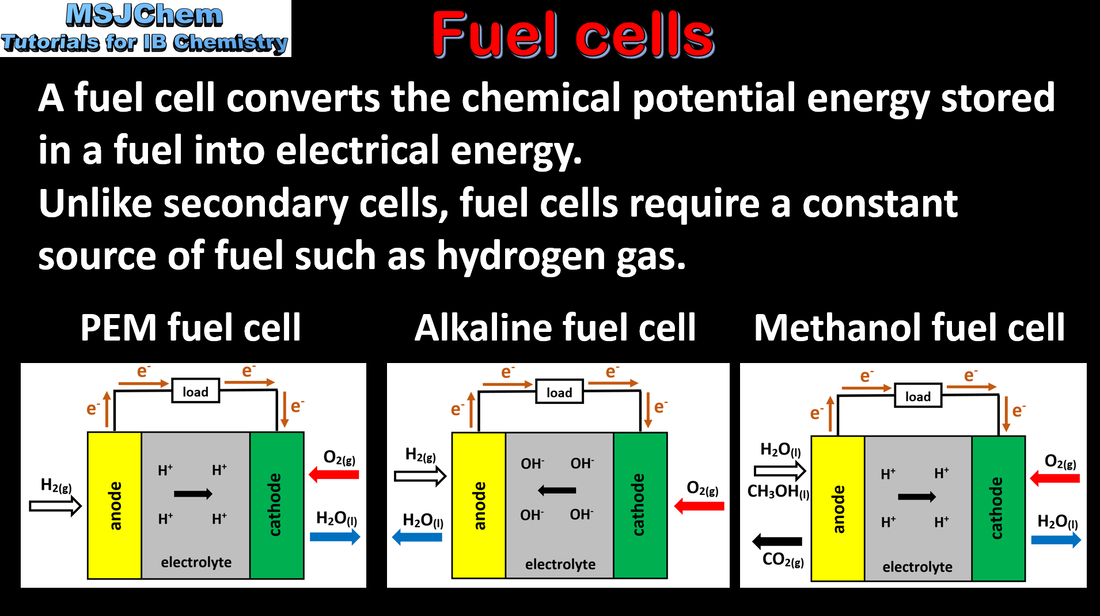
- A fuel cell can be used to convert chemical energy from a fuel directly to electrical energy.
- Deduce half-equations for the electrode reactions in a fuel cell.
- Hydrogen and methanol should be covered as fuels for fuel cells.
- The use of proton exchange membranes will not be assessed.
- Reactivity 3.2 What are the main differences between a fuel cell and a primary (voltaic) cell?