Structure 1.1 Introduction to the particluate nature of matter
Structure 1.1.1
Understandings:
Understandings:
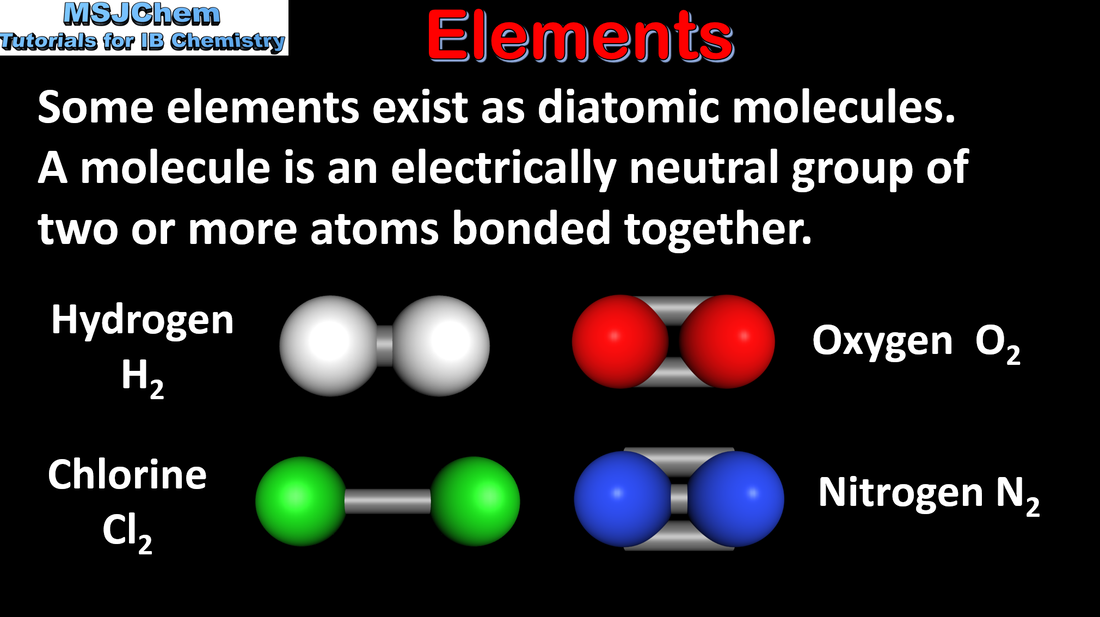
- Elements are the primary constituents of matter, which cannot be chemically broken down into simpler substances.
- Compounds consist of atoms of different elements chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio.
- Mixtures contain more than one element or compound in no fixed ratio, which are not chemically bonded and so can be separated by physical methods.
- Distinguish between the properties of elements, compounds and mixtures.
- Solvation, filtration, recrystallization, evaporation, distillation and chromatography should be covered.
- The differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures should be understood.
|
This video covers elements, compounds and mixtures.
The techniques that students need to be familiar with are:
|
Structure 1.1.2
Understandings:
Understandings:
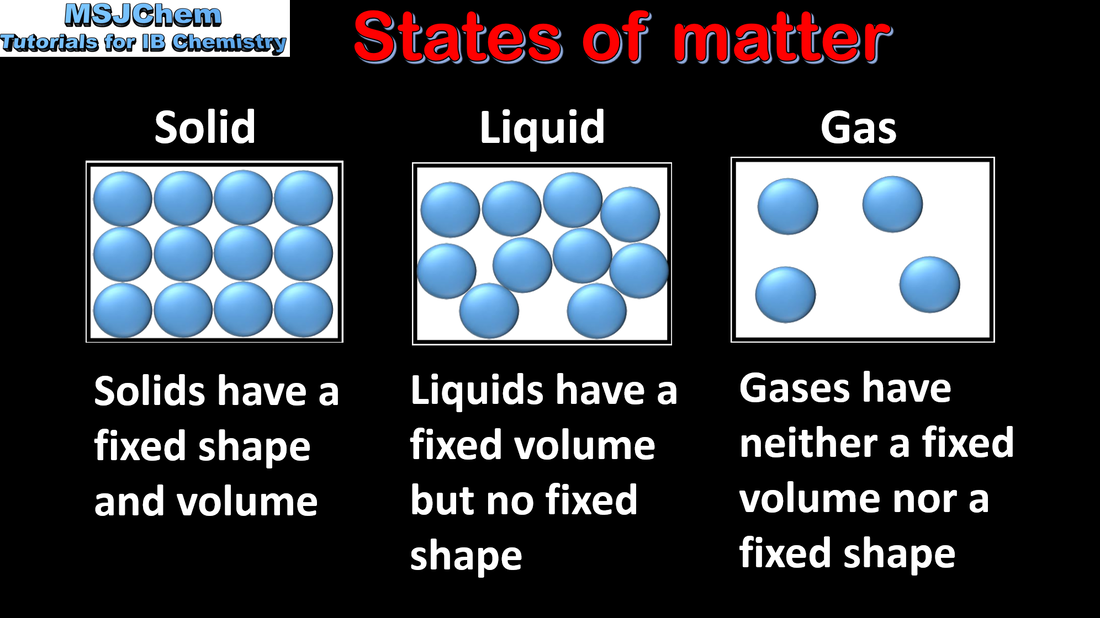
- The kinetic molecular theory is a model to explain physical properties of matter (solids, liquids and gases) and changes of state.
- Distinguish the different states of matter.
- Use state symbols (s, l, g and aq) in chemical equations.
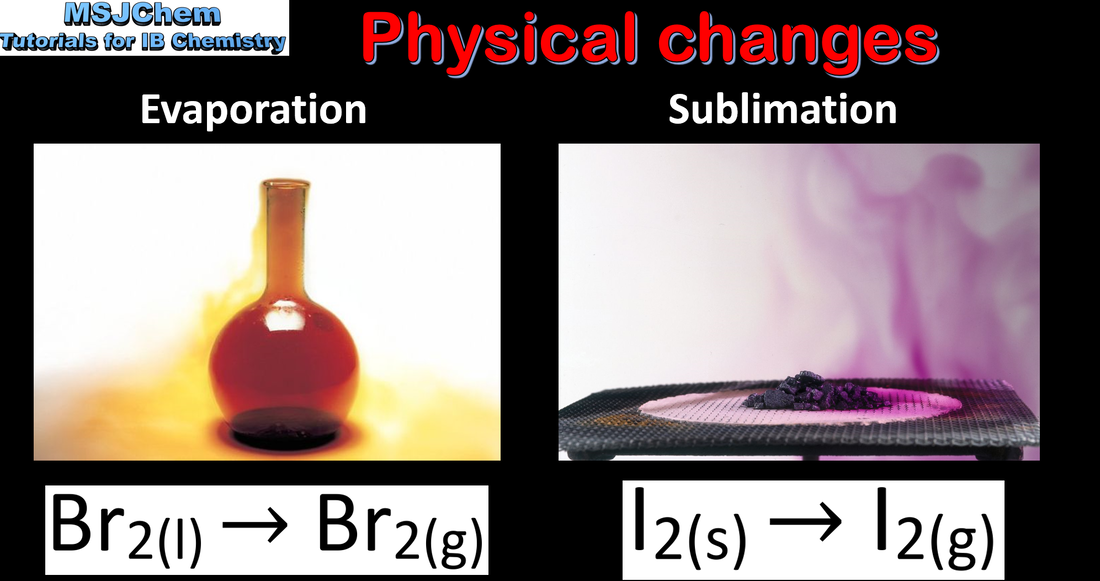
- Names of the changes of state should be covered: melting, freezing, vaporization (evaporation and boiling), condensation, sublimation and deposition.
Structure 1.1.3
Understandings:
Understandings:
- The temperature, T, in Kelvin (K) is a measure of average kinetic energy Ek of particles.
- Interpret observable changes in physical properties and temperature during changes of state.
- Convert between values in the Celsius and Kelvin scales.
- The kelvin (K) is the SI unit of temperature and has the same incremental value as the Celsius degree (°C).
|
Video coming soon
|