Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
Topic 6 Kinetics
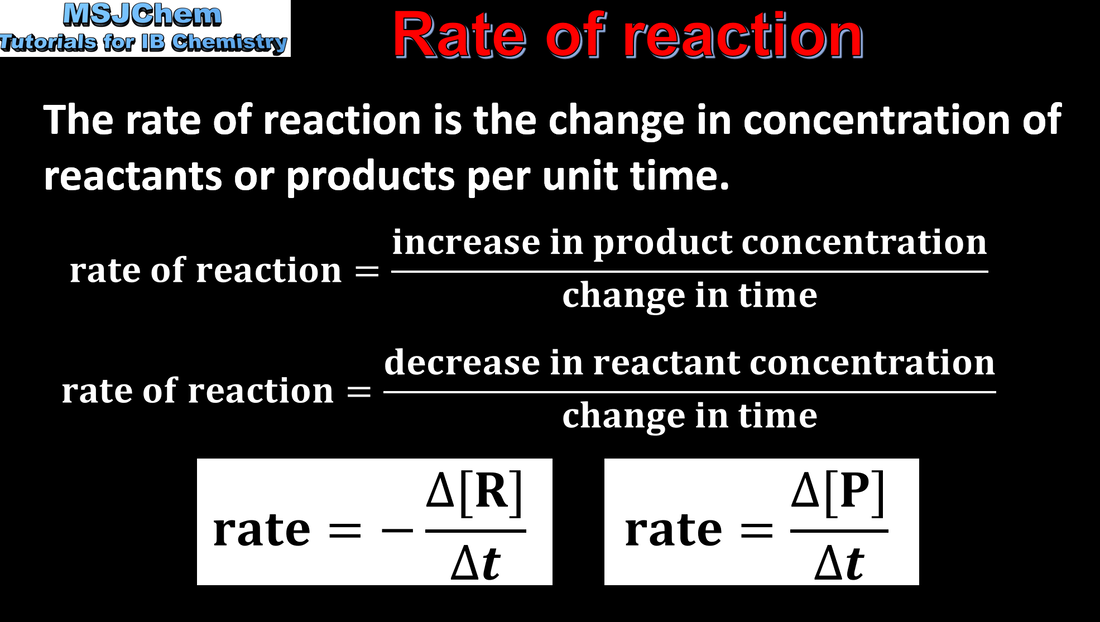
Rate of reaction
6.1 Experiments that measure rate of reaction
|
|
Understandings:
Concentration changes in a reaction can be followed indirectly by monitoring changes in mass, volume and colour. |
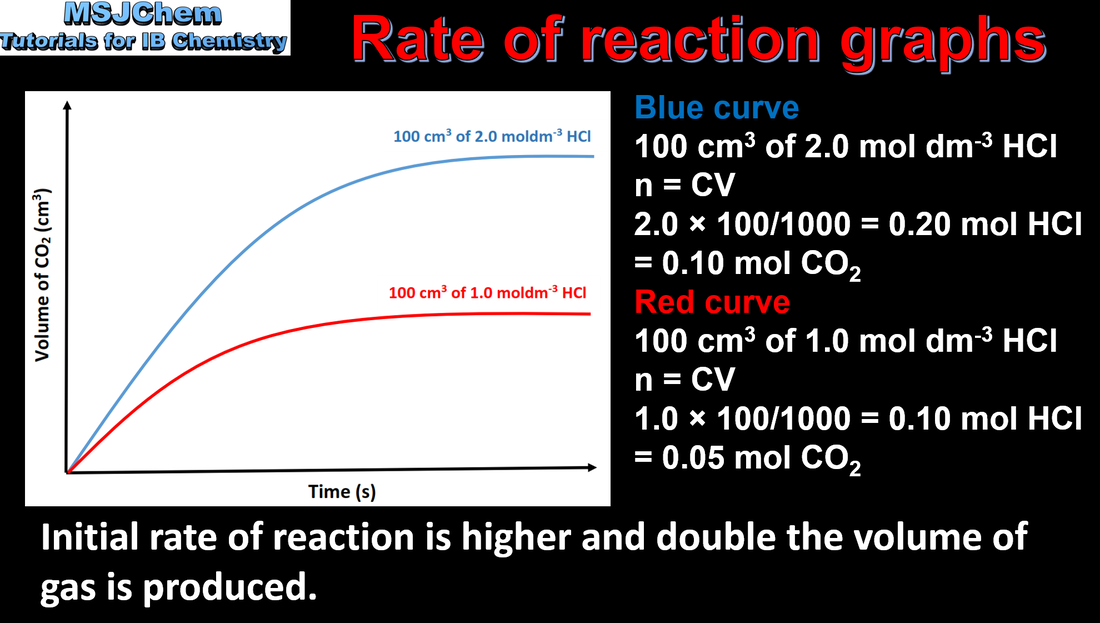
6.1 Analysing rate of reaction graphs
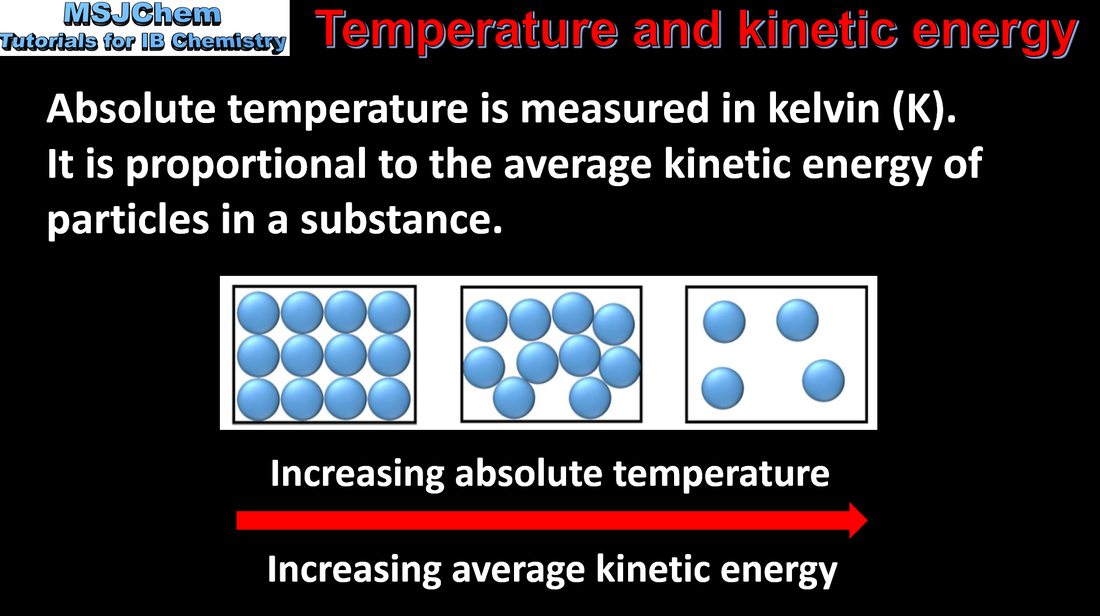
6.1 Temperature and kinetic energy
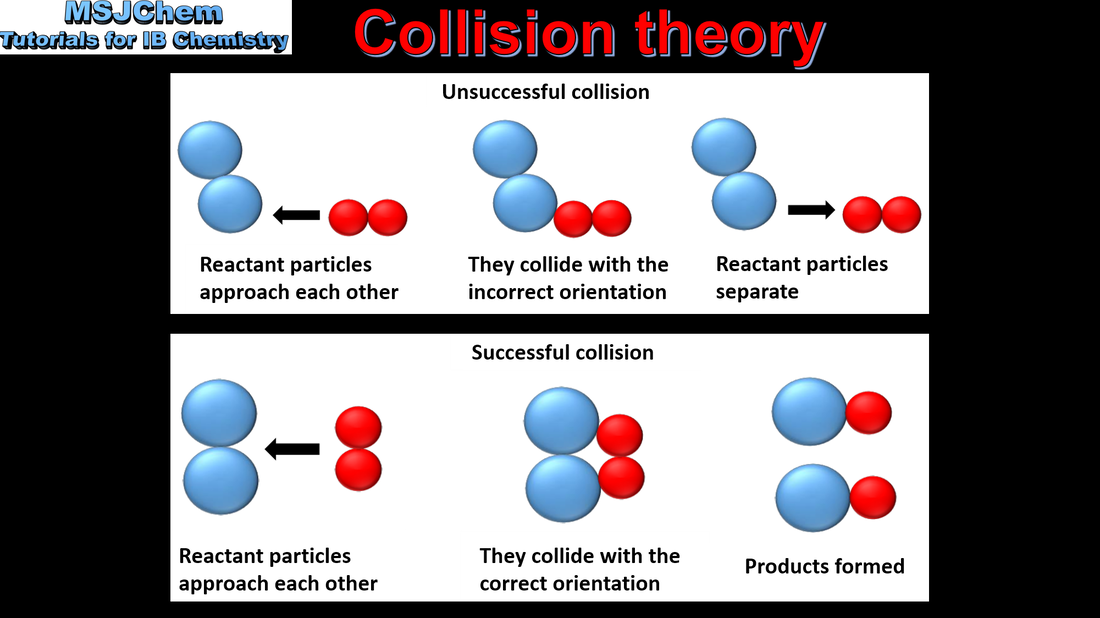
6.1 Collision theory
6.1 Activation energy
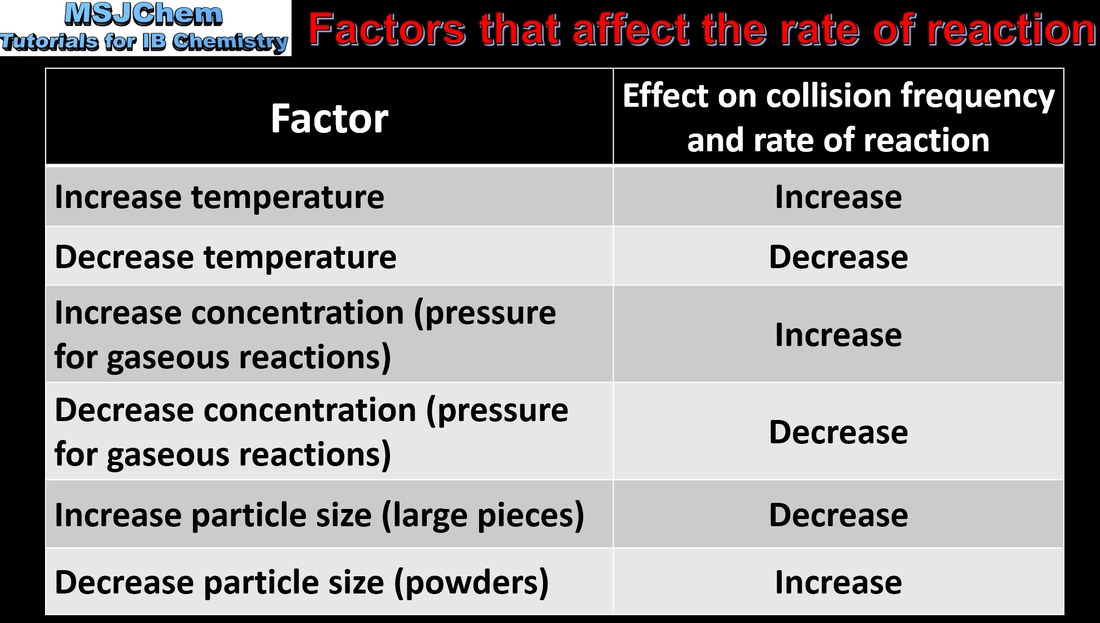
6.1 Factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction
|
Applications and skills:
Explanation of the effects of temperature, pressure/concentration and particle size on rate of reaction. Construction of Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves to account for the probability of successful collisions and factors affecting these, including the effect of a catalyst (catalysts are covered in the next video). |
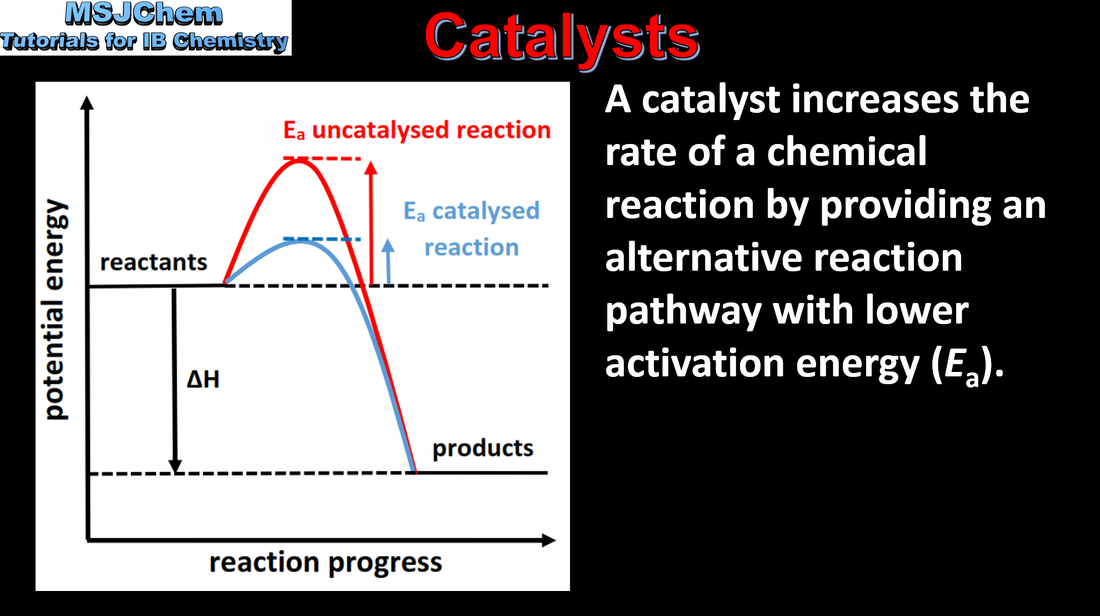
6.1 The effect of catalysts on the rate of a reaction
|
Understandings:
By decreasing Ea, a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction, without itself being permanently chemically changed. Applications and skills: Construction of Maxwell–Boltzmann energy distribution curves to account for the probability of successful collisions and factors affecting these, including the effect of a catalyst. Sketching and explanation of energy profiles with and without catalysts. |