Reactivity 3.3 Electron sharing reactions
Reactivity 3.3.1 and 3.3.2
Understandings:
Understandings:
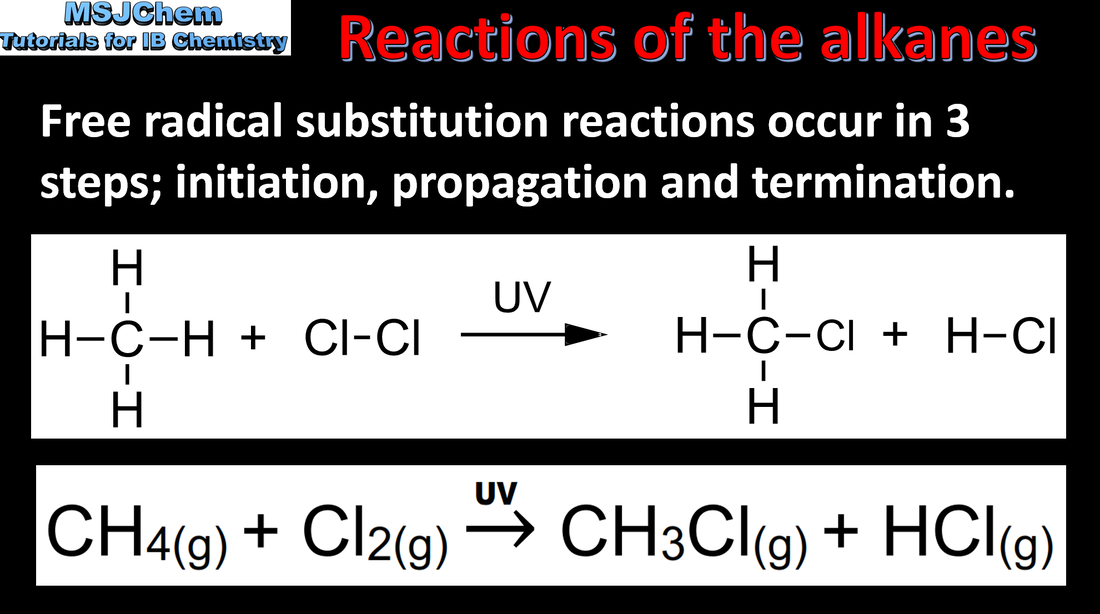
- A radical is a chemical entity that has an unpaired electron. Radicals are highly reactive.
- Radicals are produced by homolytic fission, e.g. of halogens, in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light or heat.
- Identify and represent radicals.
- Explain, including with equations, the homolytic fission of halogens, known as the initiation step in a chain reaction.
- Structure 2.1 How is it possible for a radical to be an atom, a molecule, a cation or an anion? Consider examples of each type.
Reactivity 3.3.3
Understandings:
Understandings:
- Radicals take part in substitution reactions with alkanes, producing a mixture of products.
- Explain, using equations, the propagation and termination steps in the reactions between alkanes and halogens.
- Reference should be made to the stability of alkanes due to the strengths of the C–C and C–H bonds and their essentially non-polar nature.
- Reactivity 2.2 Why are alkanes described as kinetically stable but thermodynamically unstable?