Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
|
|
Understandings:
Qualitative data includes all non-numerical information obtained from observations not from measurement. Quantitative data are obtained from measurements, and are always associated with random errors/uncertainties, determined by the apparatus, and by human limitations such as reaction times. |
|
|
Applications and skills:
Record uncertainties in all measurements as a range (+) to an appropriate precision. |
|
|
Understandings:
Experimental design and procedure usually lead to systematic errors in measurement, which cause a deviation in a particular direction. Repeat trials and measurements will reduce random errors but not systematic errors. Applications and skills: Distinction between random errors and systematic errors. Discussion of systematic errors in all experimental work, their impact on the results and how they can be reduced. |
|
|
Understandings:
Propagation of random errors in data processing shows the impact of the uncertainties on the final result. Applications and skills: Propagation of uncertainties in processed data, including the use of percentage uncertainties. |
|
|
Applications and skills:
Calculation of percentage error when the experimental result can be compared with a theoretical or accepted result. |
|
|
Understandings:
The degree of unsaturation or index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) can be used to determine from a molecular formula the number of rings or multiple bonds in a molecule. |
|
Understandings:
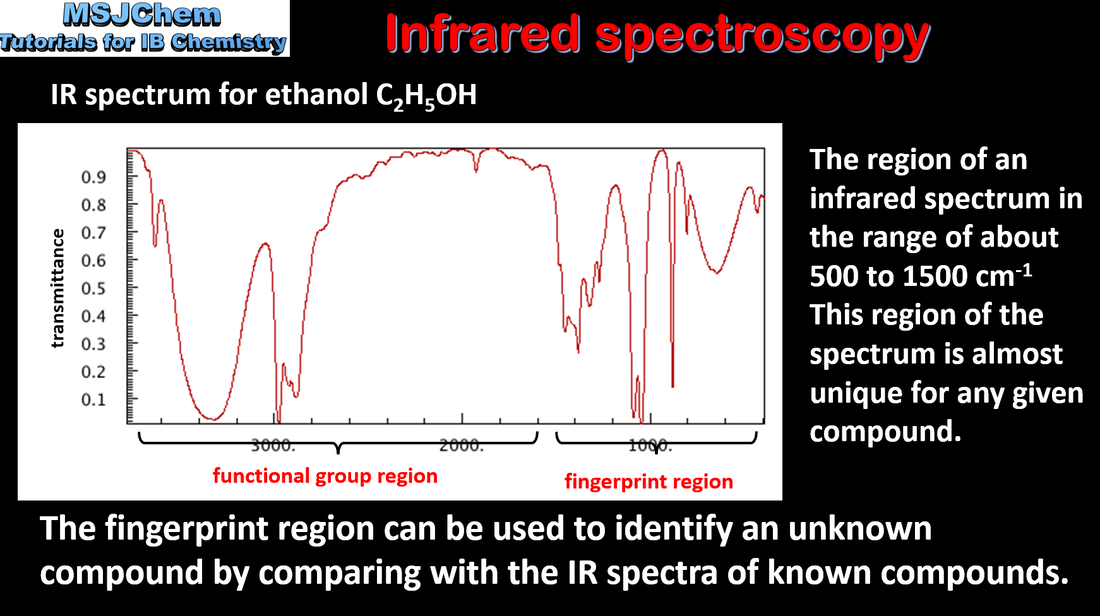
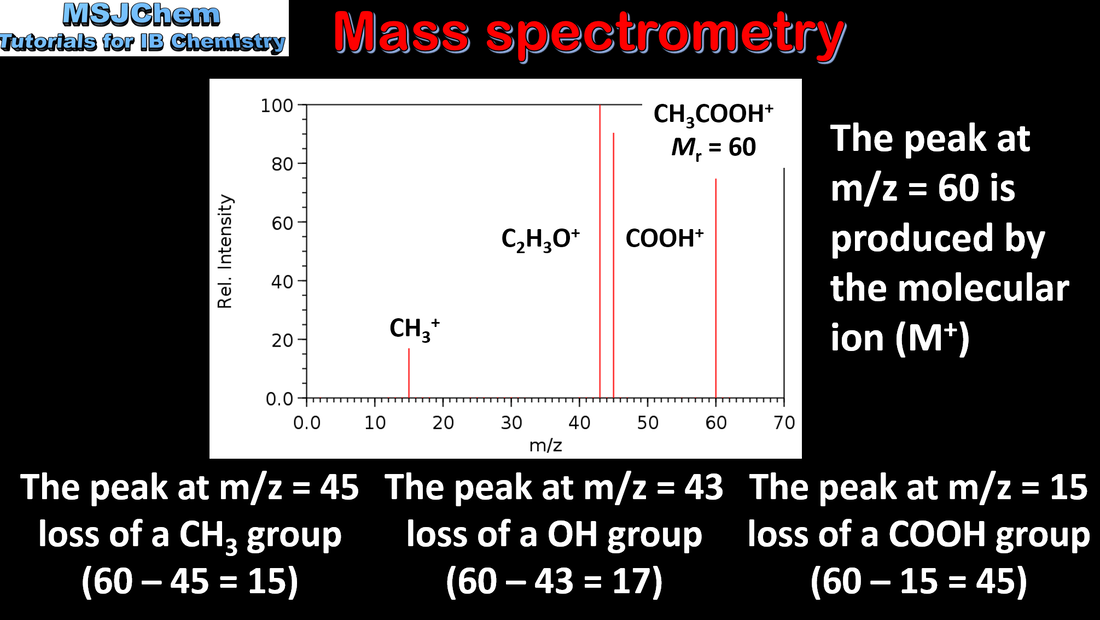
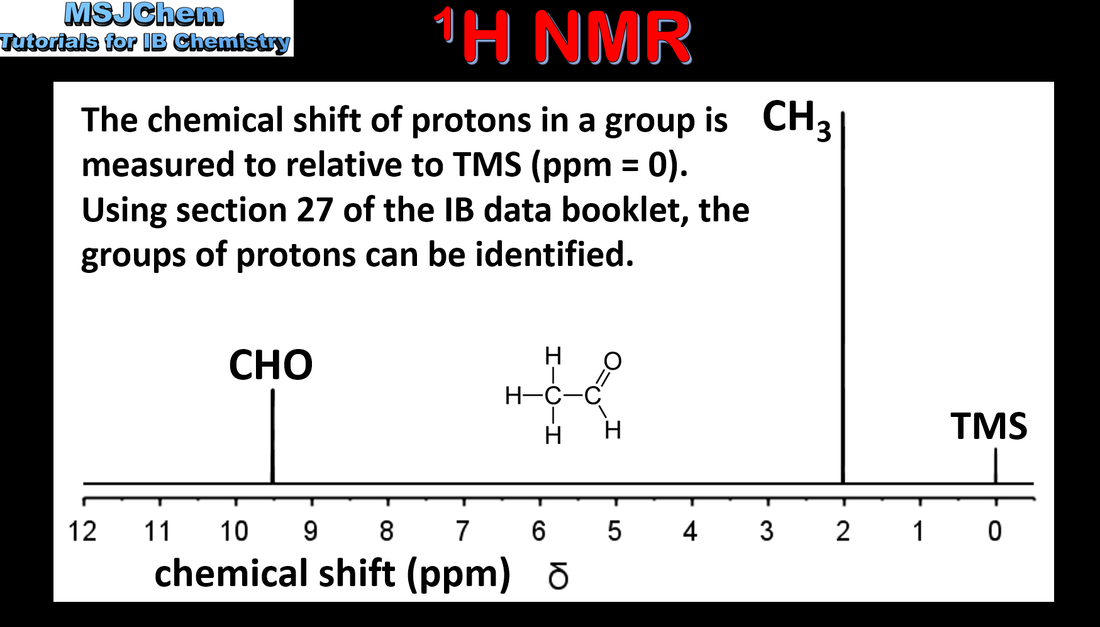
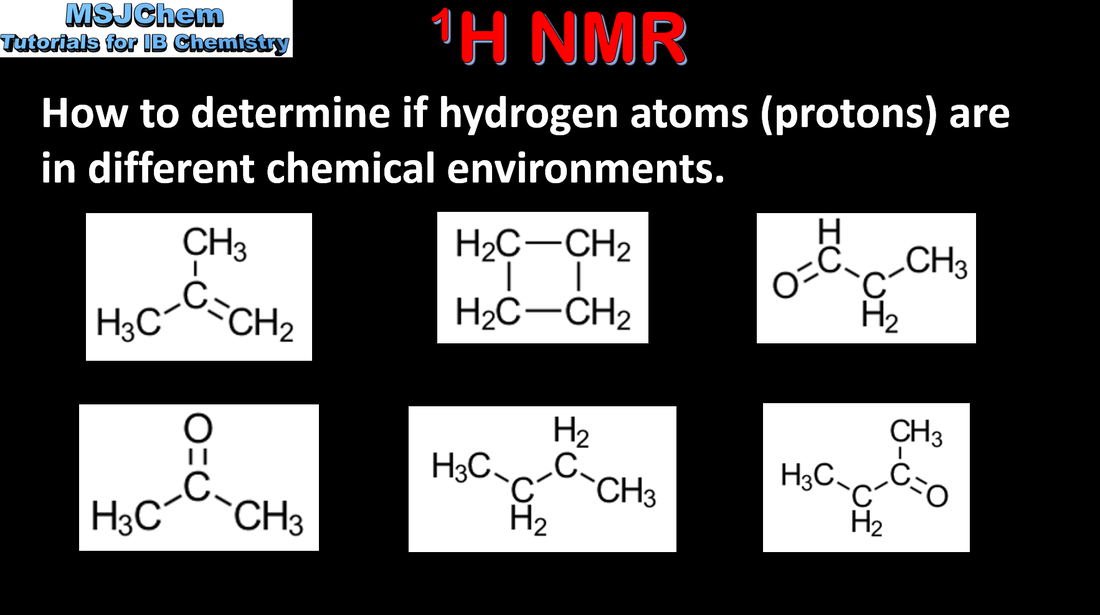
Mass spectrometry (MS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) are techniques that can be used to help identify compounds and to determine their structure. Applications and skills: Deduction of information about the structural features of a compound from percentage composition data, MS, 1H NMR or IR. Guidance: The regions employed for each technique should be understood. The operating principles are not required for any of these methods. |
|
Understandings:
Mass spectrometry (MS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) are techniques that can be used to help identify compounds and to determine their structure. Applications and skills: Deduction of information about the structural features of a compound from percentage composition data, MS, 1H NMR or IR. |
|
Understandings:
Mass spectrometry (MS), proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H NMR) and infrared spectroscopy (IR) are techniques that can be used to help identify compounds and to determine their structure. Applications and skills: Deduction of information about the structural features of a compound from percentage composition data, MS, 1H NMR or IR. |