Topic 14 Bonding HL
14.1 VSEPR (HL)
|
Understandings:
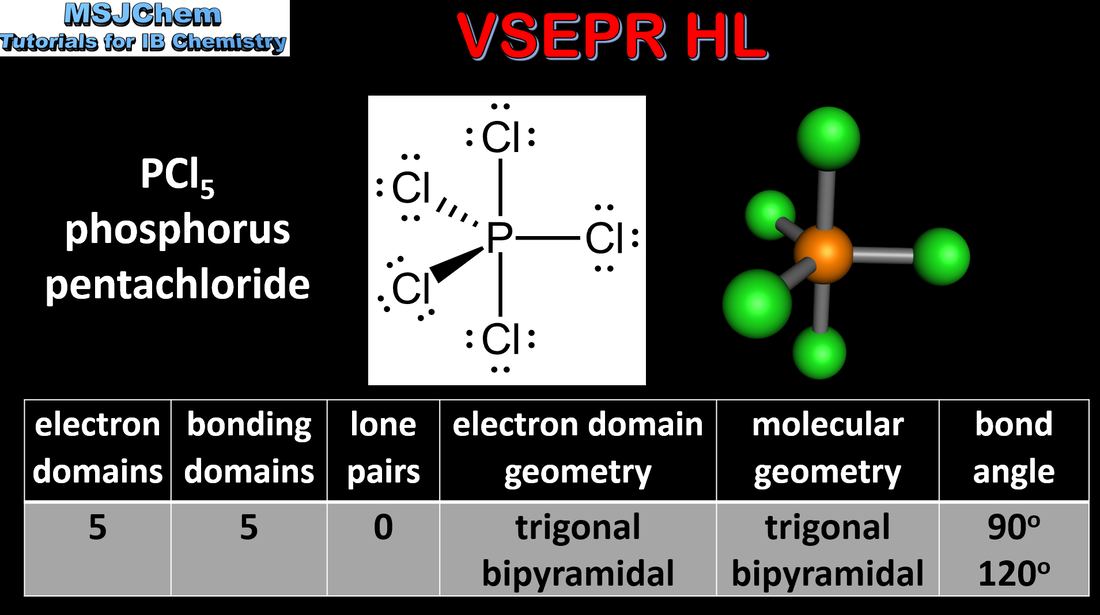
Exceptions to the octet rule include some species having incomplete octets and expanded octets. Applications and skills: Deduction using VSEPR theory of the electron domain geometry and molecular geometry with five and six electron domains and associated bond angles. Deduction of the Lewis (electron dot) structures of molecules and ions showing all valence electrons for up to six electron pairs on each atom. |
14.1 Molecular geometry (HL)
|
Understandings:
Exceptions to the octet rule include some species having incomplete octets and expanded octets. Applications and skills: Deduction using VSEPR theory of the electron domain geometry and molecular geometry with five and six electron domains and associated bond angles. Deduction of the Lewis (electron dot) structures of molecules and ions showing all valence electrons for up to six electron pairs on each atom. |
| topic_14_vsepr_theory_hl.pdf |
14.1 sigma and pi bonds
|
Understandings:
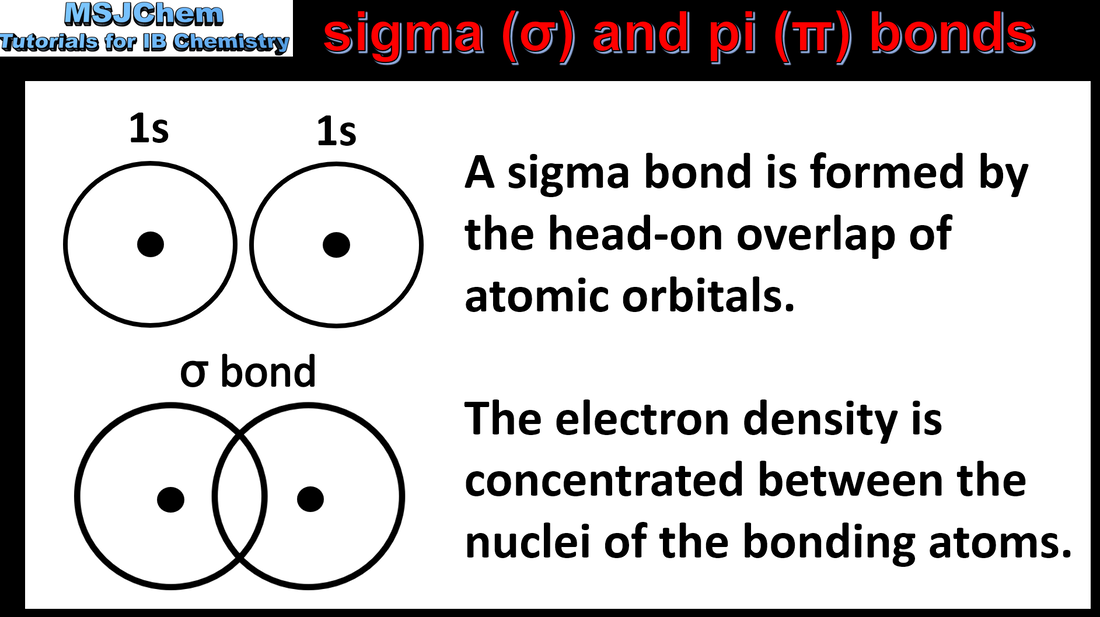
Covalent bonds result from the overlap of atomic orbitals. A sigma bond (σ) is formed by the direct head-on/end-to-end overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density concentrated between the nuclei of the bonding atoms. A pi bond (π) is formed by the sideways overlap of atomic orbitals, resulting in electron density above and below the plane of the nuclei of the bonding atoms. Applications and skills: Prediction whether sigma (σ) or pi (π) bonds are formed from the linear combination of atomic orbitals. |
| topic_4_sigma_and_pi_bonds.pdf |
|
Understandings:
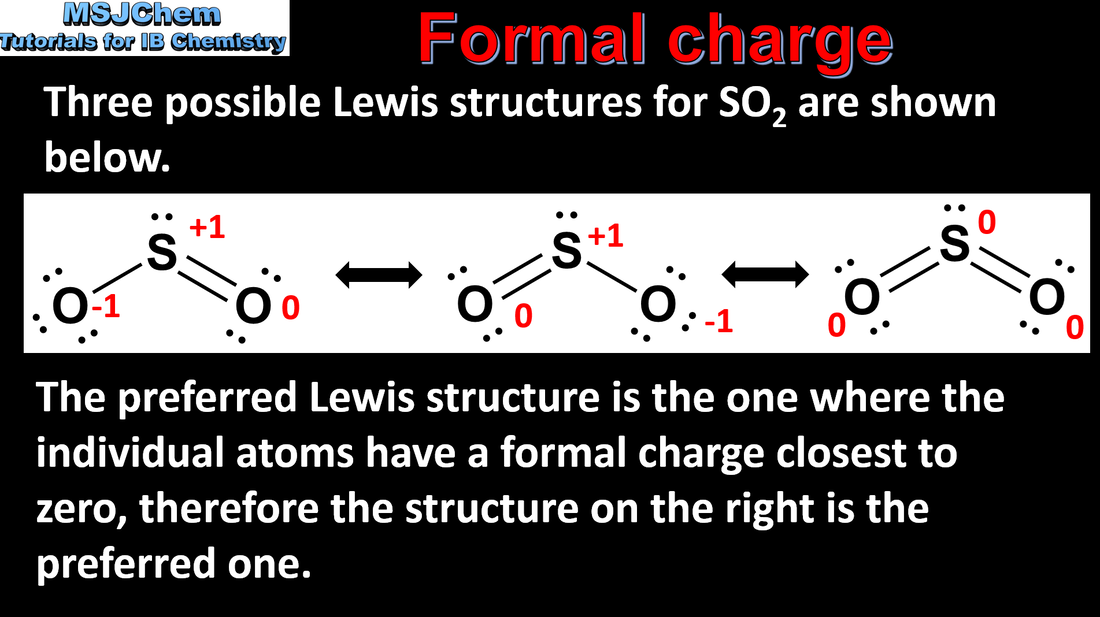
Formal charge (FC) can be used to decide which Lewis (electron dot) structure is preferred from several. The FC is the charge an atom would have if all atoms in the molecule had the same electronegativity. FC = (Number of valence electrons)-½(Number of bonding electrons)-(Number of non-bonding electrons). The Lewis (electron dot) structure with the atoms having FC values closest to zero is preferred. Applications and skills: Application of FC to ascertain which Lewis (electron dot) structure is preferred from different Lewis (electron dot) structures. |
| topic_14_formal_charge.pdf |
14.1 Molecules and ions with delocalised pi electrons
|
Understandings:
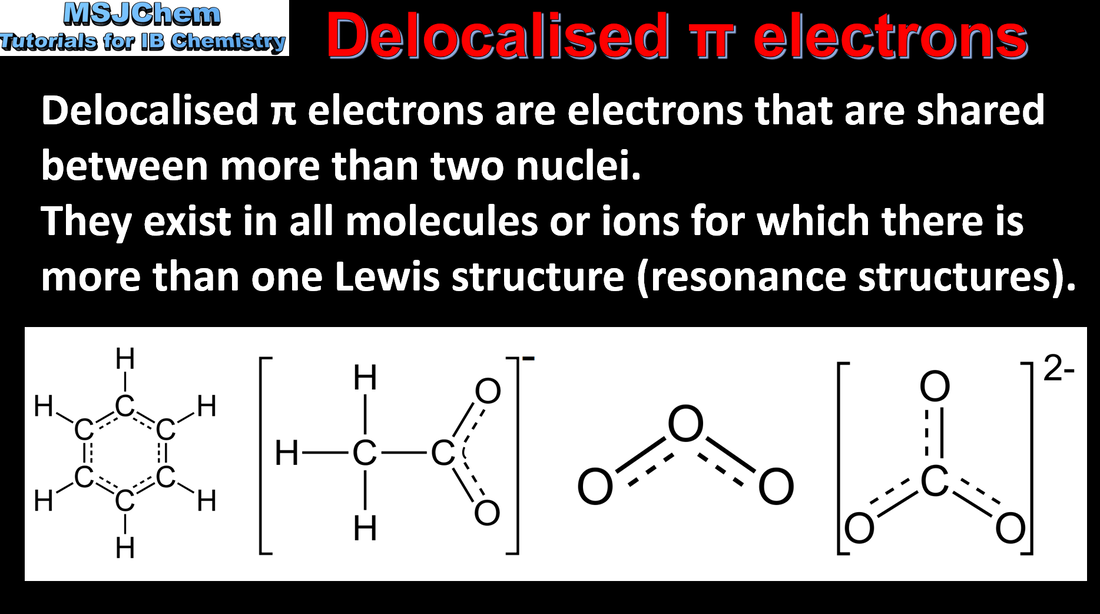
Delocalisation involves electrons that are shared by/between more than two nuclei. Resonance involves using two or more Lewis (electron dot) structures to represent a particular molecule or ion. A resonance structure is one of two or more alternative Lewis (electron dot) structures for a molecule or ion that cannot be described fully with one Lewis (electron dot) structure alone. |
| topic_14_delocalized_pi_electrons.pdf |
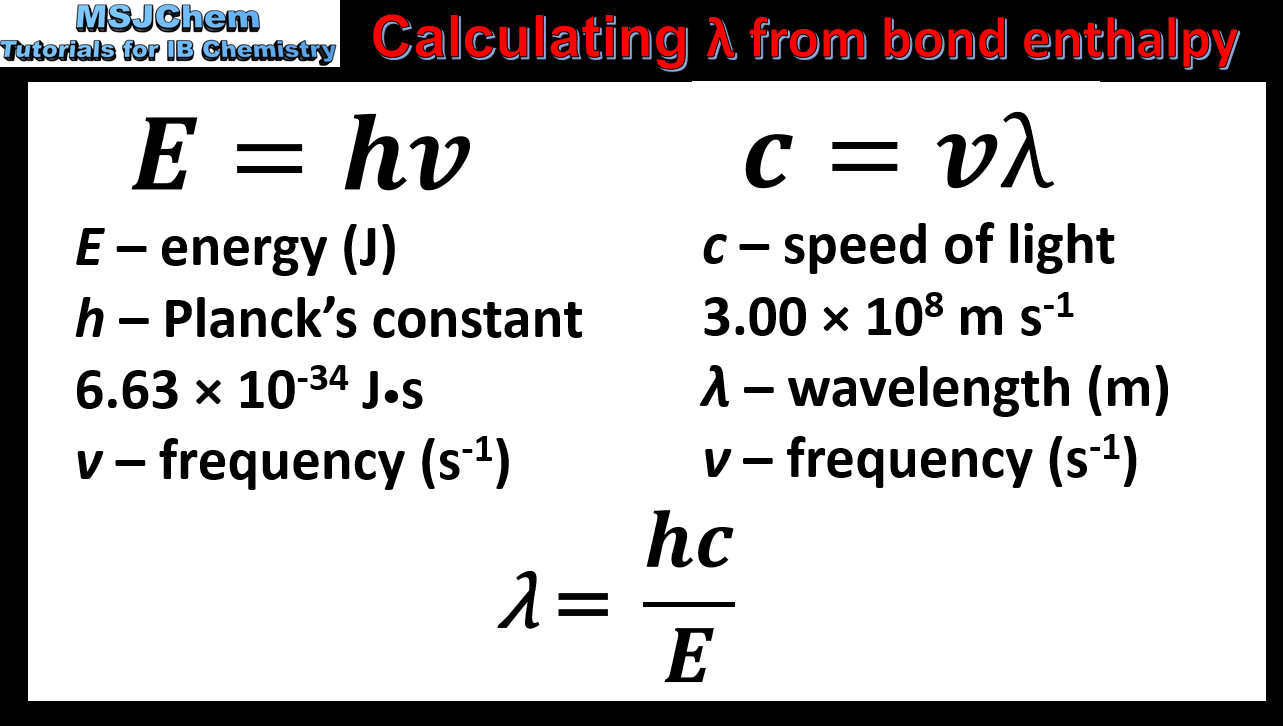
14.1 Calculating wavelength from bond enthalpy values (O2 and O3)
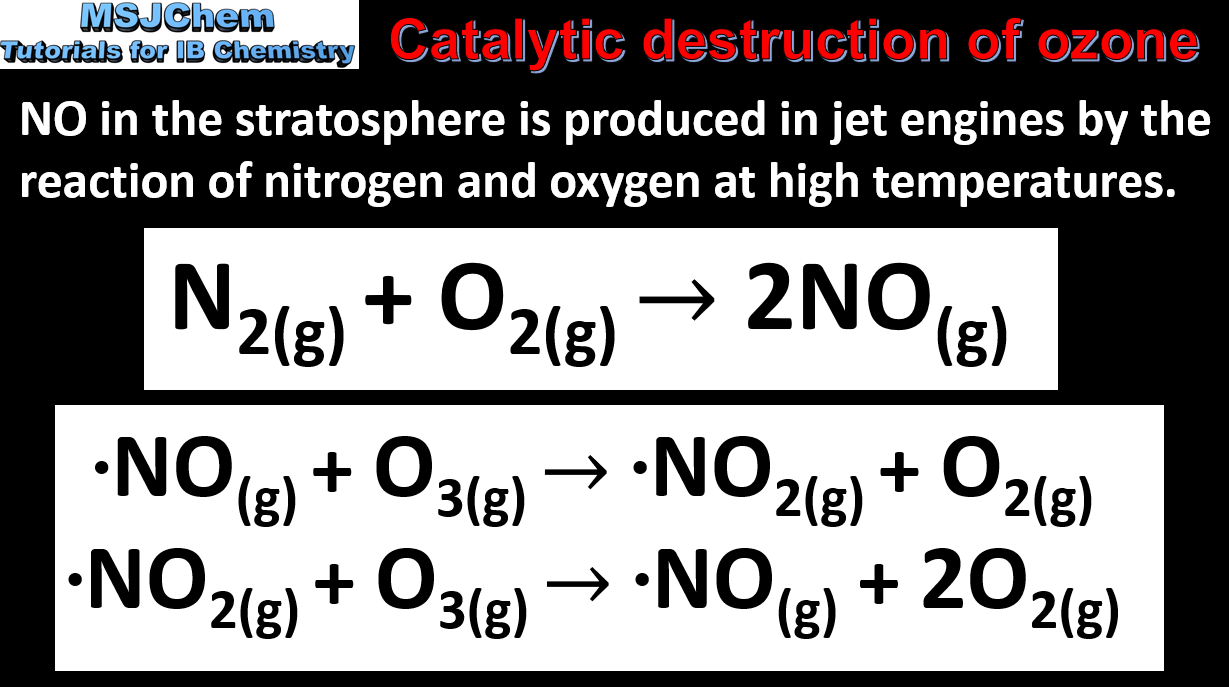
14.1 Catalytic destruction of ozone
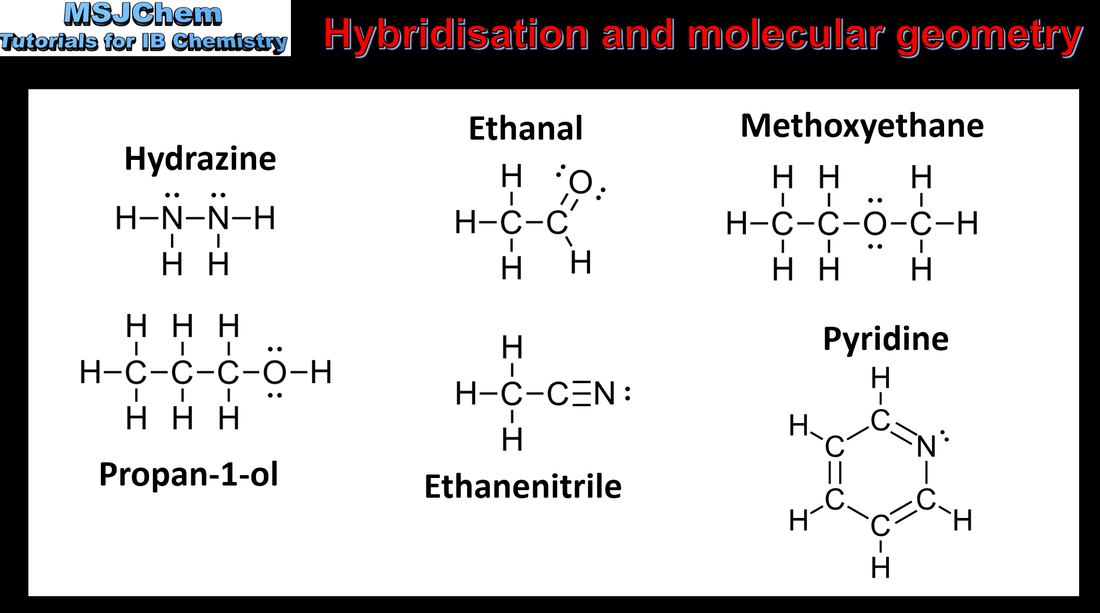
14.2 Hybridisation
|
Understandings:
A hybrid orbital results from the mixing of different types of atomic orbitals on the same atom. Applications: Explanation of the formation of sp3, sp2 and sp hybrid orbitals in methane, ethene and ethyne. Identification and explanation of the relationships between Lewis (electron dot) structures, electron domains, molecular geometries and types of hybridisation. |
| topic_14_hybridization.pdf |