Topic 13 Periodicity HL
13.1 Introduction to transition elements
|
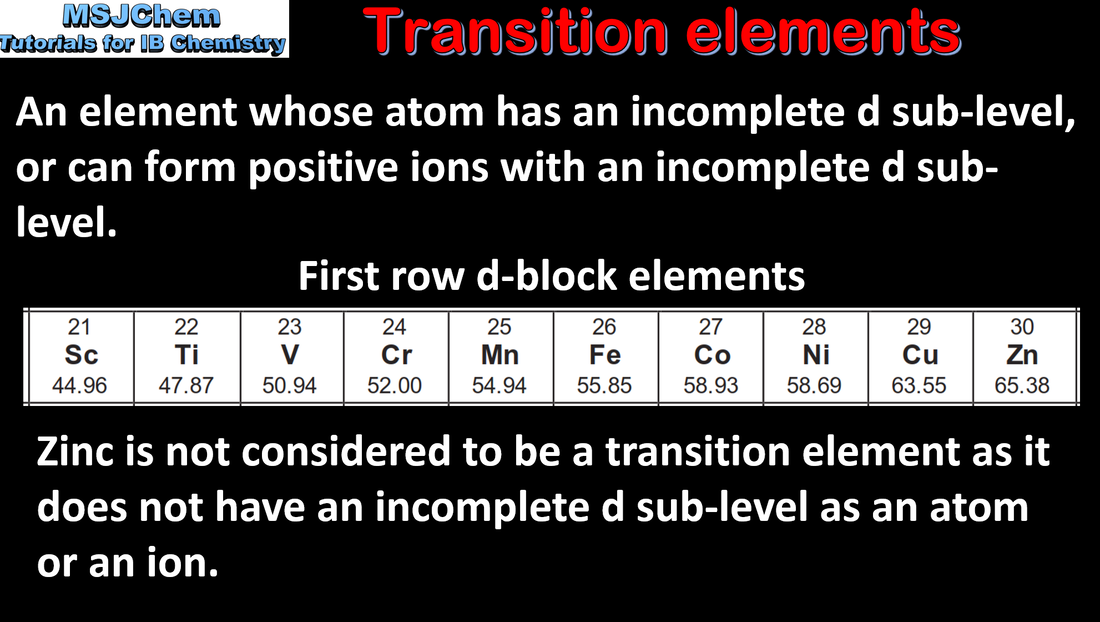
Essential idea: The transition elements have characteristic properties; these properties are related to their all having incomplete d sub-levels.
Understandings: Zn is not considered to be a transition element as it does not form ions with incomplete d-orbitals. Transition elements have variable oxidation states, form complex ions with ligands, have coloured compounds, and display catalytic and magnetic properties. |
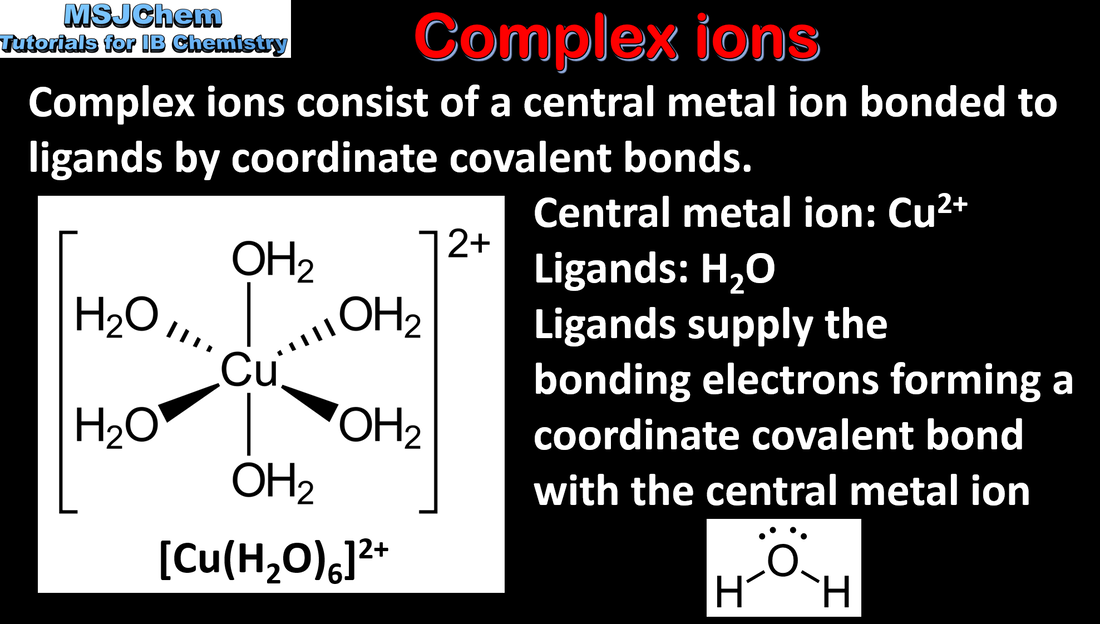
13.1 Complex ions
|
|
Understandings:
Transition elements have variable oxidation states, form complex ions with ligands, have coloured compounds, and display catalytic and magnetic properties. Essential idea: The transition elements have characteristic properties; these properties are related to their all having incomplete d sub-levels. |
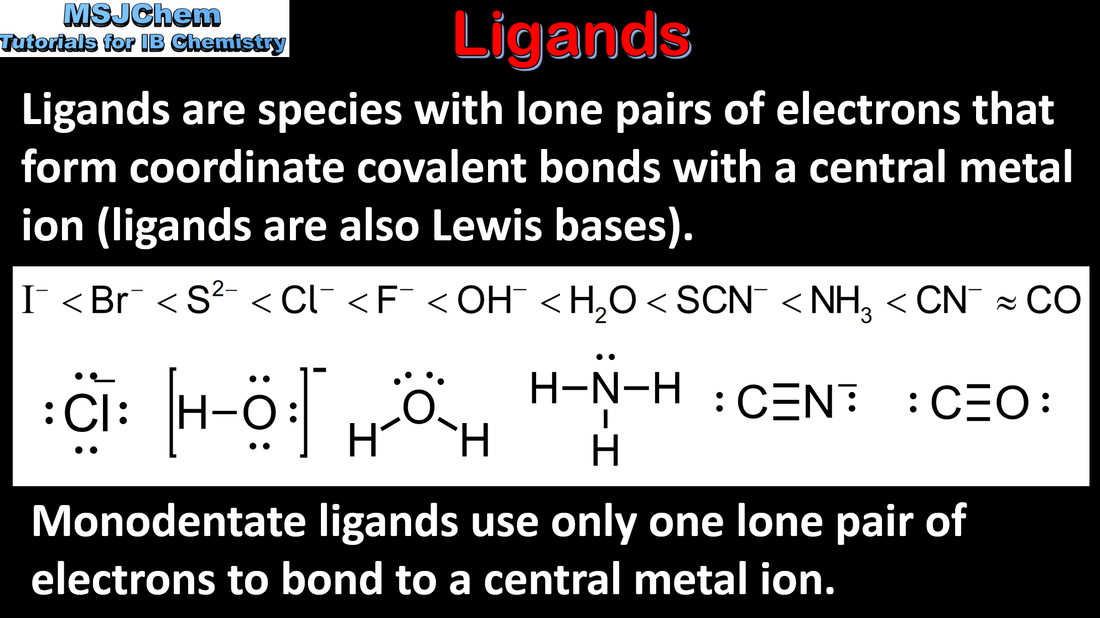
13.1 Ligands
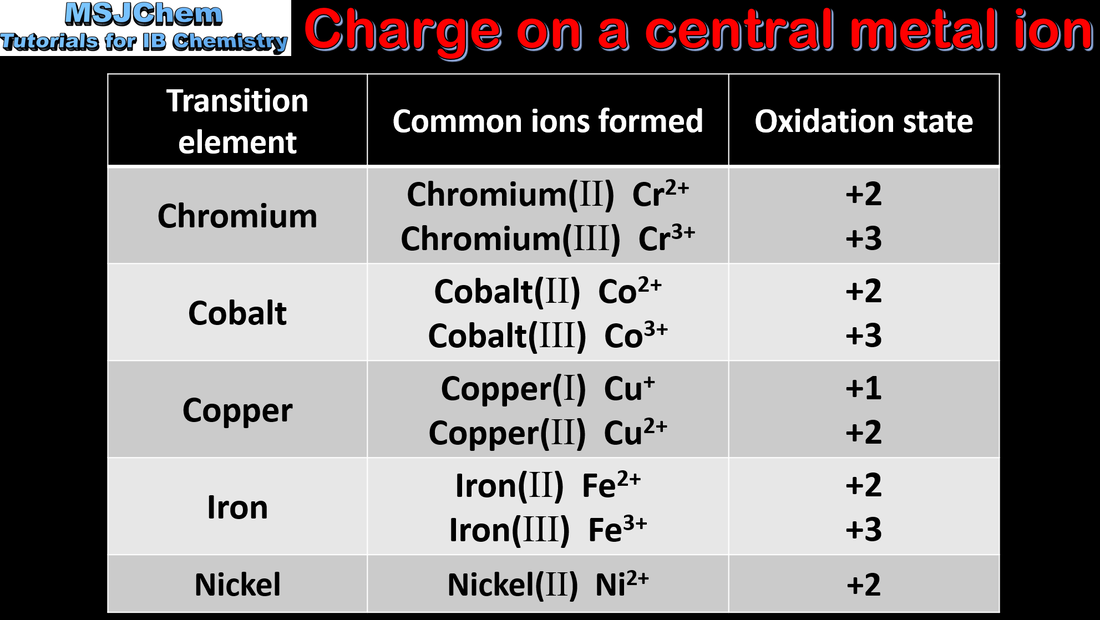
13.1 Deduce the charge and oxidation state of a central metal ion
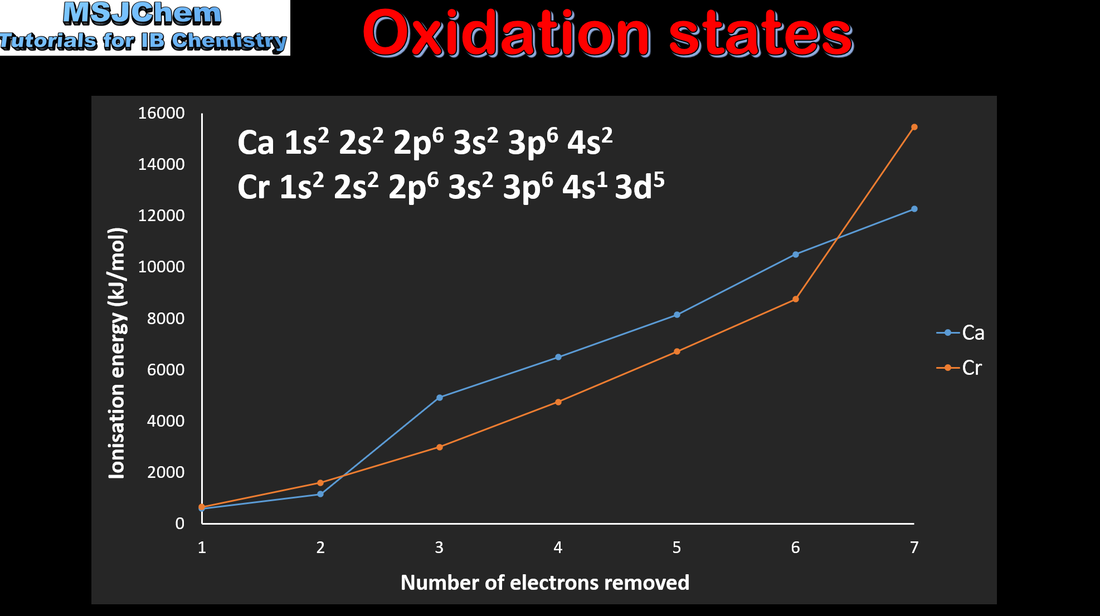
13.1 Variable oxidation states of the transition elements
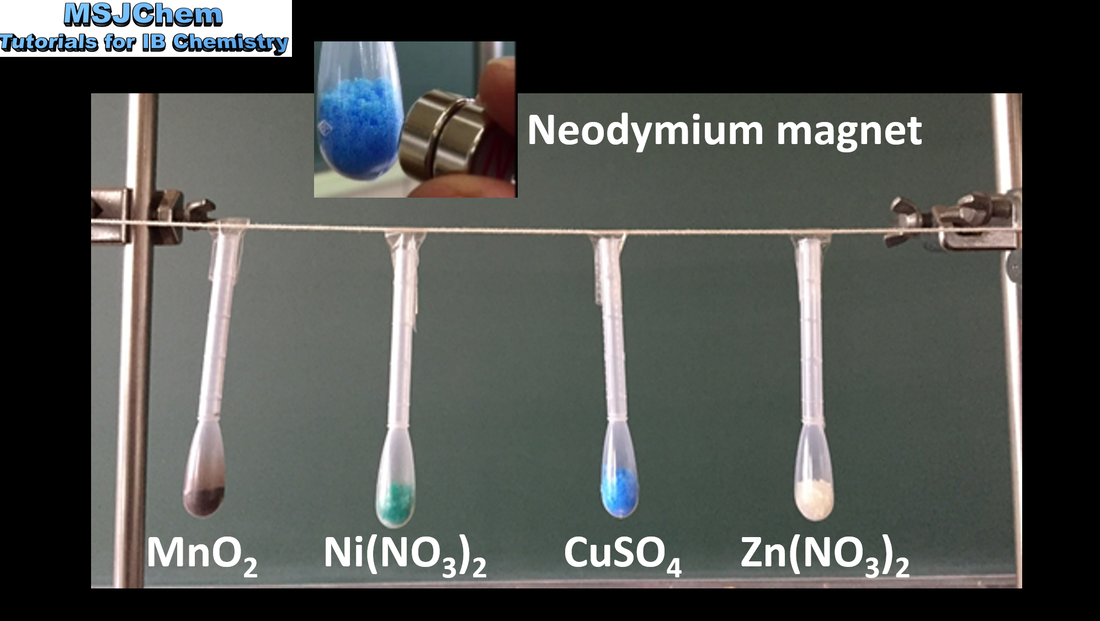
13.1 Magnetic properties of the transition elements
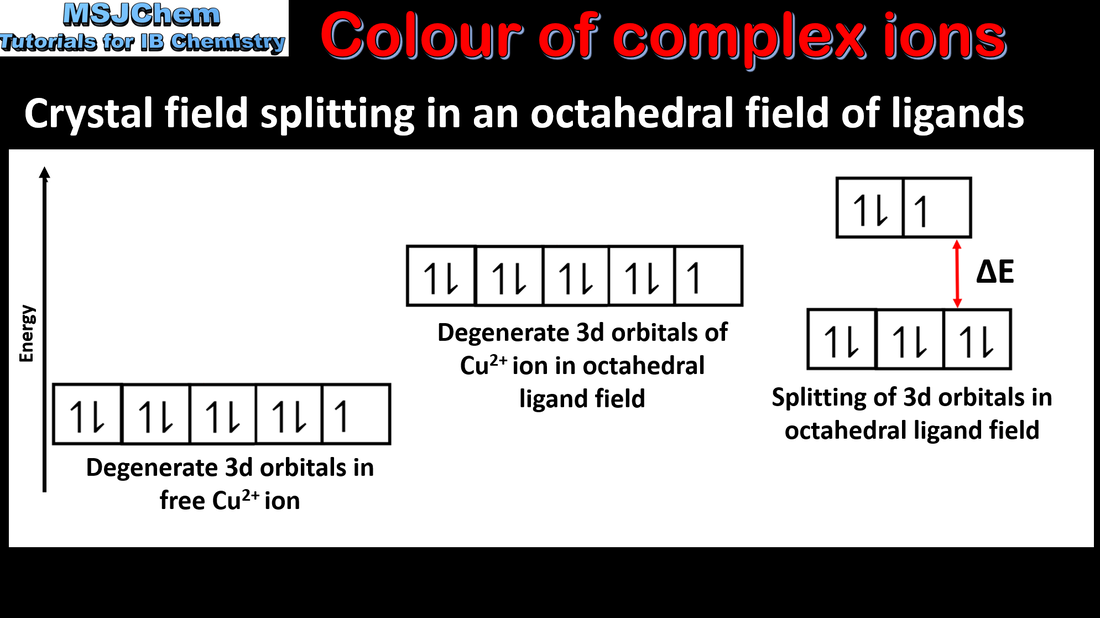
13.2 Colour of complex ions
|
Understandings:
The d sub-level splits into two sets of orbitals of different energy in a complex ion. Complexes of d-block elements are coloured, as light is absorbed when an electron is excited between the d-orbitals. The colour absorbed is complementary to the colour observed. Guidance: Students are not expected to know the different splitting patterns and their relation to the coordination number. Only the splitting of the 3-d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field is required. |
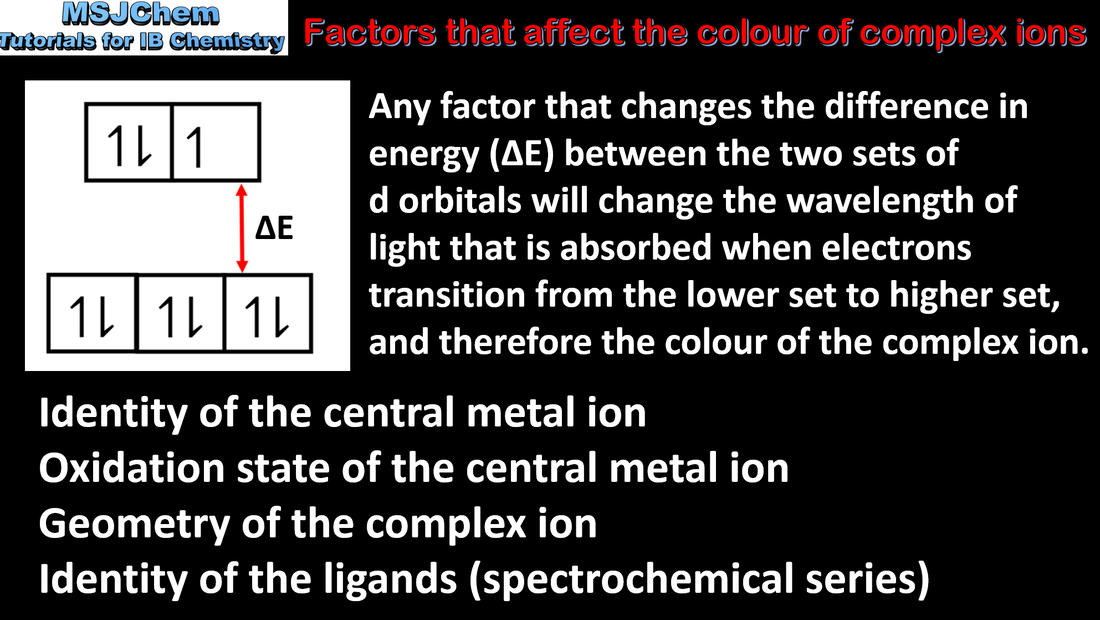
13.2 Factors that affect the colour of complex ions
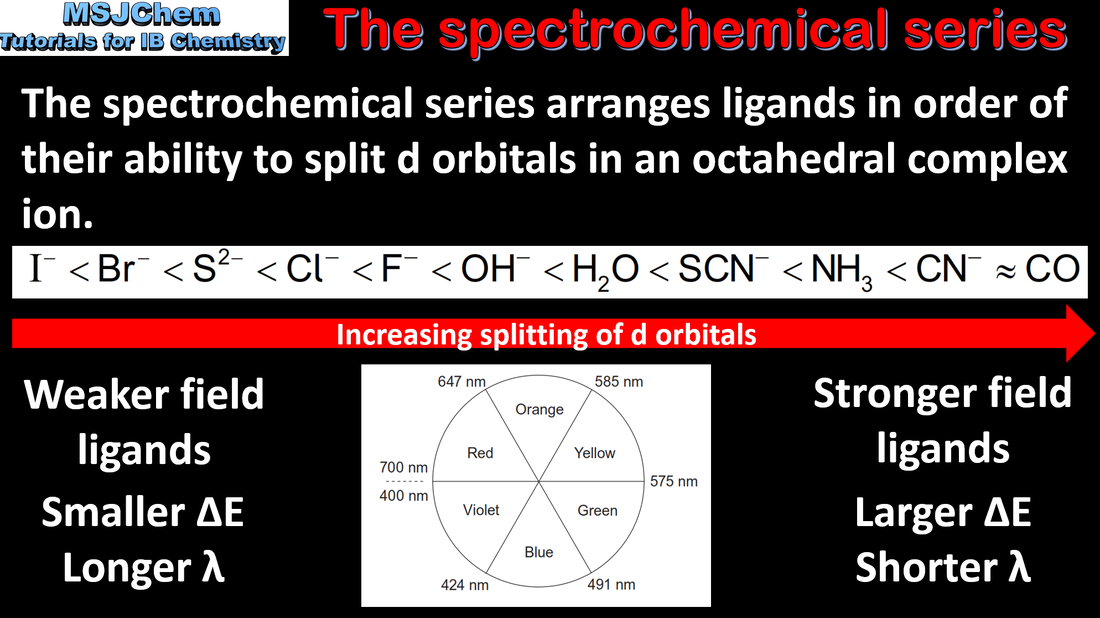
13.2 The Spectrochemical series