Reactivity 1.4 Entropy and spontaneity (HL)
Reactivity 1.4.1
Understandings:
Understandings:
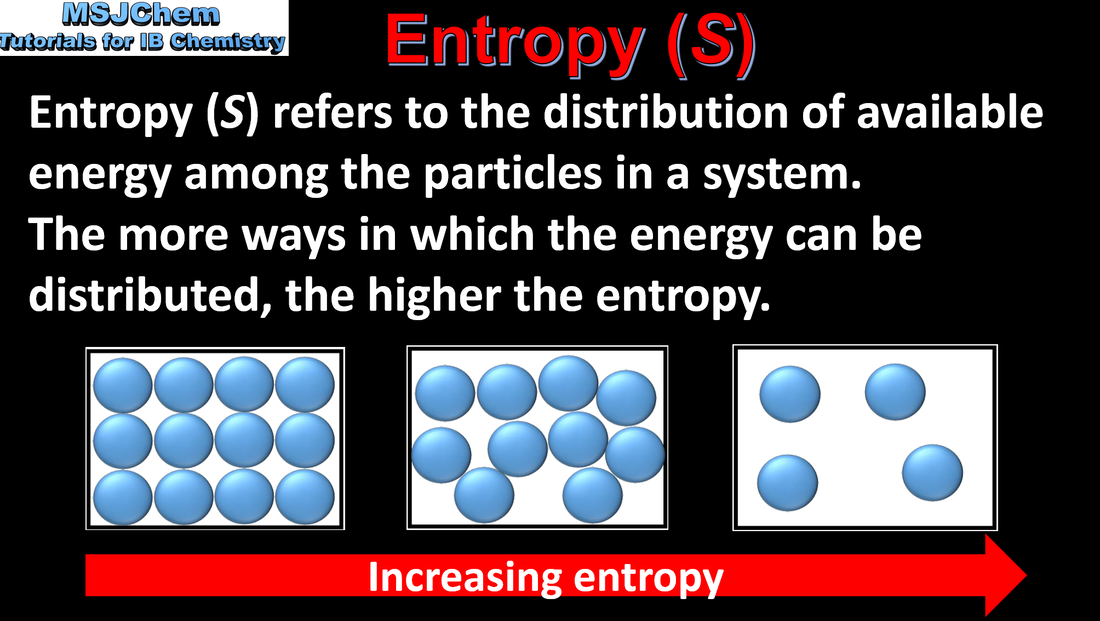
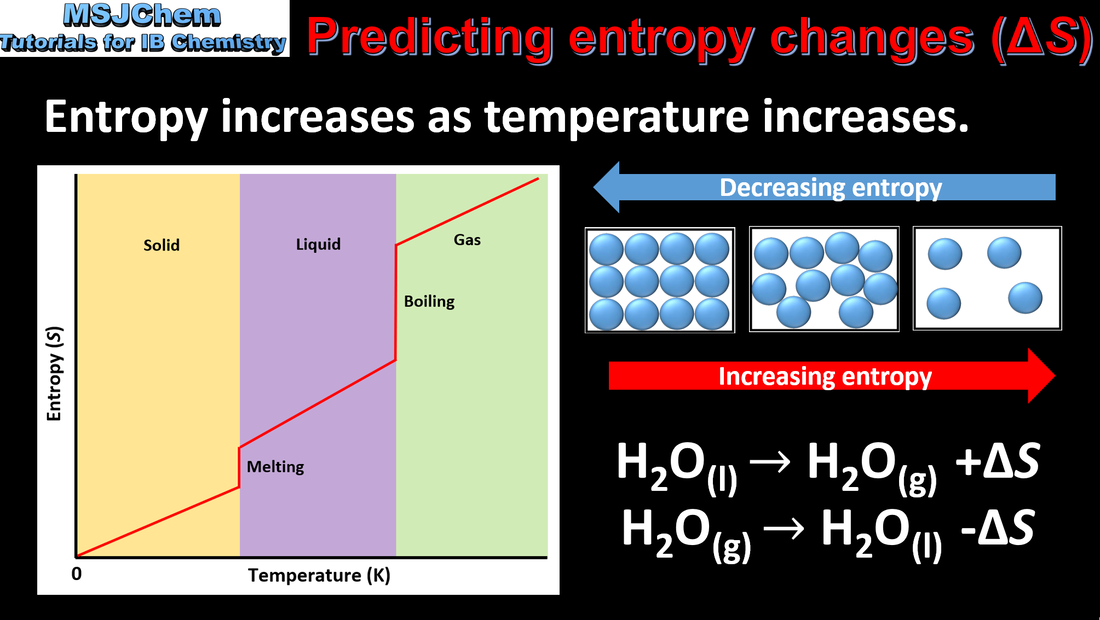
- Entropy, S, is a measure of the dispersal or distribution of matter and/or energy in a system. The more ways the energy can be distributed, the higher the entropy. Under the same conditions, the entropy of a gas is greater than that of a liquid, which in turn is greater than that of a solid.
- Predict whether a physical or chemical change will result in an increase or decrease in entropy of a system.
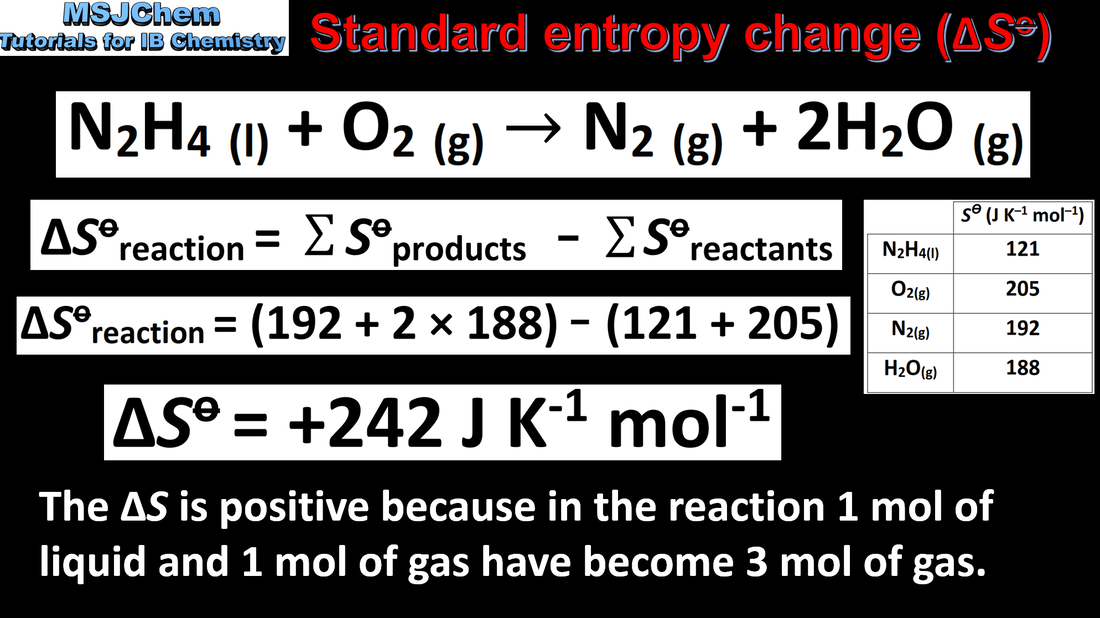
- Calculate standard entropy changes, ΔS, from standard entropy values, S.
- Standard entropy values are given in the data booklet.
- Structure 1.1 Why is the entropy of a perfect crystal at 0 K predicted to be zero?
Reactivity 1.4.2 and 1.4.3
Understandings:
Understandings:
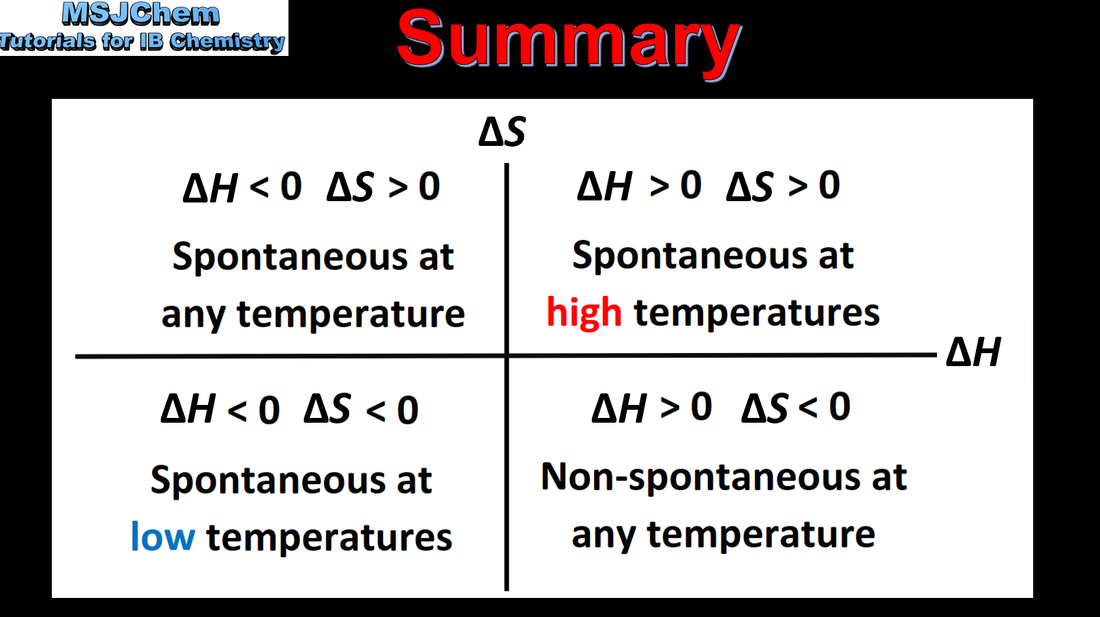
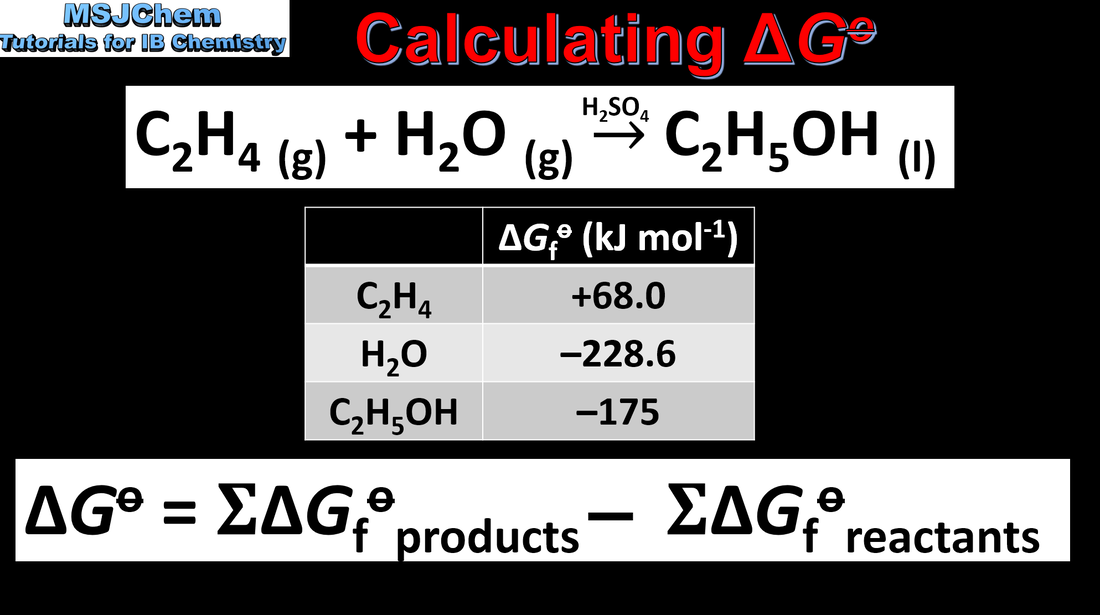
- Change in Gibbs energy, ΔG, relates the energy that can be obtained from a chemical reaction to the change in enthalpy, ΔH, change in entropy, ΔS, and absolute temperature, T (1.4.2).
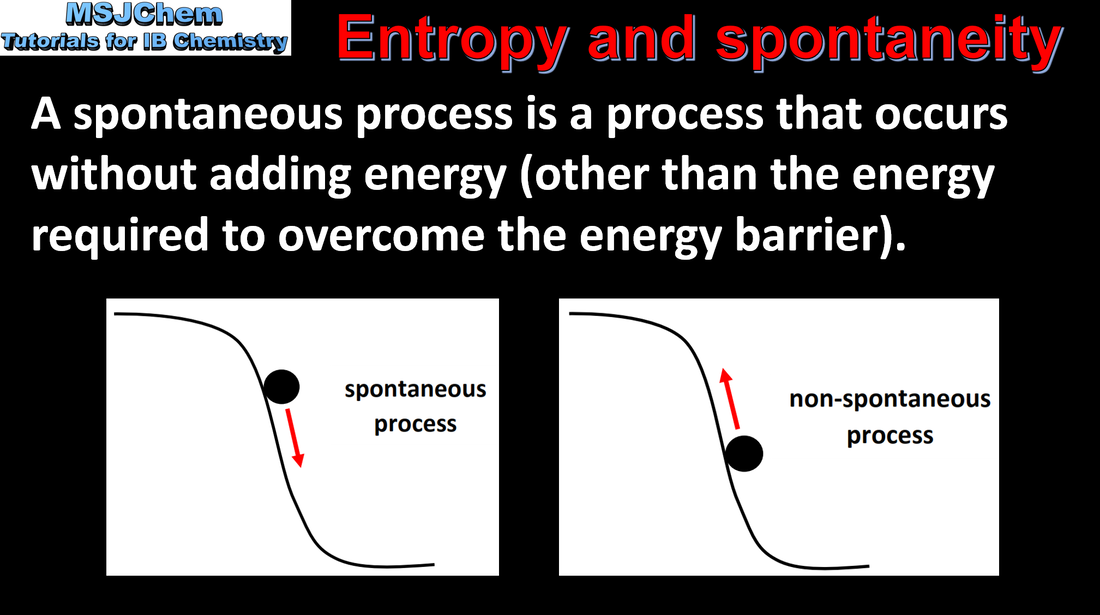
- At constant pressure, a change is spontaneous if the change in Gibbs energy, ΔG, is negative (1.4.2).
- Interpret the sign of ΔG calculated from thermodynamic data (1.4.3).
- Determine the temperature at which a reaction becomes spontaneous (1.4.3).
- Apply the equation ΔG = ΔH − TΔS to calculate unknown values of these terms (1.4.2).
- ΔG takes into account the direct entropy change resulting from the transformation of the chemicals and the indirect entropy change of the surroundings resulting from the transfer of heat energy (1.4.3).
- Thermodynamic data values are given in the data booklet.
- Note the units: ΔH kJ mol–1; ΔS J K–1 mol–1; ΔG kJ mol–1.
- Reactivity 3.2 How can electrochemical data also be used to predict the spontaneity of a reaction?
Reactivity 1.4.4
Understandings:
Understandings:
- As a reaction approaches equilibrium, ΔG becomes less negative and finally reaches zero.
- Perform calculations using the equation ΔG = ΔG⦵ + RT lnQ and its application to a system at equilibrium ΔG⦵ = −RT lnK.
- The equations are given in the data booklet.
- Reactivity 2.3—What is the likely composition of an equilibrium mixture when ΔG⦵ is positive?