Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
Topic 2 Atomic structure
Link to YouTube Playlist
Link to YouTube Playlist
|
Understandings:
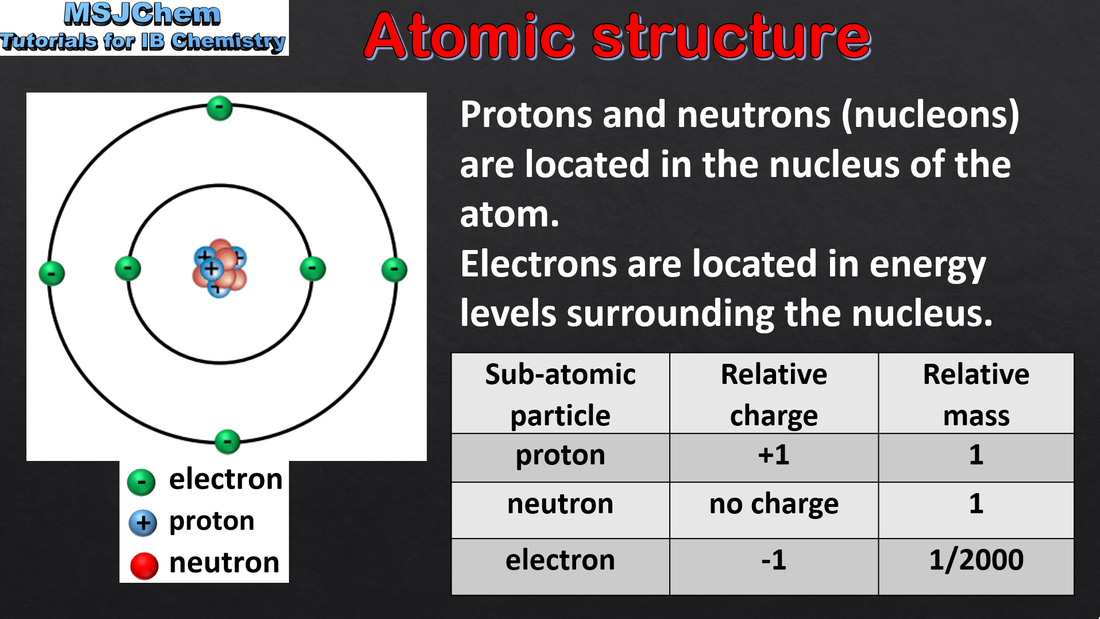
Atoms contain a positively charged dense nucleus composed of protons and neutrons (nucleons). Negatively charged electrons occupy the space outside the nucleus. The main energy level or shell is given an integer number, n, and can hold a maximum number of electrons, 2n2. A more detailed model of the atom describes the division of the main energy level into s, p, d and f sub-levels of successively higher energies. |
2.1 Atomic number and mass number
2.1 Isotopes
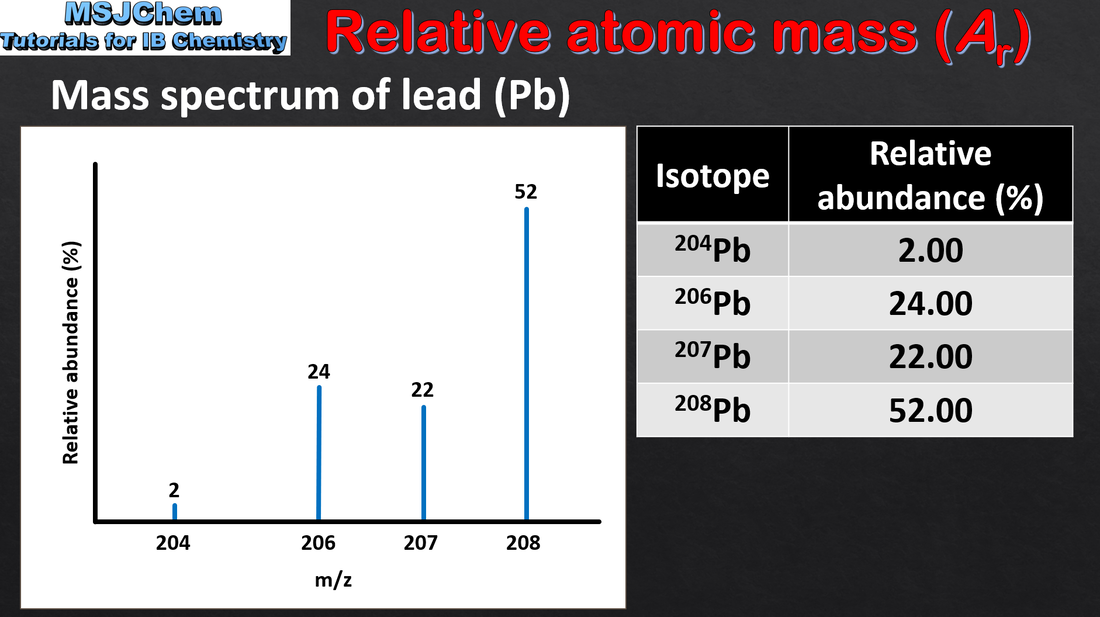
2.1 Calculating relative atomic mass
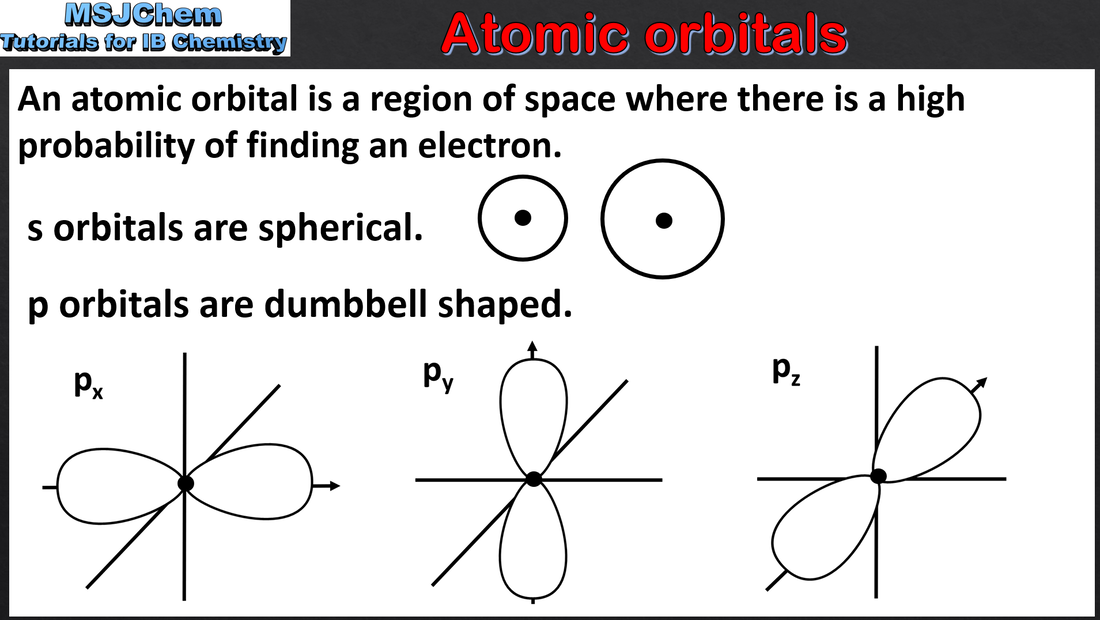
2.2 Atomic orbitals and sub-levels
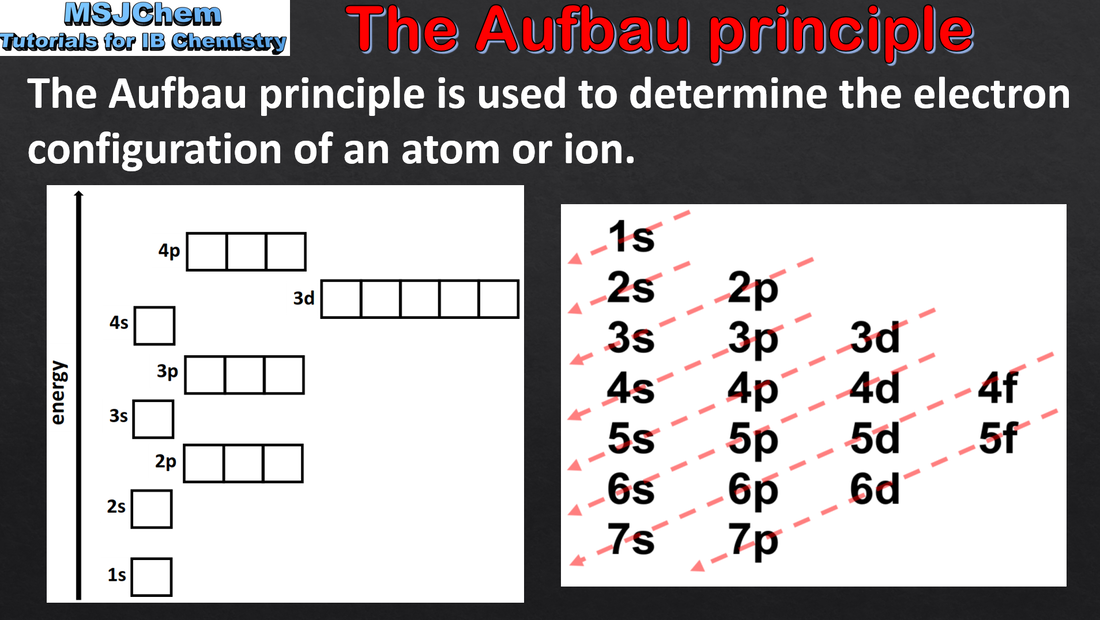
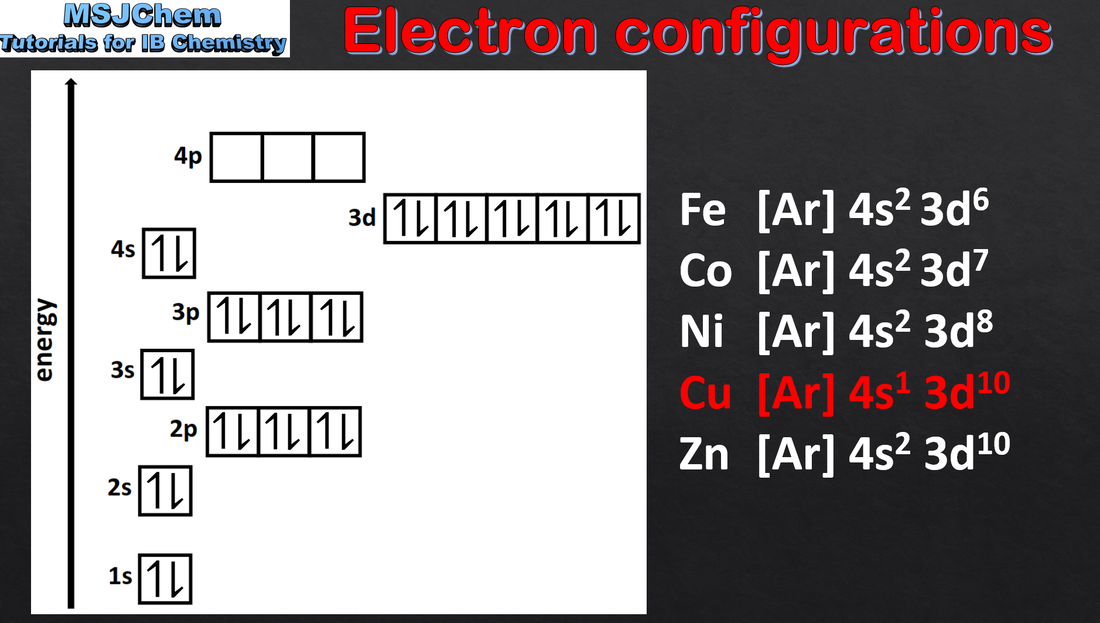
2.2 Electron configurations and the Aufbau principle (part one and part two)
|
Understandings:
Each orbital has a defined energy state for a given electronic configuration and chemical environment and can hold two electrons of opposite spin. Applications and skills: Application of the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle to write electron configurations for atoms and ions up to Z = 36. Guidance: Orbital diagrams should be used to represent the character and relative energy of orbitals. Applications and skills: Application of the Aufbau principle, Hund’s rule and the Pauli exclusion principle to write electron configurations for atoms and ions up to Z = 36. Guidance: Orbital diagrams should be used to represent the character and relative energy of orbitals. The electron configurations of Cr and Cu as exceptions should be covered. |
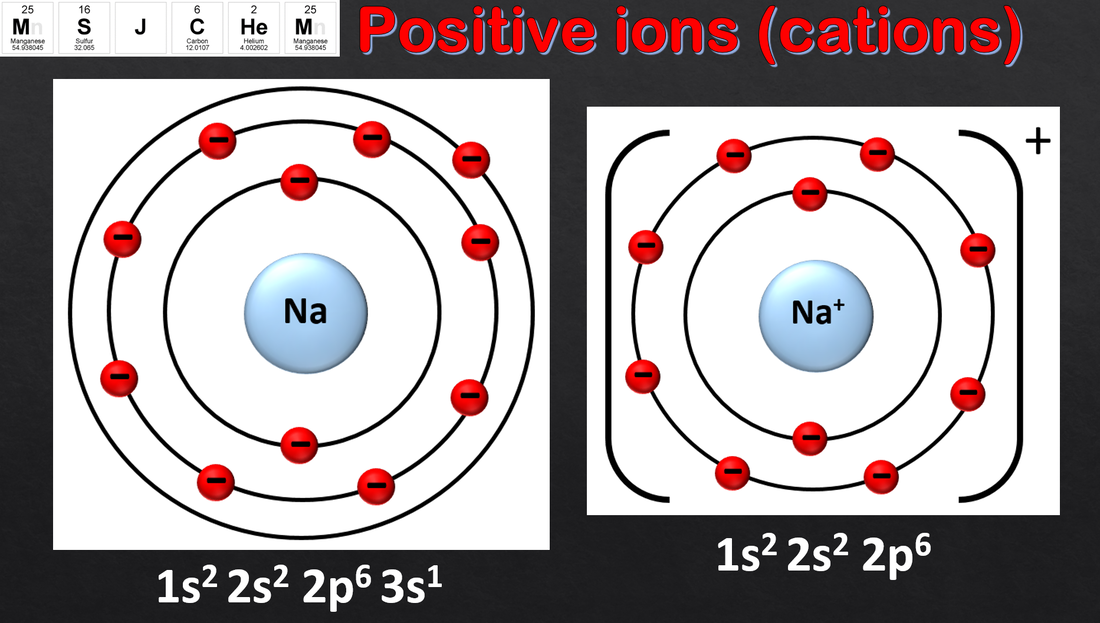
2.2 Electron configurations of ions
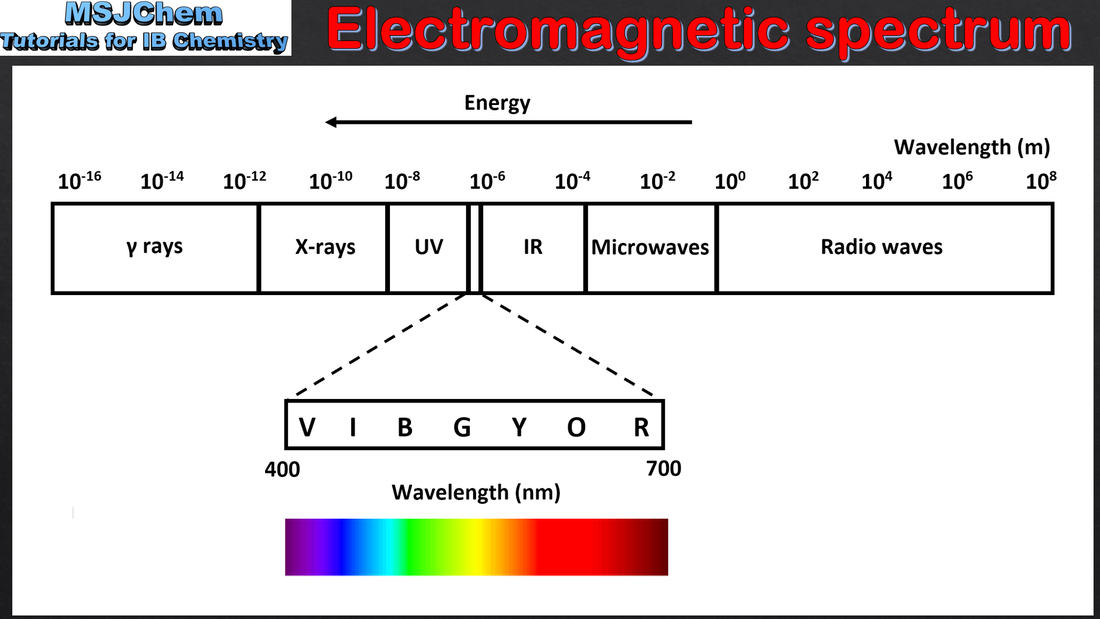
2.2 Electromagnetic spectrum
2.2 Line spectra
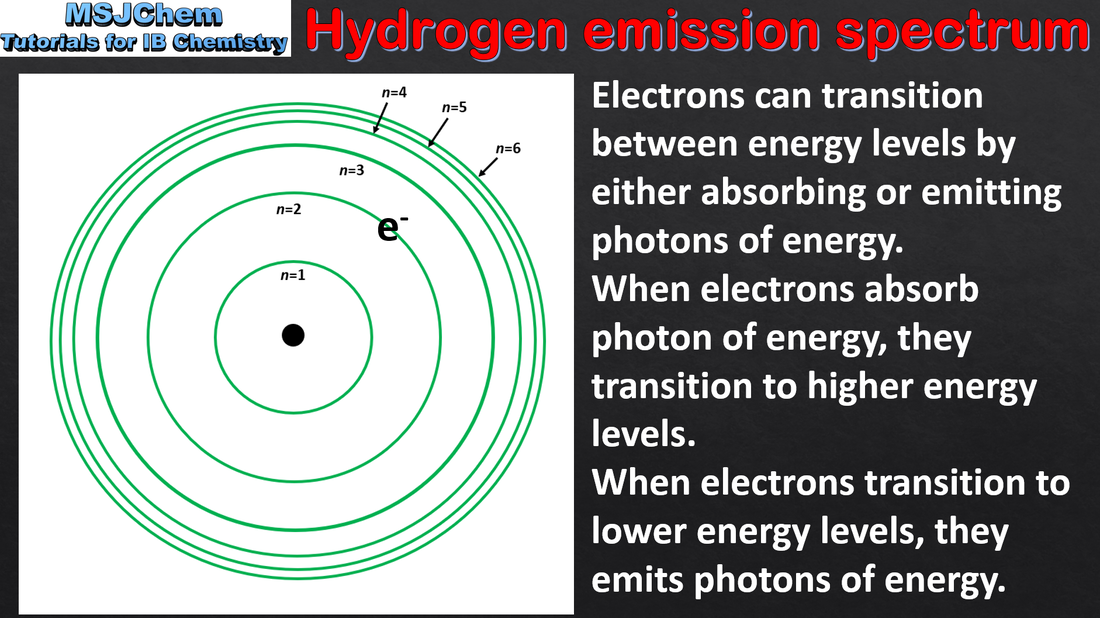
2.2 Hydrogen emission spectrum
|
Understandings:
Emission spectra are produced when photons are emitted from atoms as excited electrons return to a lower energy level. The line emission spectrum of hydrogen provides evidence for the existence of electrons in discrete energy levels, which converge at higher energies. Applications and skills: Description of the emission spectrum of the hydrogen atom, including the relationships between the lines and energy transitions to the first, second and third energy levels. |
2.2 Flame tests
|
|
This video covers the flame tests.
|