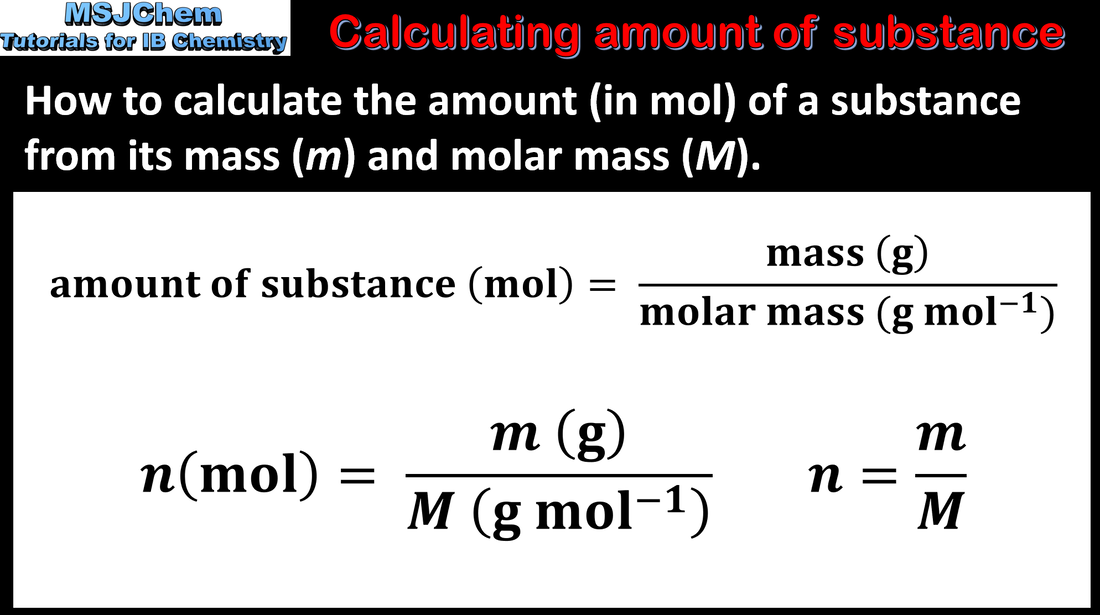Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
Topic 1 Stoichiometric relationships
Link to playlist on Youtube
Link to playlist on Youtube
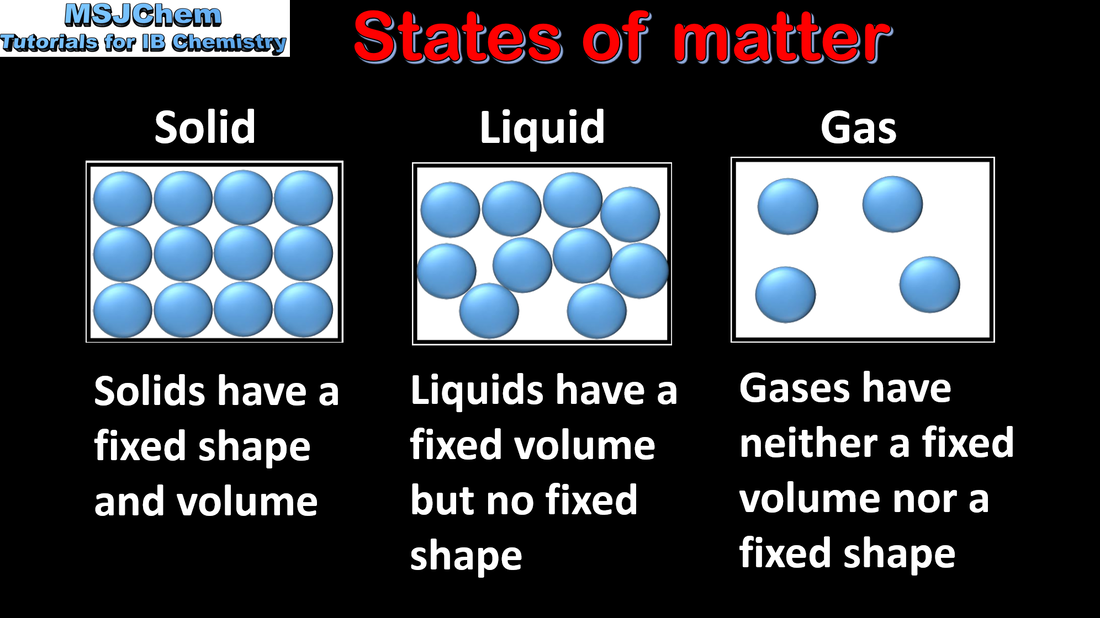
1.1 States of matter, changes of state and state symbols
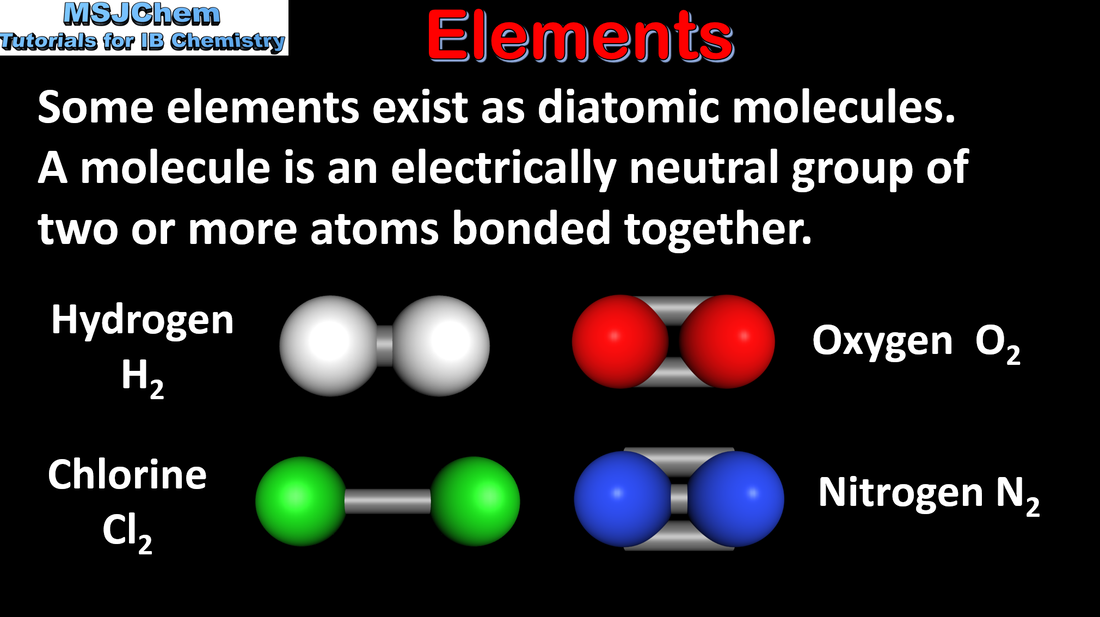
1.1 Elements, compounds, mixtures
|
Understandings:
Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios to form compounds, which have different properties from their component elements. Mixtures contain more than one element and/or compound that are not chemically bonded together and so retain their individual properties. Mixtures are either homogeneous or heterogeneous. Applications and skills: Explanation of observable changes in physical properties and temperature during changes of state. |
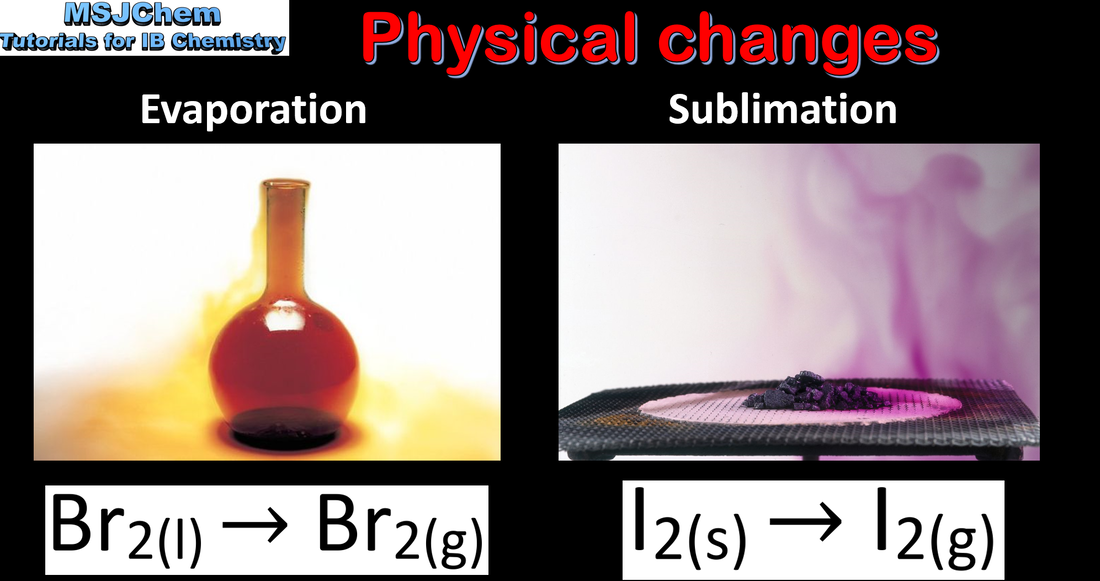
1.1 Physical and chemical changes
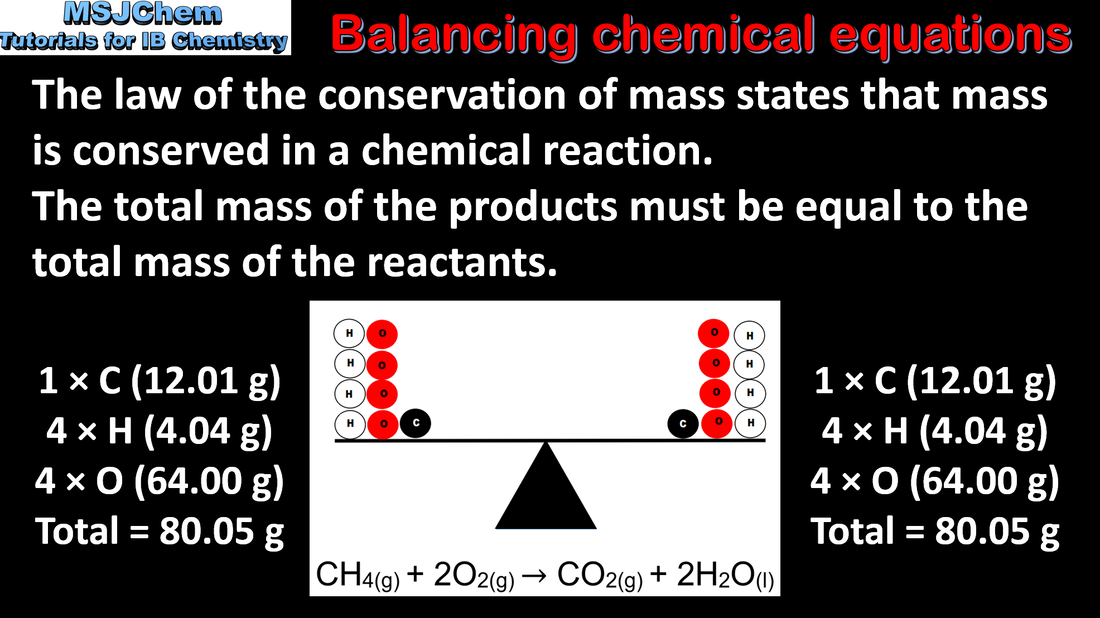
1.1 Balancing chemical equations
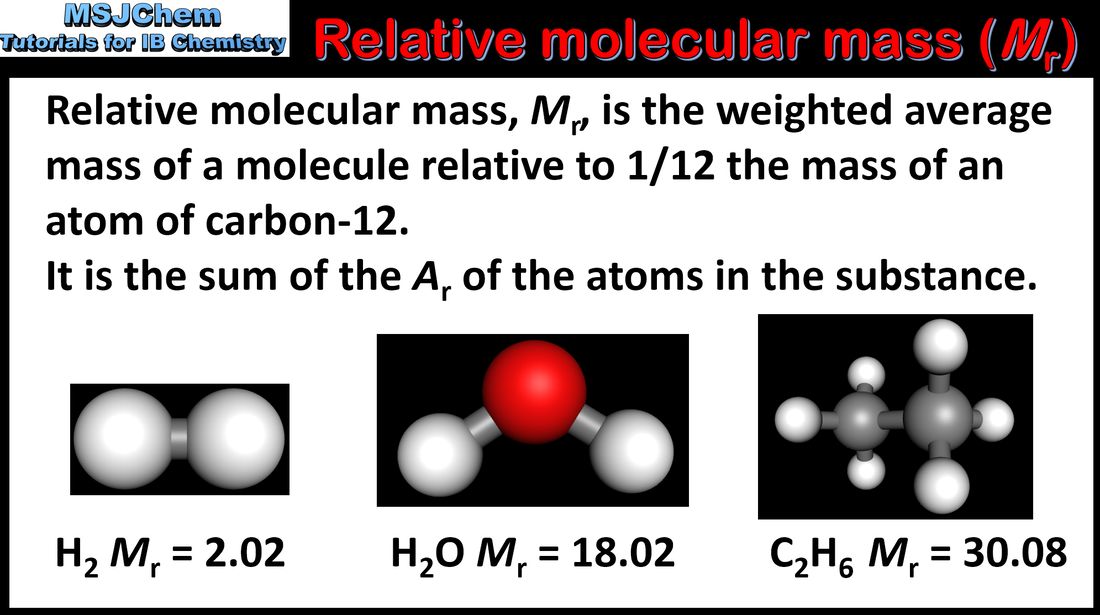
1.2 Relative atomic mass and molecular mass
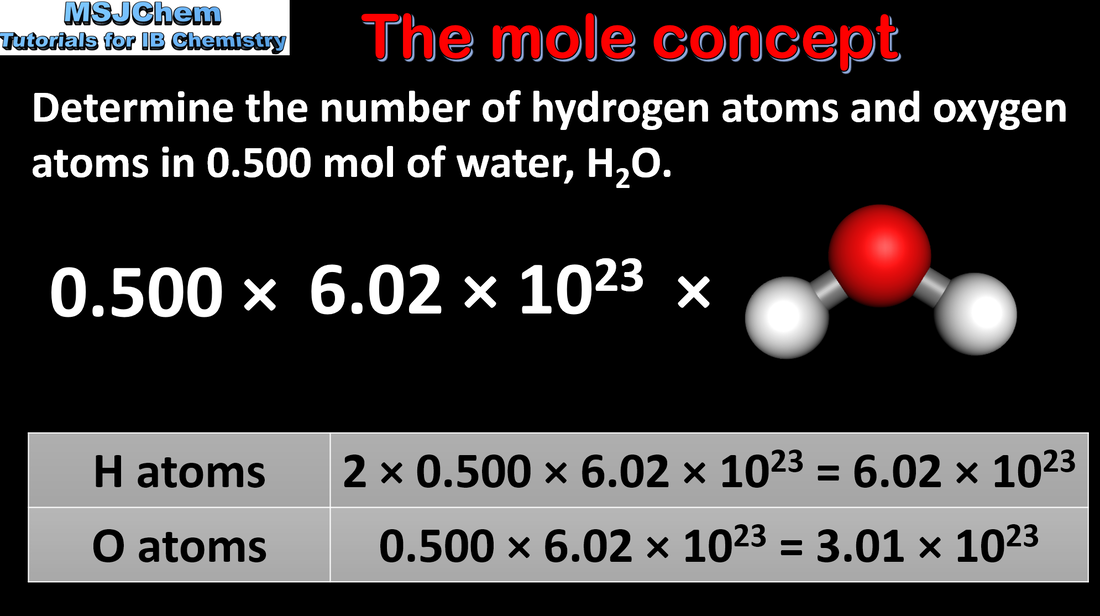
1.2 The mole concept
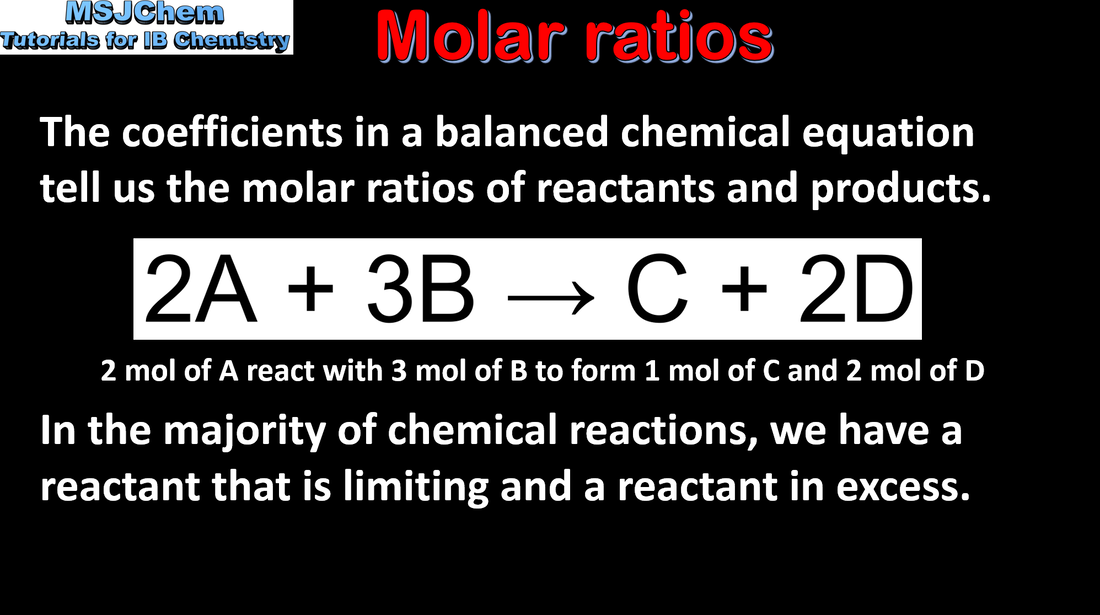
1.2 Molar ratio
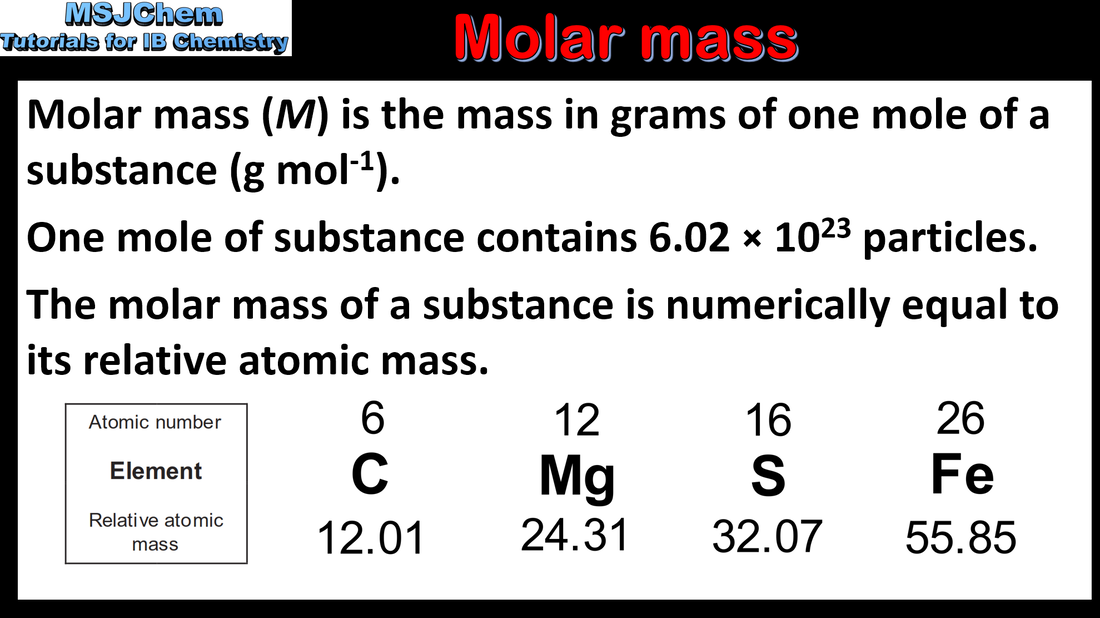
1.2 Molar mass
1.2 Calculating amount of substance (in mol)
1.2 Calculating mass in grams from amount (in mol)
Although this is not mentioned in the IB syllabus, an example involving mole percent came up in the May 2021 exams.
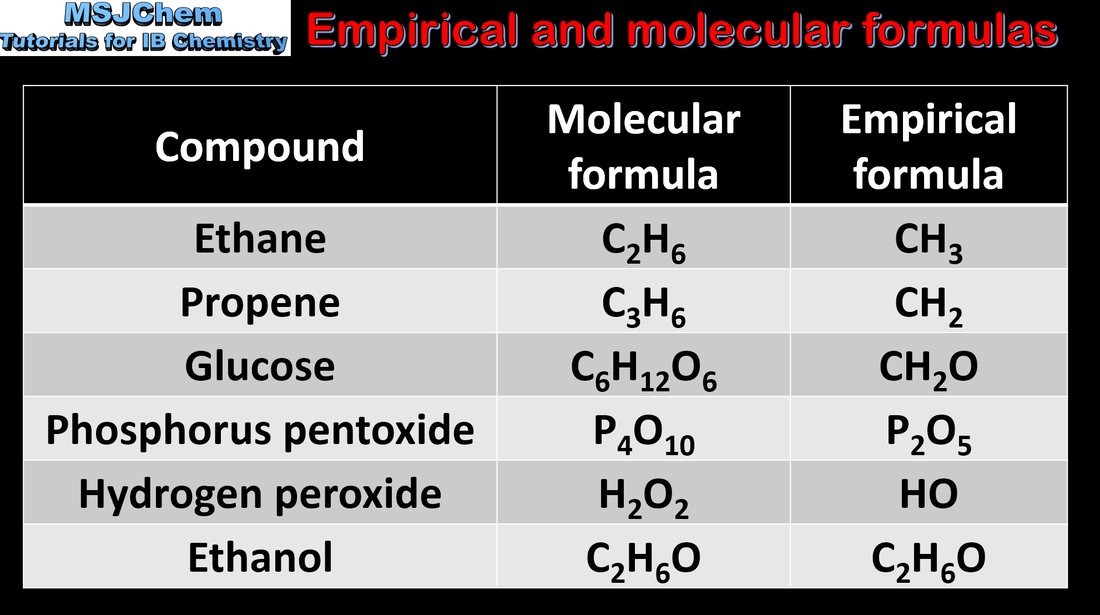
1.2 Empirical and molecular fomula
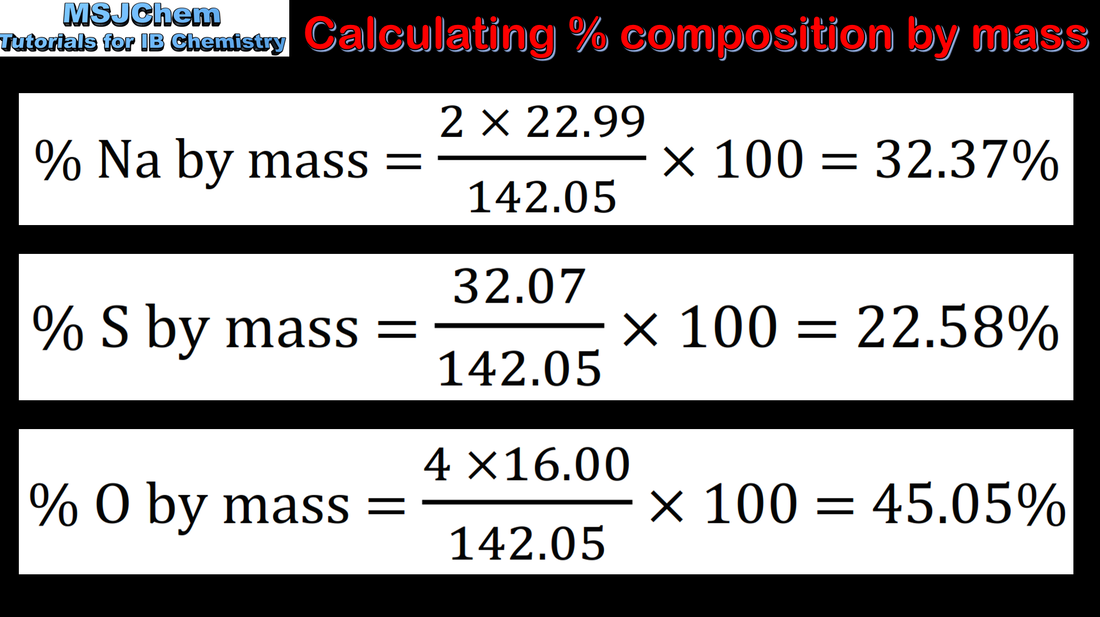
1.2 Calculating percentage composition by mass
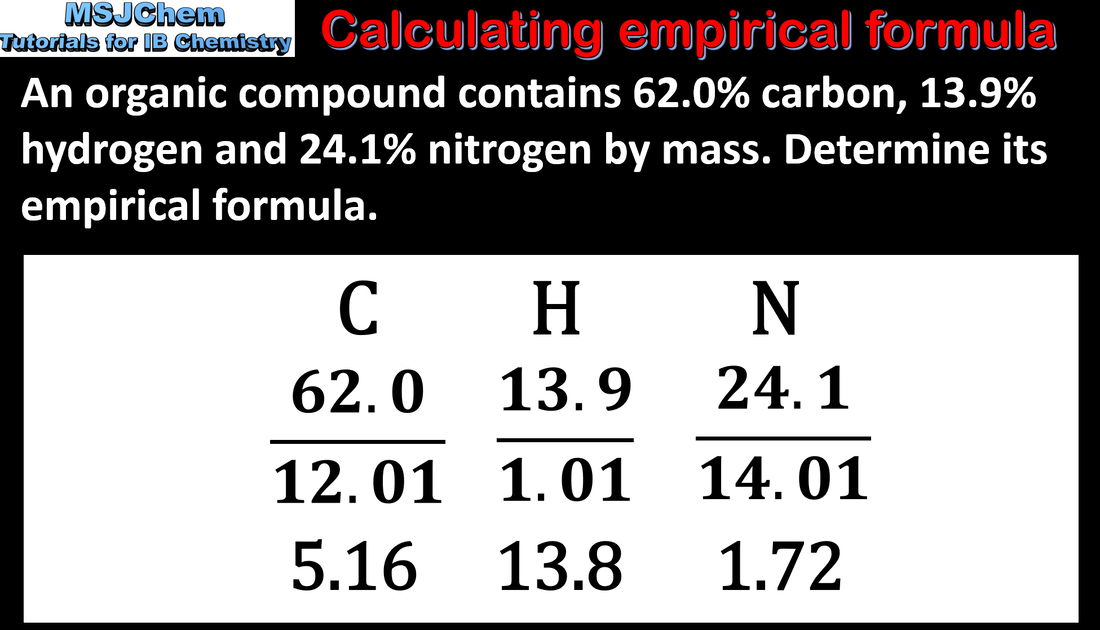
1.2 Calculating empirical formula from % composition by mass
This video covers how to calculate the empirical formula organic compound from combustion data.
This video covers how to calculate the water of crystallisation from experimental data.
Applications and skills:
Obtaining and using experimental data for deriving empirical formulas from reactions involving mass changes.
Obtaining and using experimental data for deriving empirical formulas from reactions involving mass changes.
1.3 Limiting and excess reactants
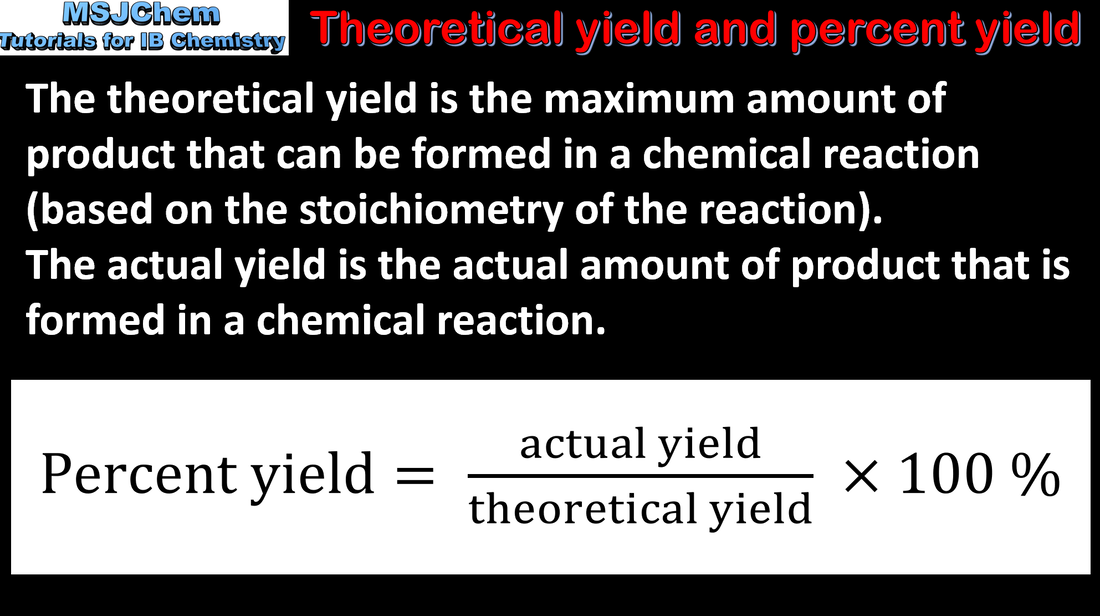
1.3 Percent yield
This video covers how to calculate percentage purity.
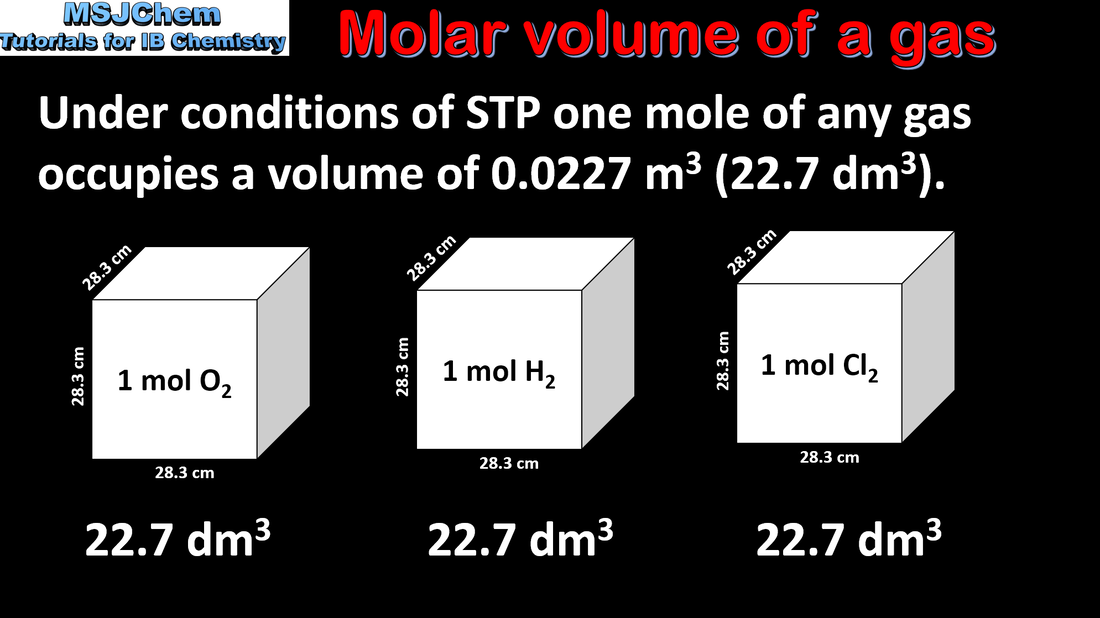
1.3 Molar volume of a gas
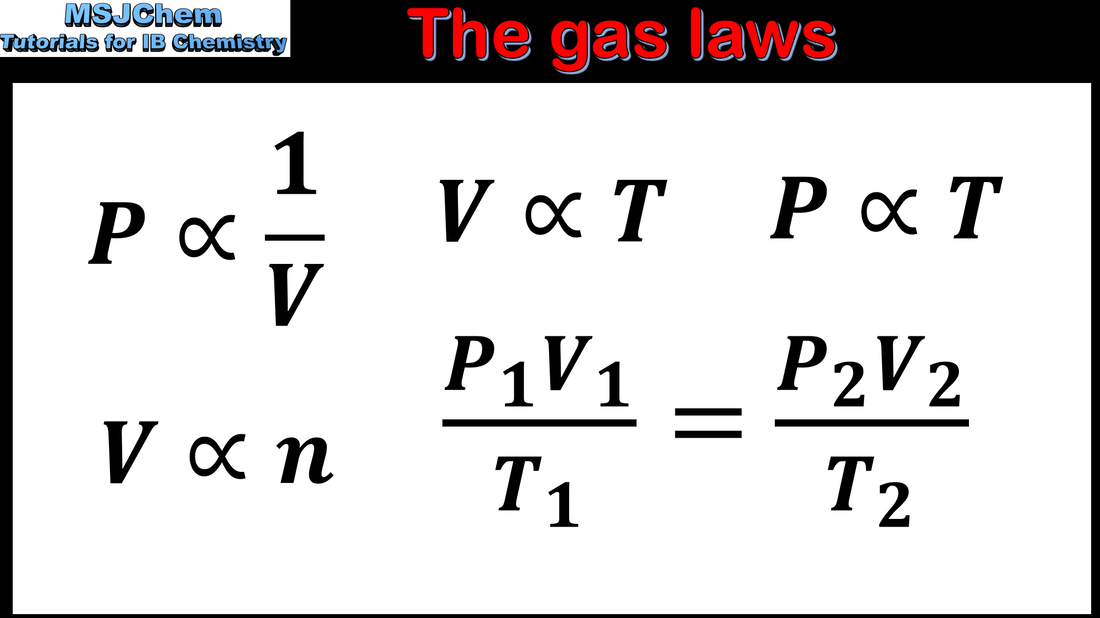
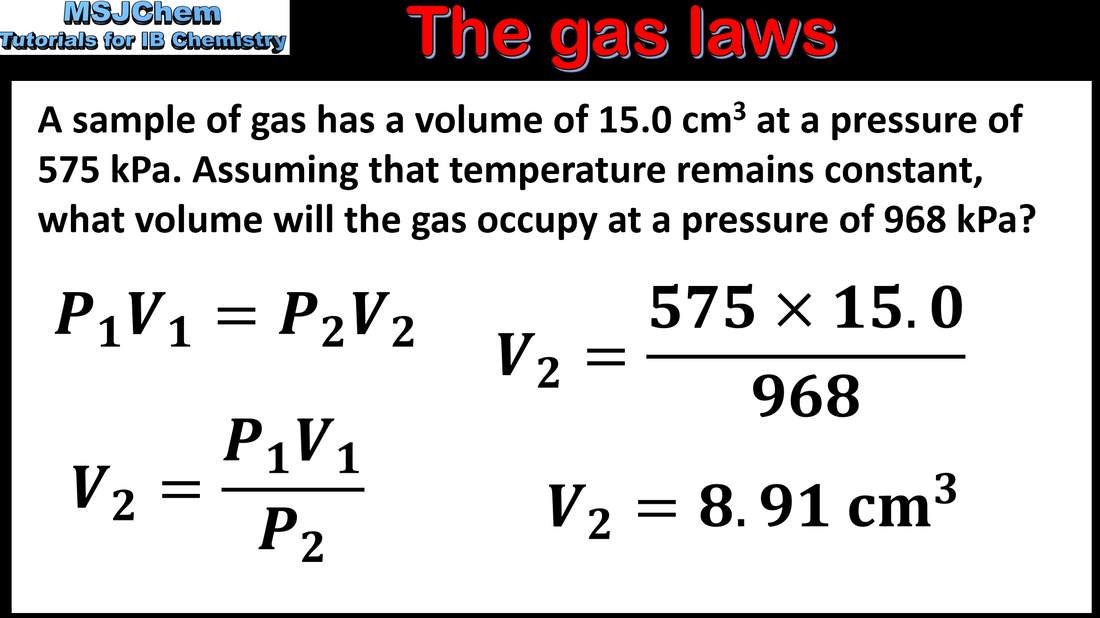
1.3 The gas laws (part 2)
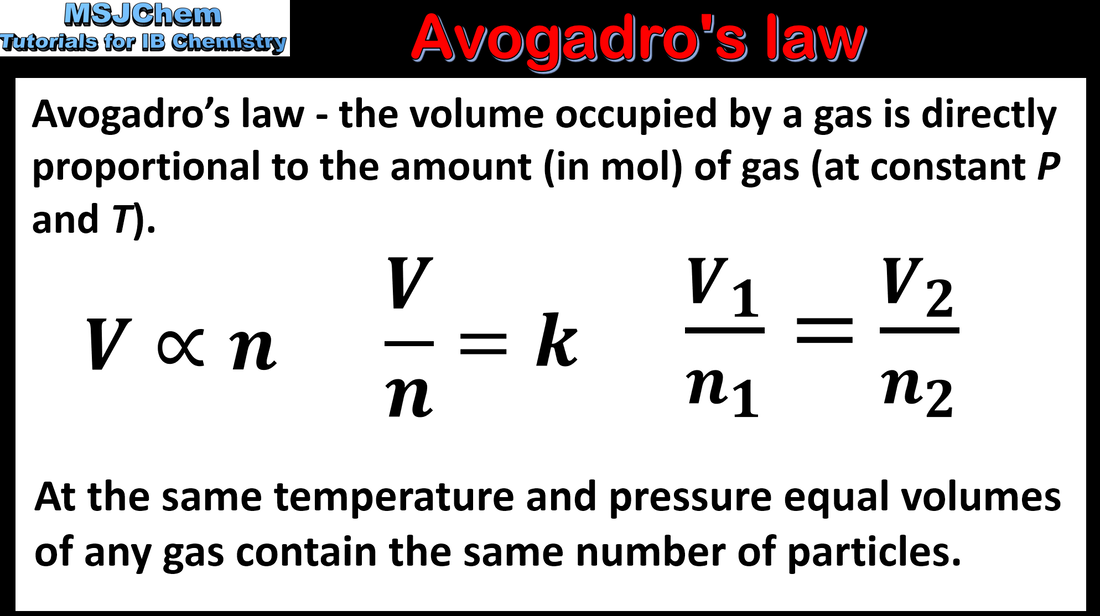
1.3 Avogadro's law
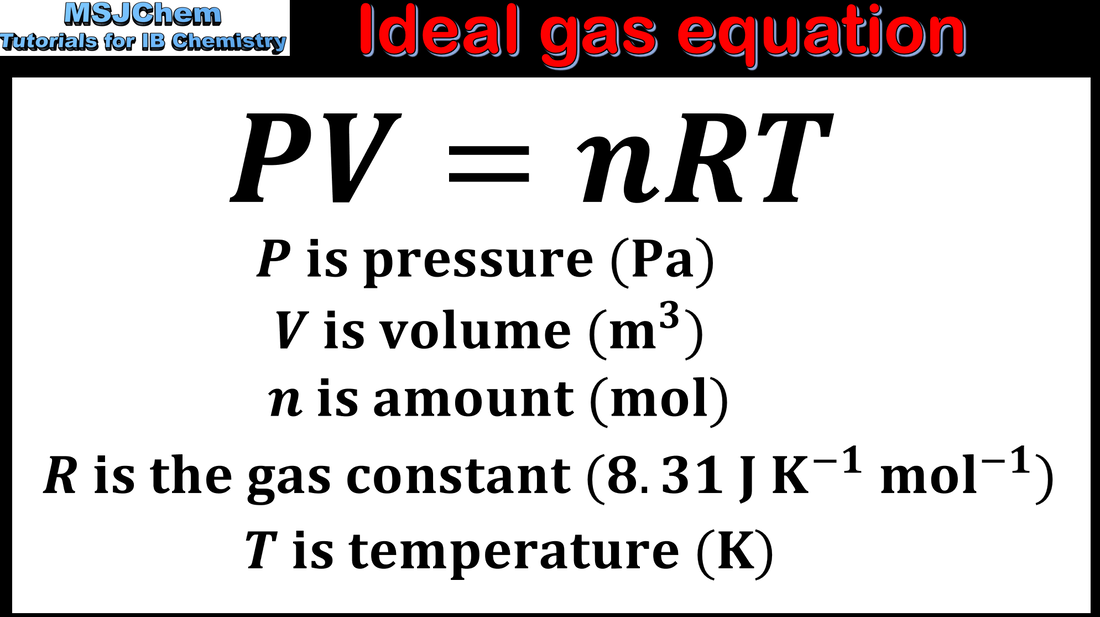
1.3 Ideal gas equation
Applications and skills:
Solve problems relating to the ideal gas equation.
Obtaining and using experimental values to calculate the molar mass of a gas from the ideal gas equation.
Solve problems relating to the ideal gas equation.
Obtaining and using experimental values to calculate the molar mass of a gas from the ideal gas equation.
Applications and skills:
Obtaining and using experimental values to calculate the molar mass of a gas from the ideal gas equation.
Obtaining and using experimental values to calculate the molar mass of a gas from the ideal gas equation.
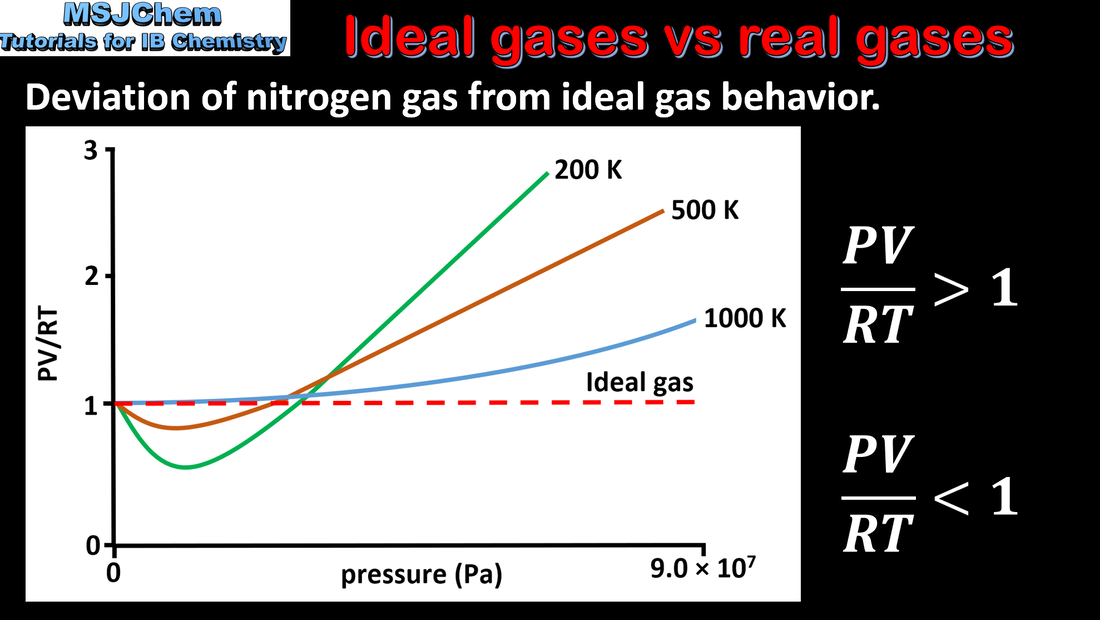
1.3 Deviation from ideal gas behaviour
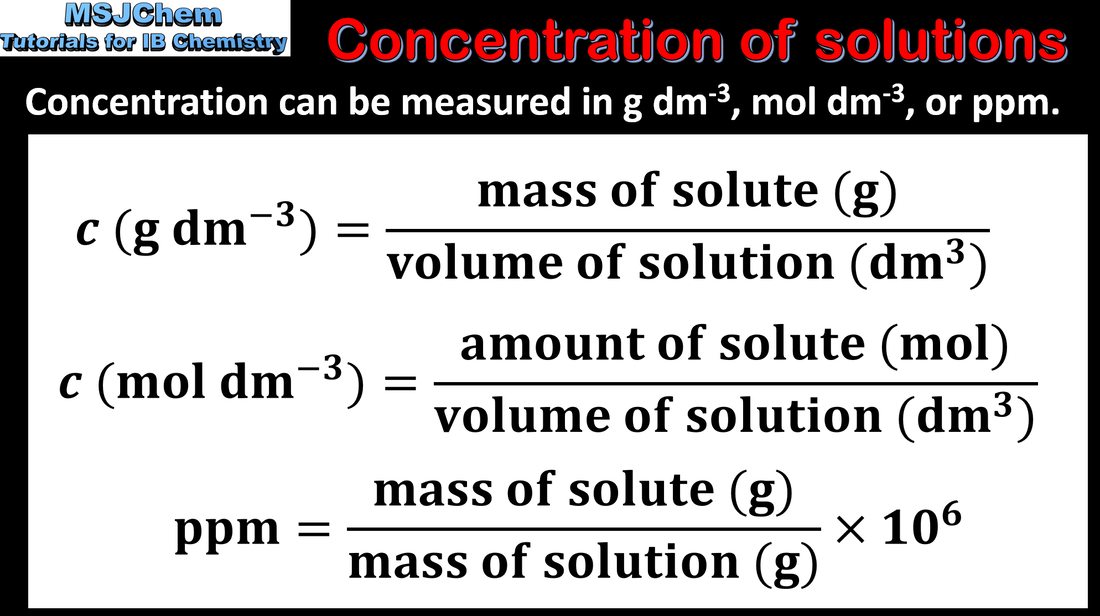
1.3 Concentration of solutions
|
Understandings:
The molar concentration of a solution is determined by the amount of solute and the volume of solution. Applications and skills: Solve problems involving molar concentration, amount of solute and volume of solution. Units of concentration to include: g dm-3, mol dm-3 and parts per million (ppm). |
This video covers how to calculate the concentration of a solution using a thermometric titration.
This video covers how to determine the percentage calcium carbonate in an egg shell using a back titration.
Review of past exam questions (old syllabus) but still relevant for new syllabus.
|
|
A review of some past quantitative chemistry exam questions for the old syllabus.
|