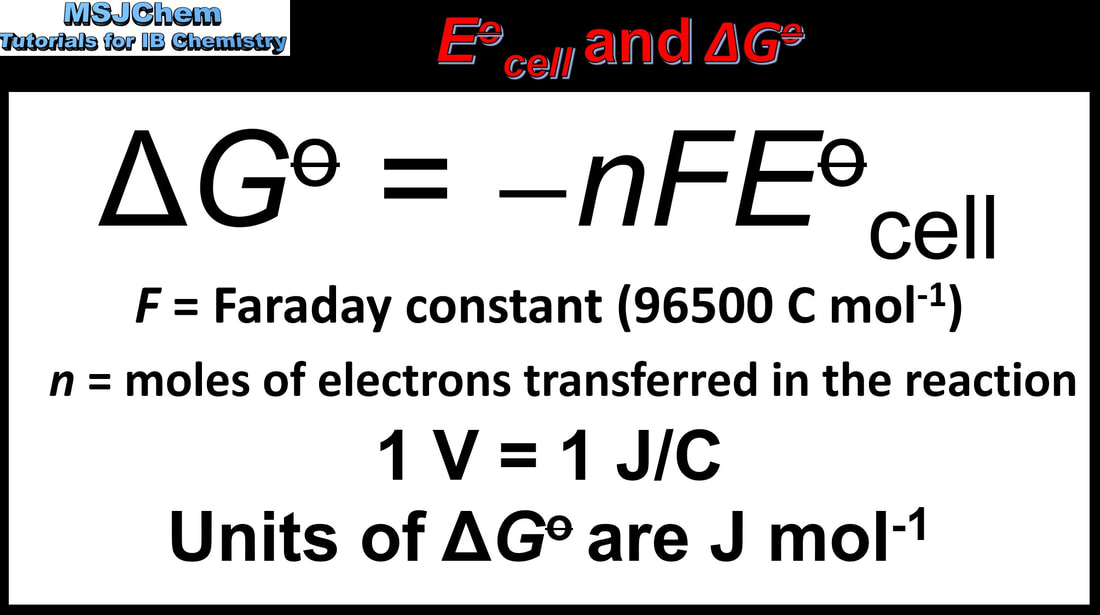Topic 19 Oxidation and reduction HL
19.1 Standard electrode potentials
|
Understandings:
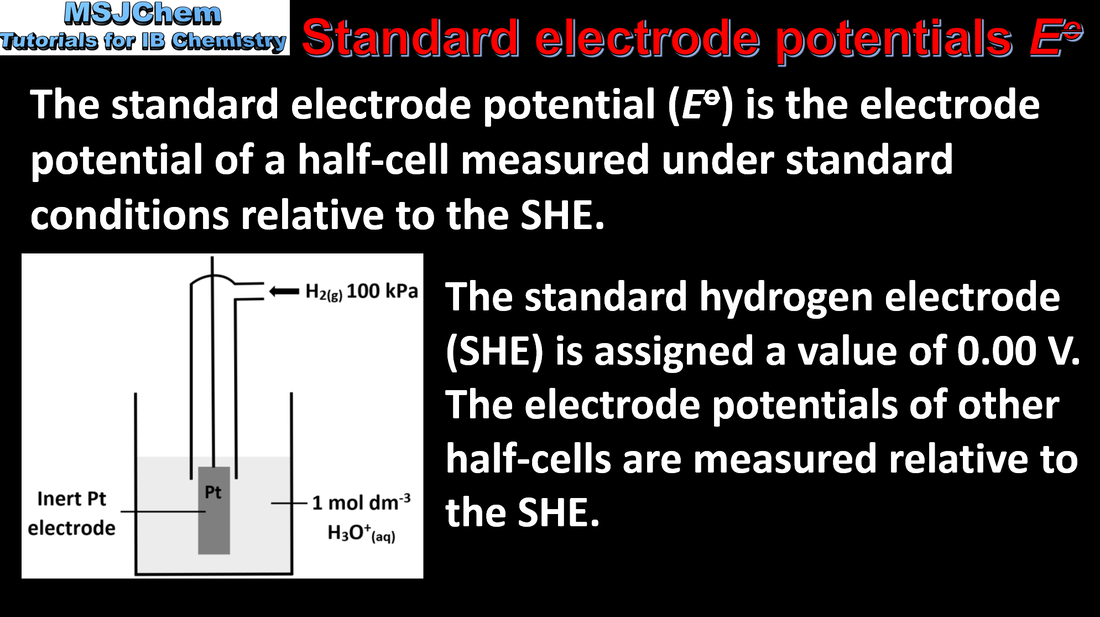
The standard hydrogen electrode (SHE) consists of an inert platinum electrode in contact with 1 mol dm-3 hydrogen ion and hydrogen gas at 100 kPa and 298 K. The Eº of the SHE is 0 V. The standard electrode potential (Eº) is the potential (voltage) of the reduction half-equation under standard conditions measured relative to the SHE. |
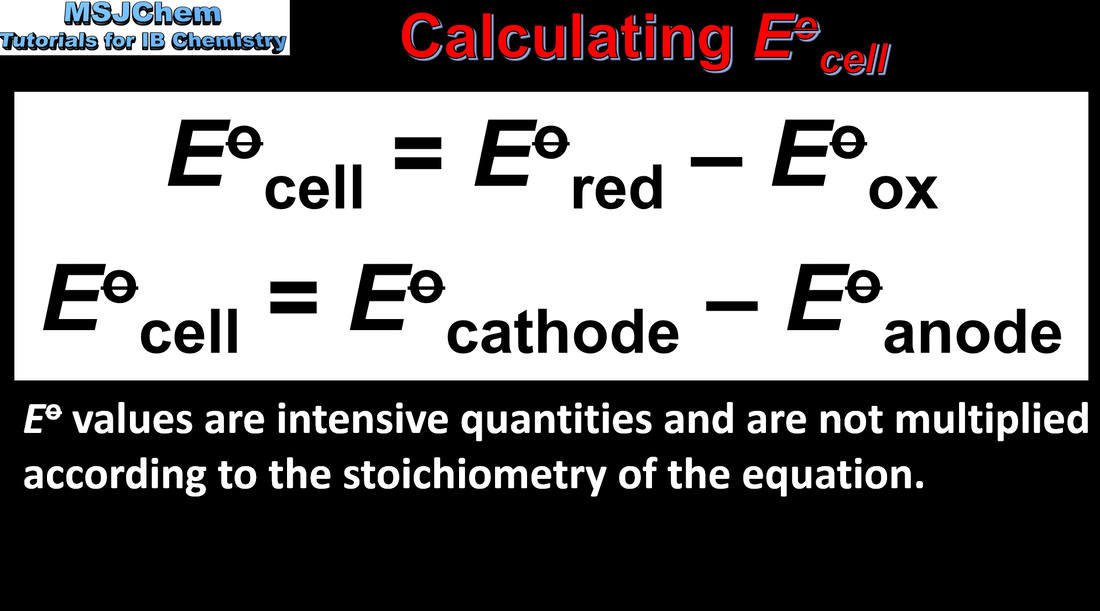
19.1 Calculating cell potential
|
|
Applications and skills
Prediction of whether a reaction is spontaneous or not using electrode potential values. |
19.1 Cell potential and Gibbs free energy
19.1 Electroplating
|
Understandings:
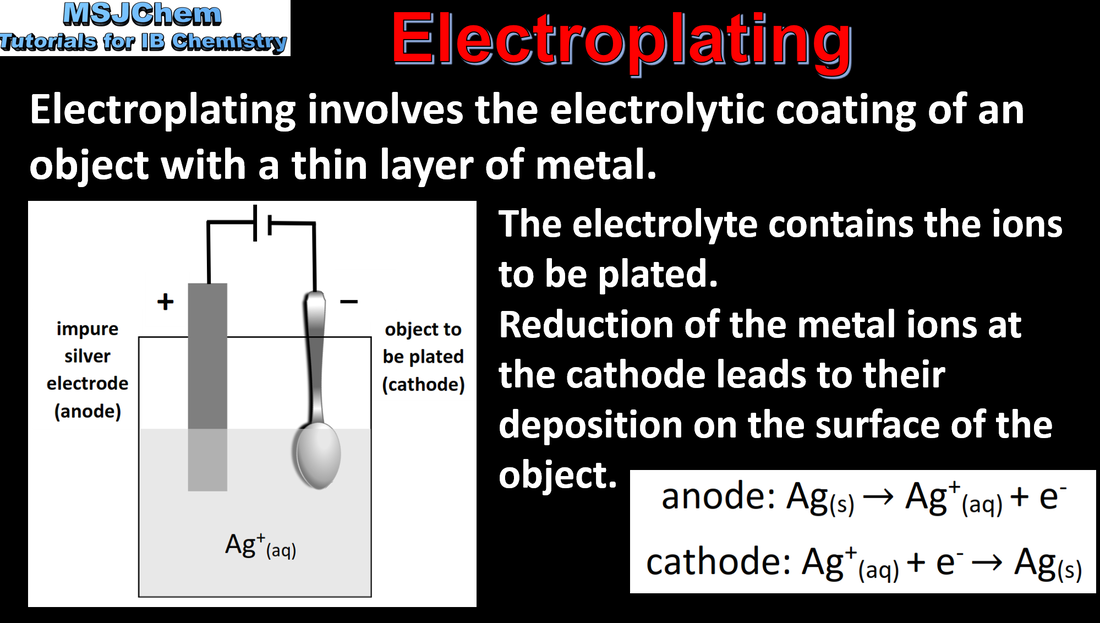
Electroplating involves the electrolytic coating of an object with a metallic thin layer. Current, duration of electrolysis and charge on the ion affect the amount of product formed at the electrodes during electrolysis Applications and skills: Explanation of the process of electroplating. |
19.1 Electrolysis of aqueous solutions
|
Understandings:
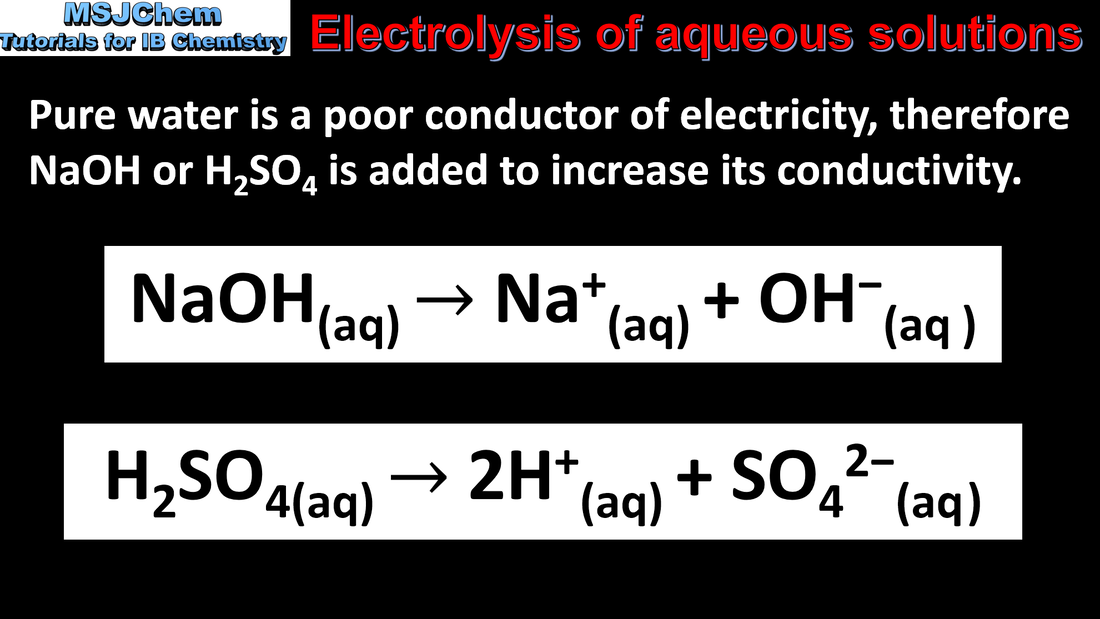
When aqueous solutions are electrolysed, water can be oxidized to oxygen at the anode and reduced to hydrogen at the cathode. Applications and skills: Explanation of the products formed during the electrolysis of aqueous solutions. Guidance: Electrolytic processes to be covered in theory should include the electrolysis of aqueous solutions (eg sodium chloride, copper(II) sulfate etc) and water using both inert platinum or graphite electrodes and copper electrodes. Explanations should refer to Eº values, nature of the electrode and concentration of the electrolyte. |
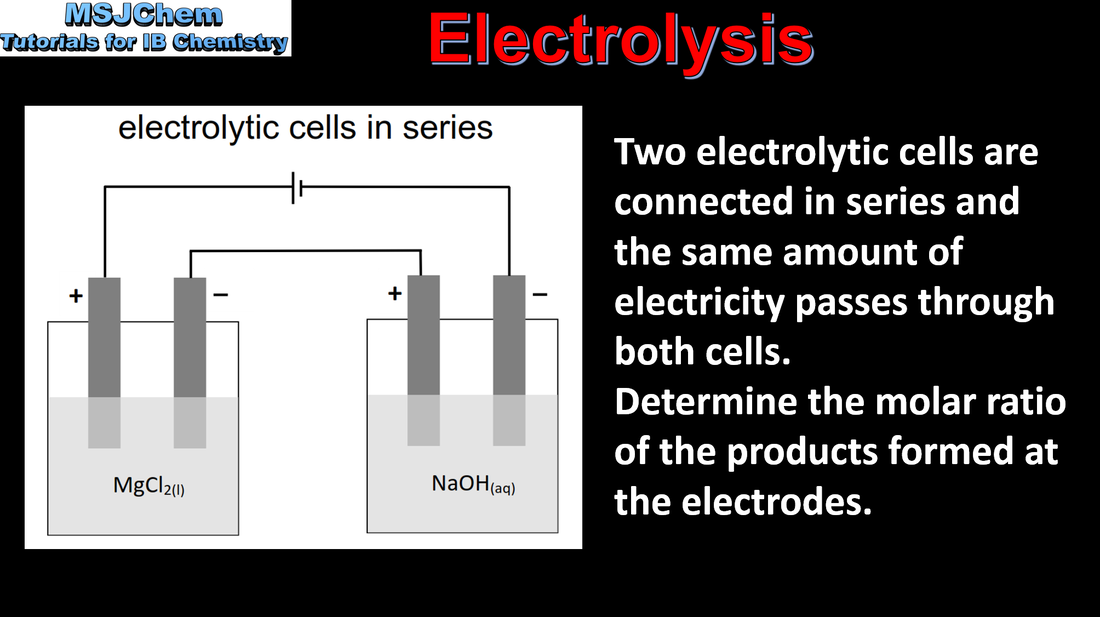
19.1 Factors that affect the amount of product formed in electrolysis