Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
Topic 5 Energetics
YouTube playlist
YouTube playlist
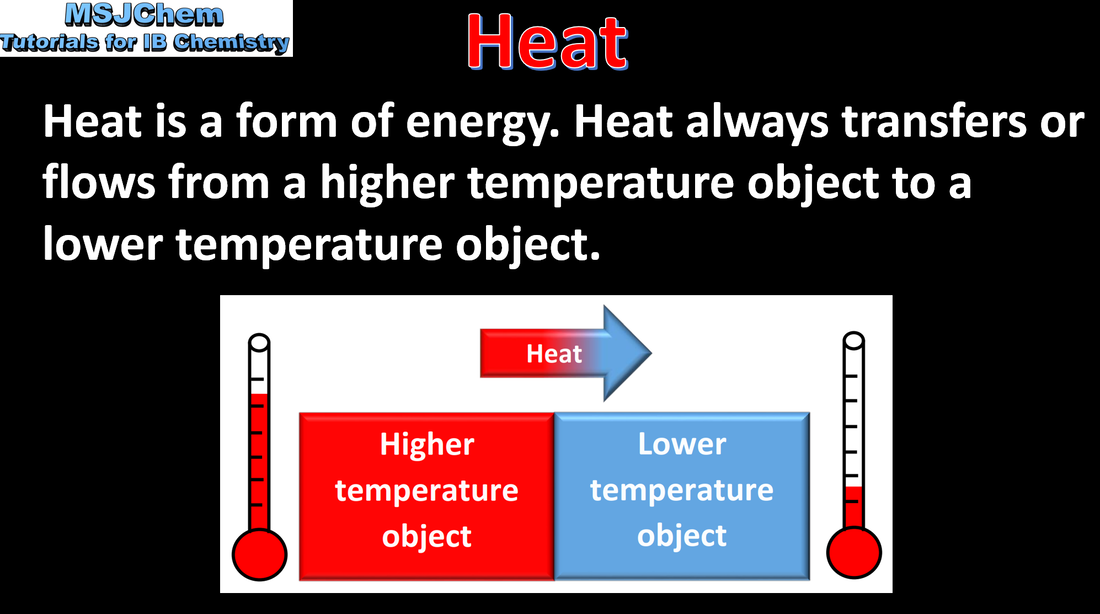
5.1 Heat and temperature
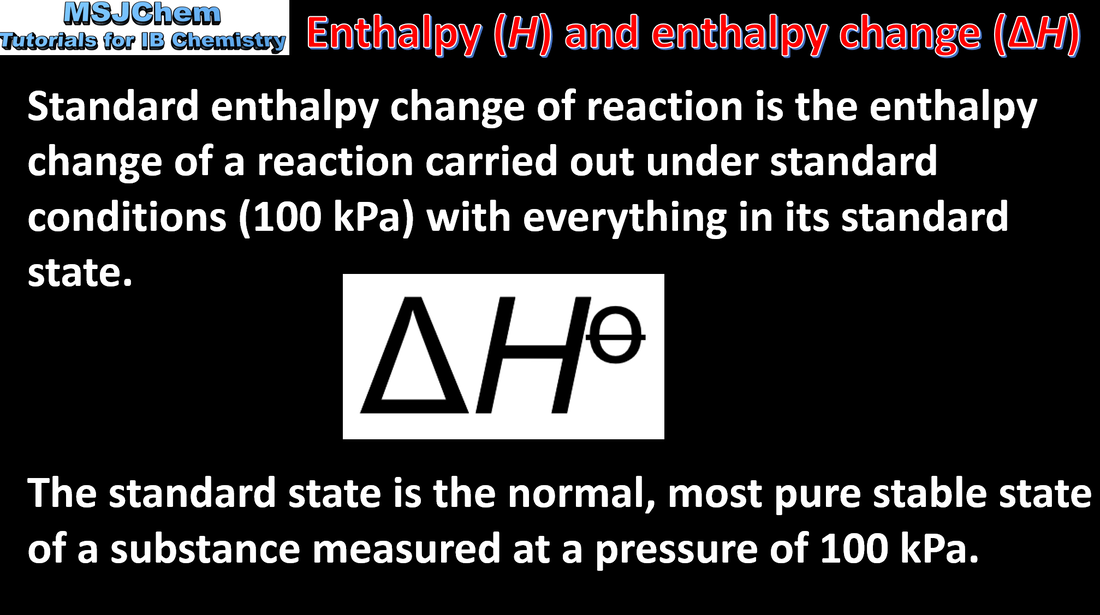
5.1 Enthalpy and enthalpy change
|
Understandings:
∆H values are usually expressed under standard conditions, given by ∆H°, including standard states. Guidance: Standard state refers to the normal, most pure stable state of a substance measured at 100 kPa. Temperature is not a part of the definition of standard state, but 298 K is commonly given as the temperature of interest. |
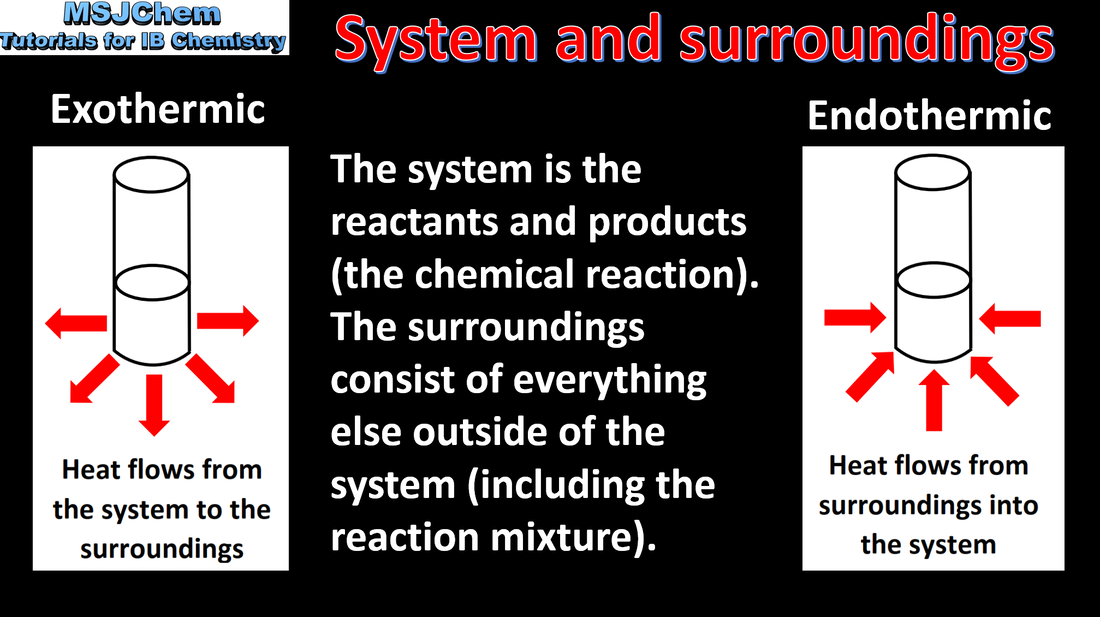
5.1 Exothermic and endothermic reactions
|
Understandings:
Chemical reactions that involve transfer of heat between the system and the surroundings are described as exothermic or endothermic. Applications and skills: Sketching and evaluation of potential energy profiles in determining whether reactants or products are more stable and if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. |
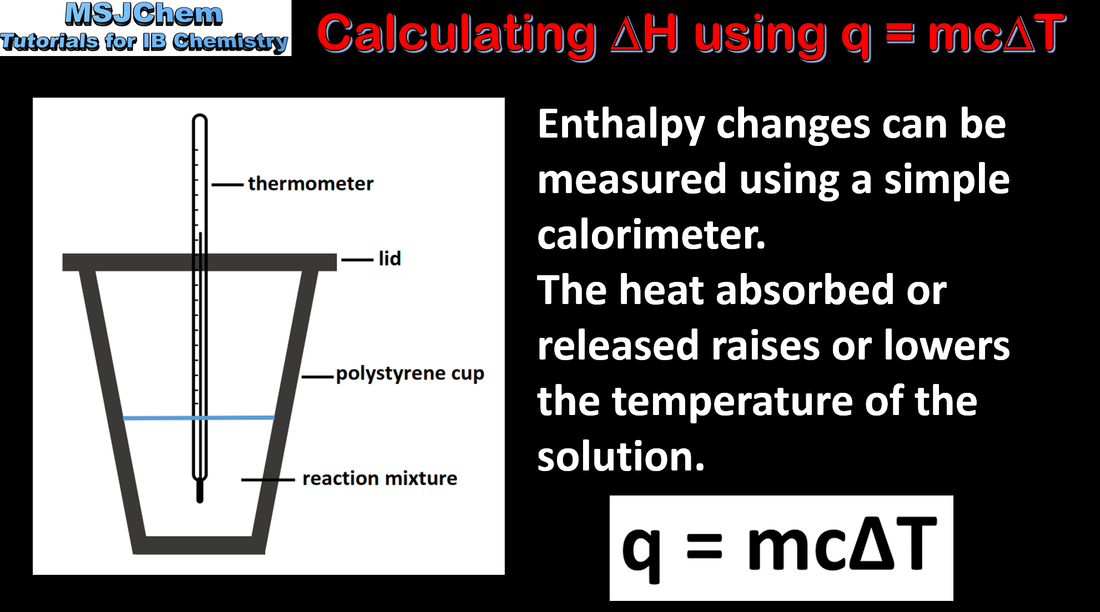
5.1 Calculating ΔH using q = mcΔT
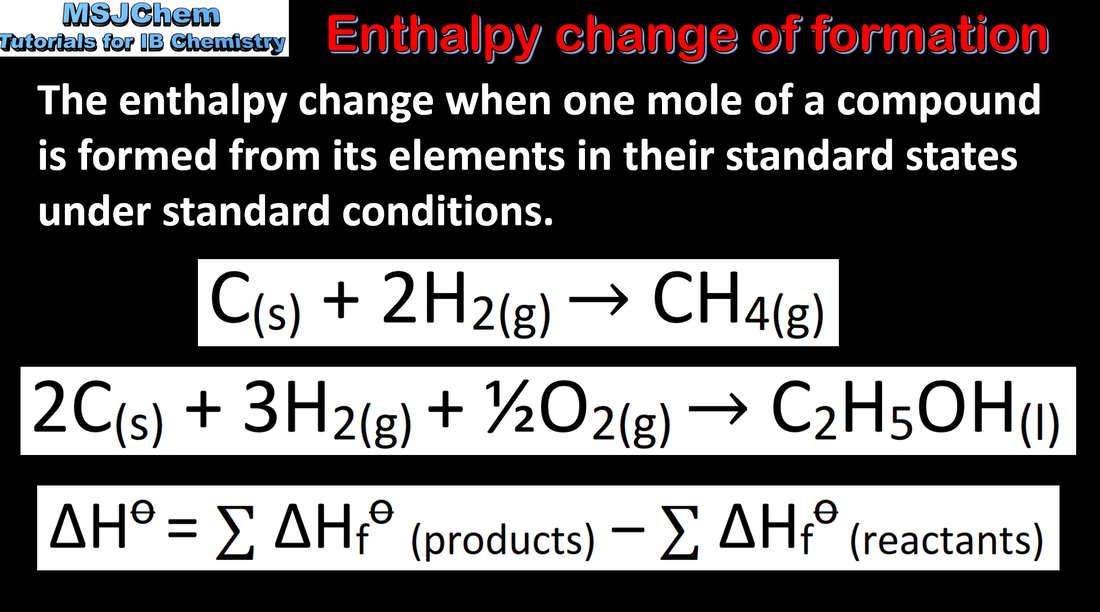
5.1 Standard enthalpy change of formation
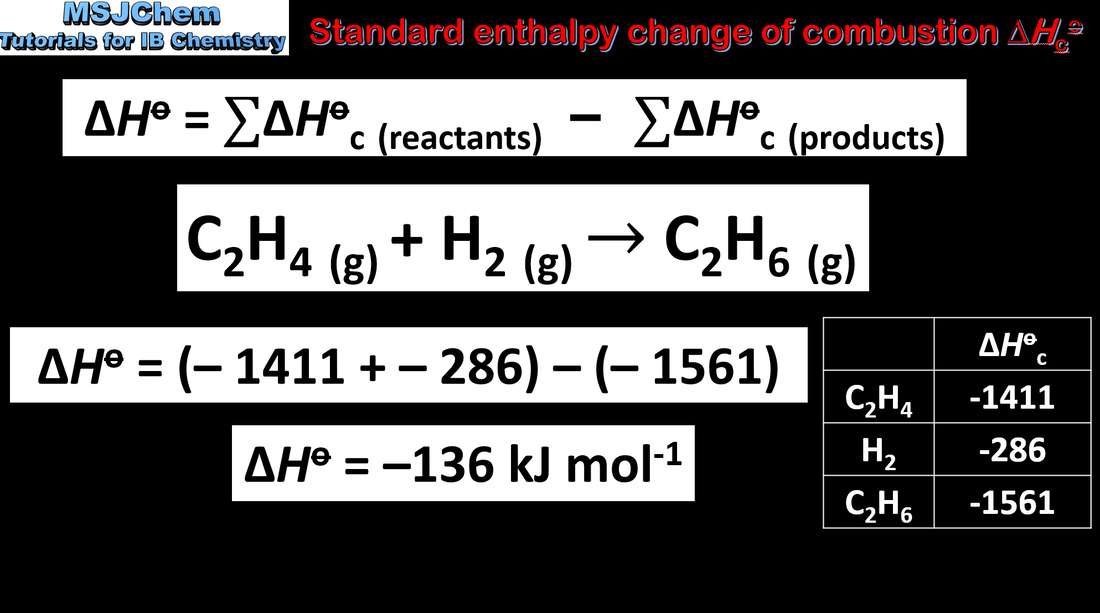
5.1 Standard enthalpy change of combustion
|
|
This video covers the standard enthalpy changes of formation and combustion.
Please note that the standard conditions are now 298 K and 100.0 kPa. |
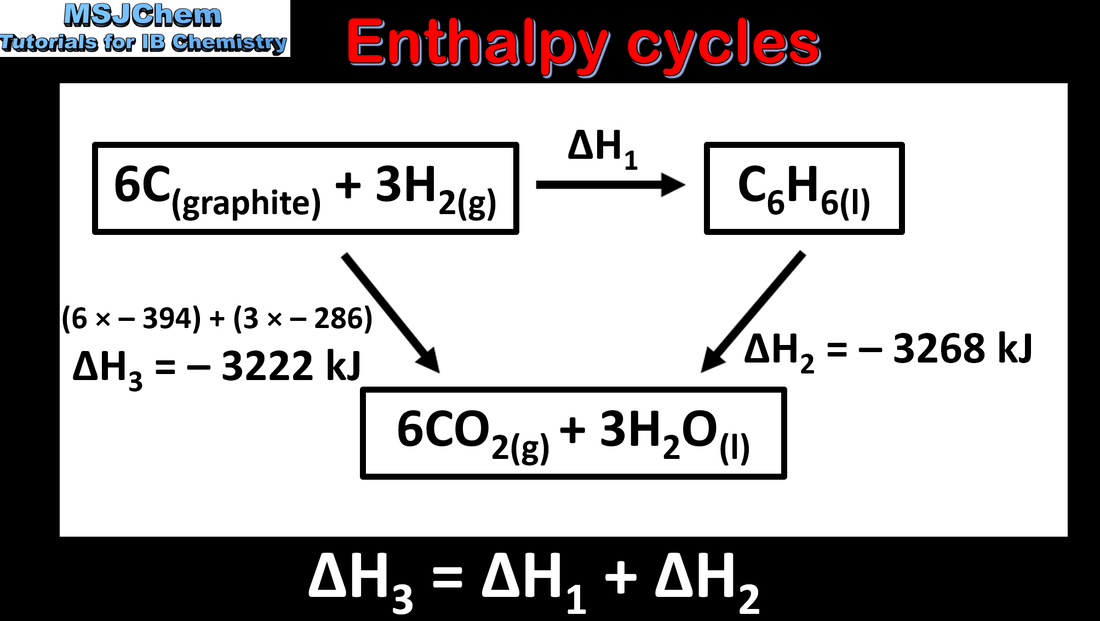
5.2 Enthalpy cycles
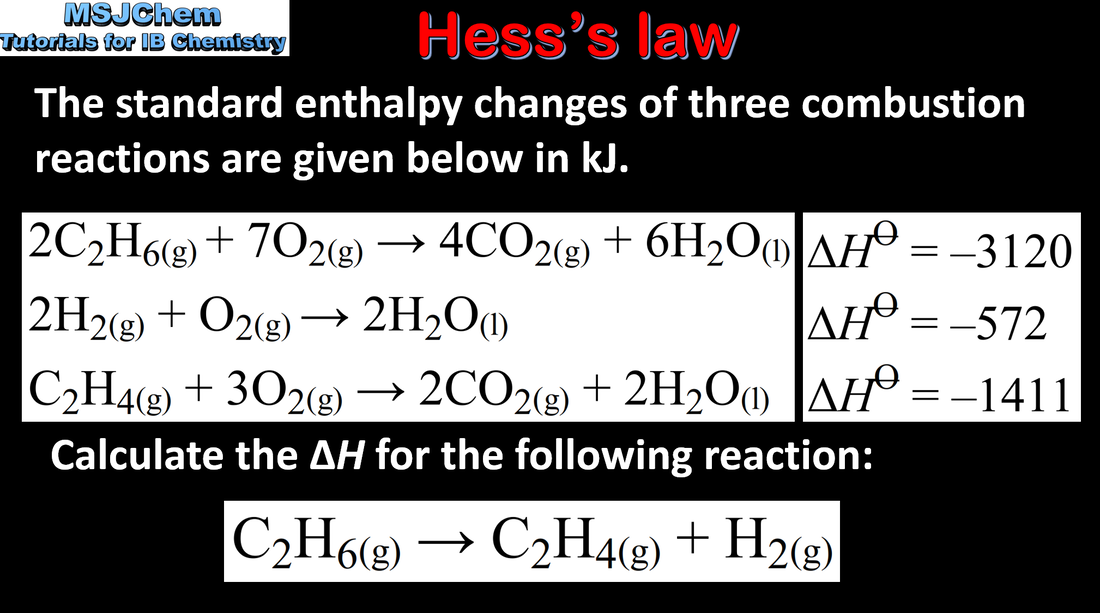
5.2 Hess's law example
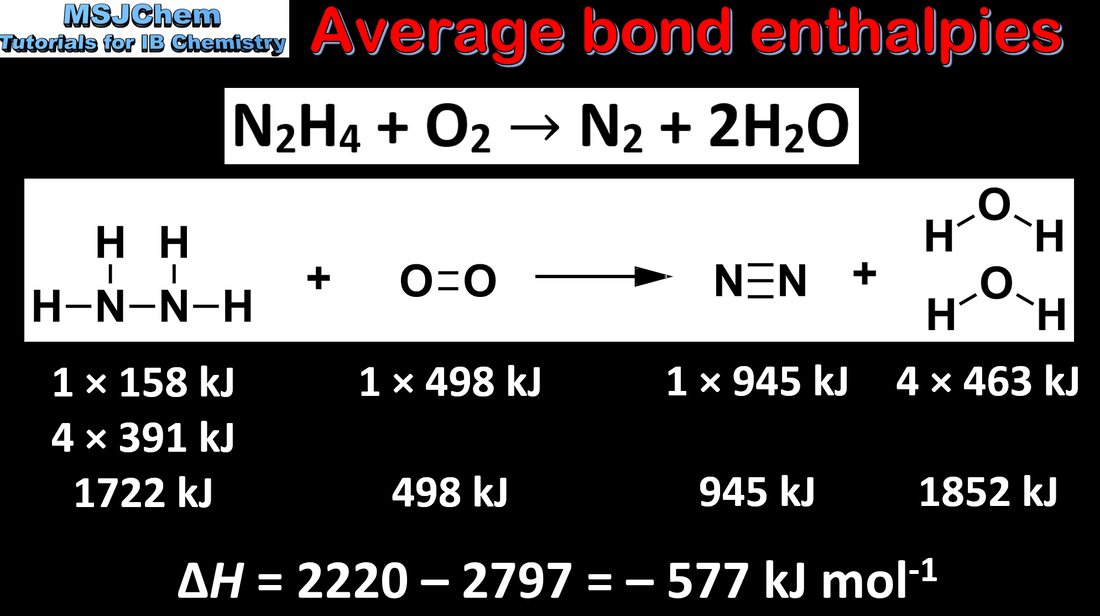
5.3 Average bond enthalpies
|
Understandings:
Bond-forming releases energy and bond-breaking requires energy. Average bond enthalpy is the energy needed to break one mol of a bond in a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds. Applications and skills: Calculation of the enthalpy changes from known bond enthalpy values and comparison of these to experimentally measured values. |
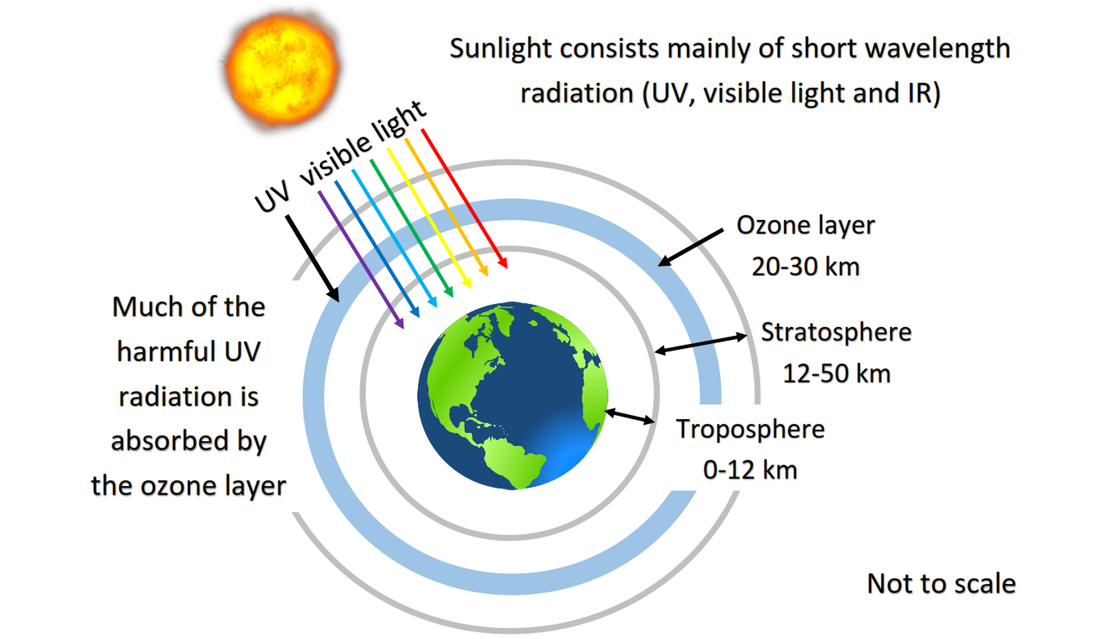
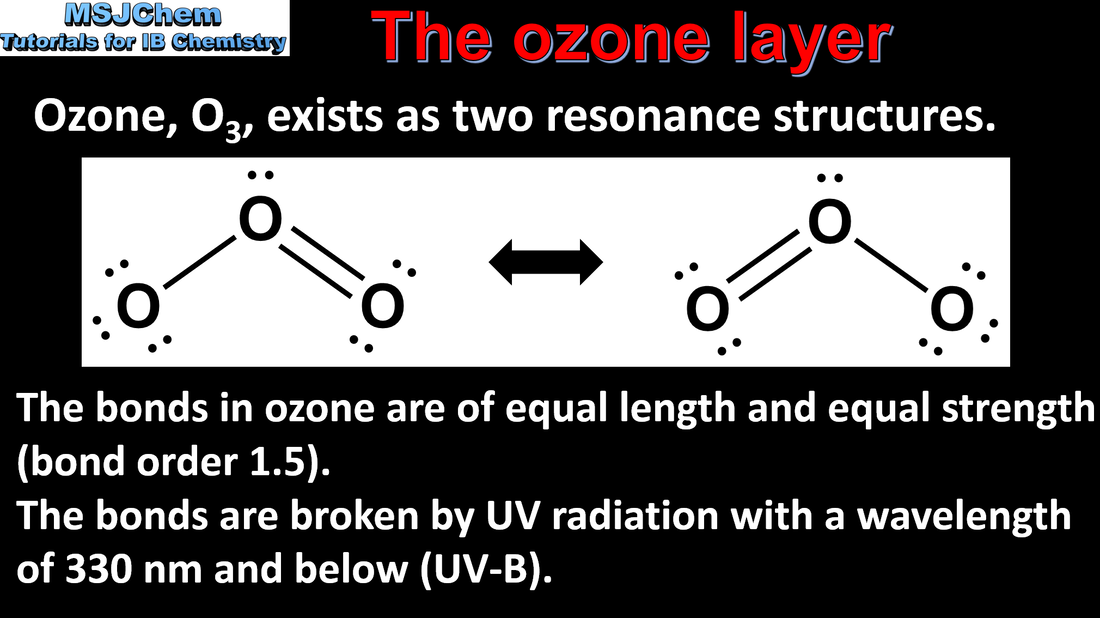
5.3 Bonding in ozone and oxygen
5.3 Bond strength in oxygen and ozone
|
Applications and skills:
Discussion of the bond strength in ozone relative to oxygen in its importance to the atmosphere. This video goes into more detail about the energy and wavelength required to break the bonds in ozone and oxygen. |