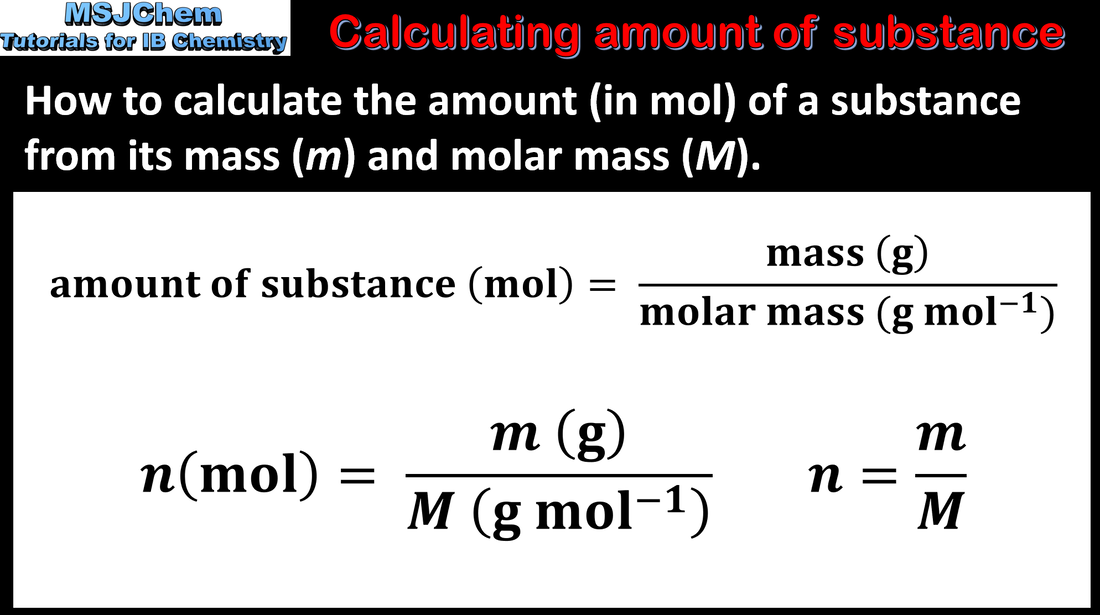Structure 1.4 Counting particles by mass: The mole
Structure 1.4.1
Understandings:
Understandings:
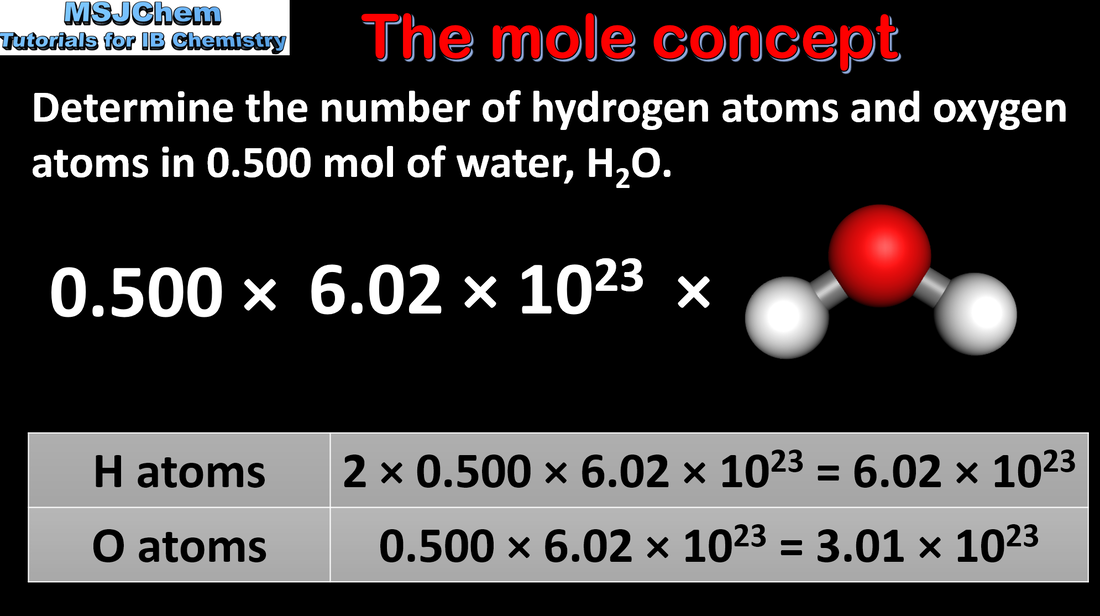
- The mole (mol) is the SI unit of amount of substance. One mole contains exactly the number of elementary entities given by the Avogadro constant.
- Convert the amount of substance, n, to the number of specified elementary entities.
- An elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an electron, any other particle or a specified group of particles.
- The Avogadro constant NA is given in the data booklet. It has the units mol–1.
Structure 1.4.2
Understandings:
Understandings:
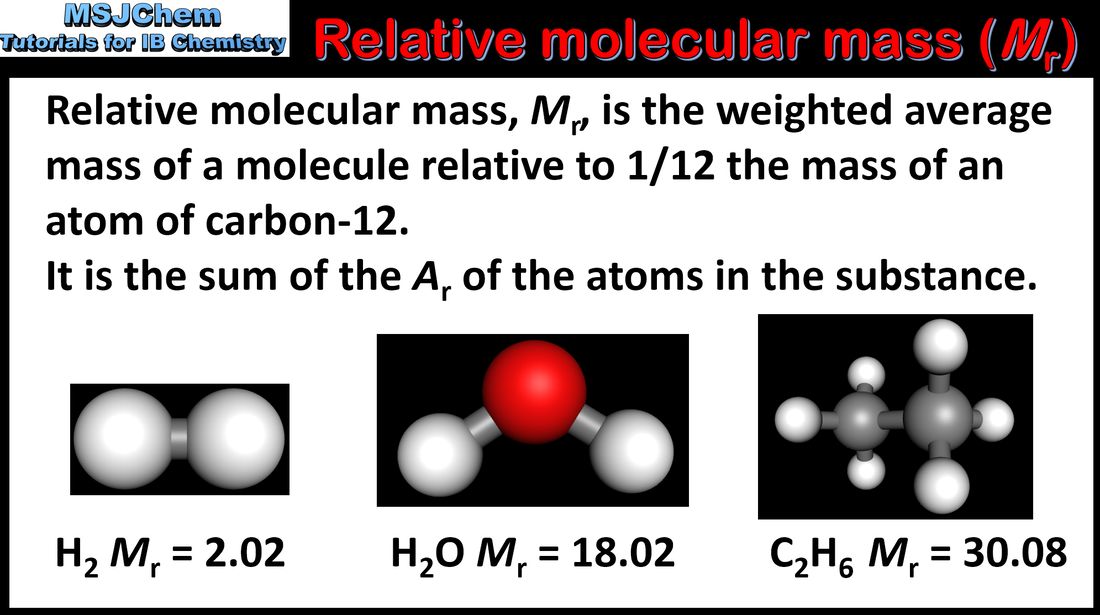
- Masses of atoms are compared on a scale relative to 12C and are expressed as relative atomic mass Ar and relative formula mass Mr .
- Determine relative formula masses Mr from relative atomic masses Ar .
- Relative atomic mass and relative formula mass have no units.
- The values of relative atomic masses given to two decimal places in the data booklet should be used in calculations.
Structure 1.4.3
Understandings:
Understandings:
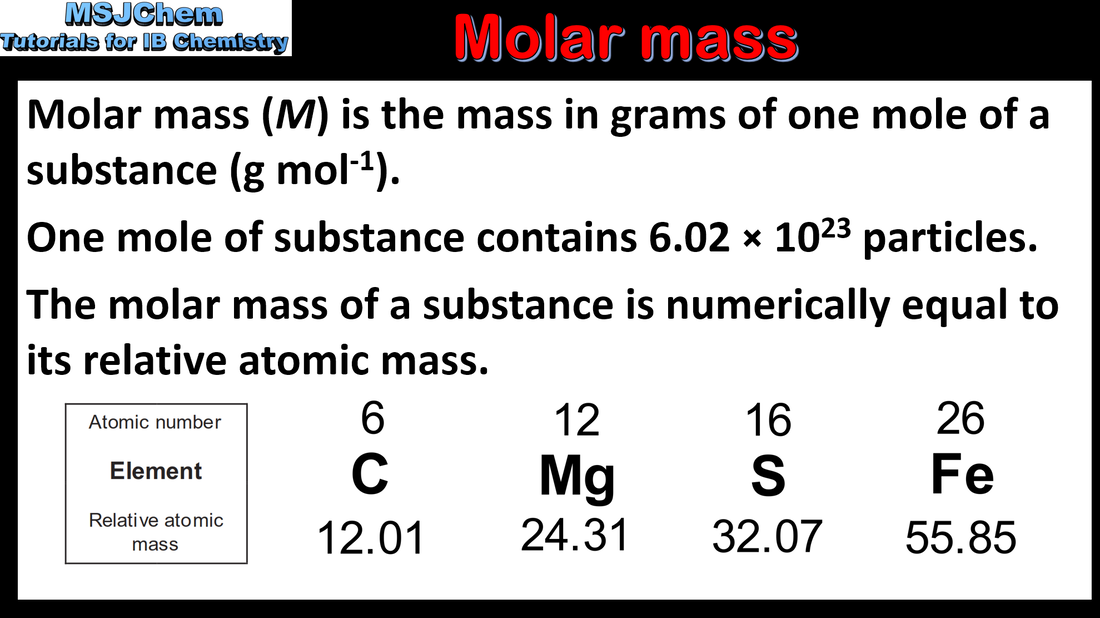
- Molar mass M has the units g mol–1
- Solve problems involving the relationships between the number of particles, the amount of substance in moles and the mass in grams.
- The relationship n = m/M is given in the data booklet.
Structure 1.4.4
Understandings:
Understandings:
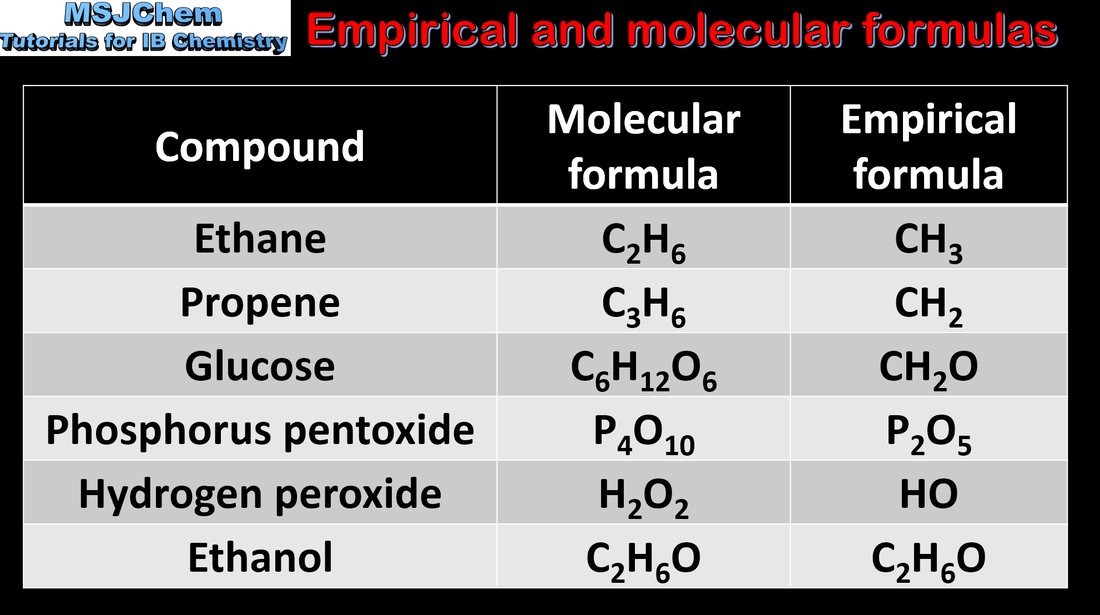
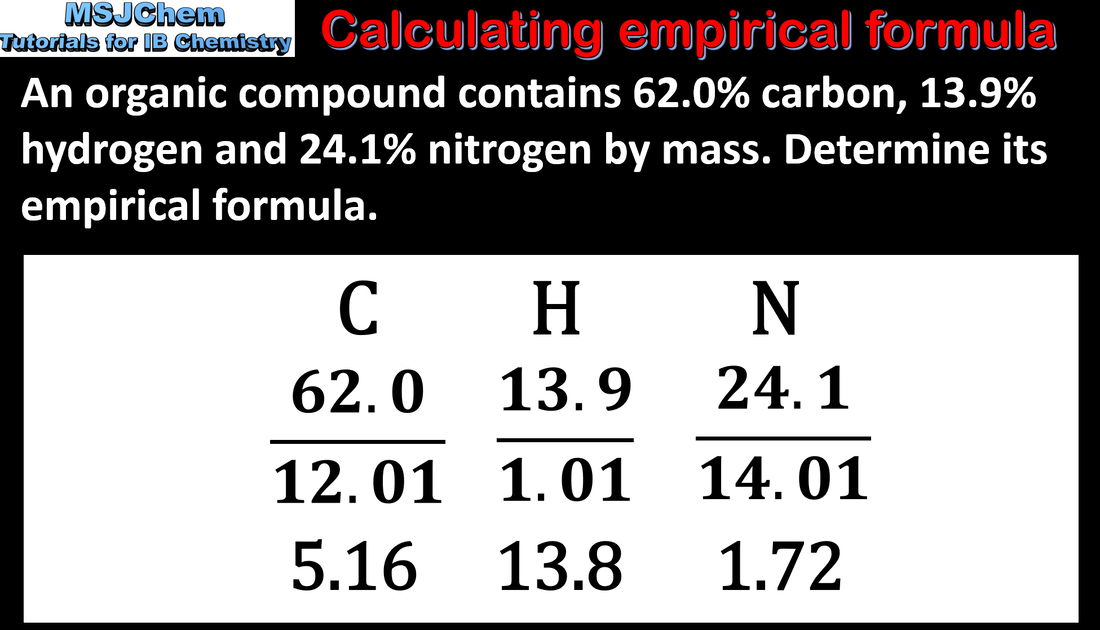
- The empirical formula of a compound gives the simplest ratio of atoms of each element present in that compound.
- The molecular formula gives the actual number of atoms of each element present in a molecule.
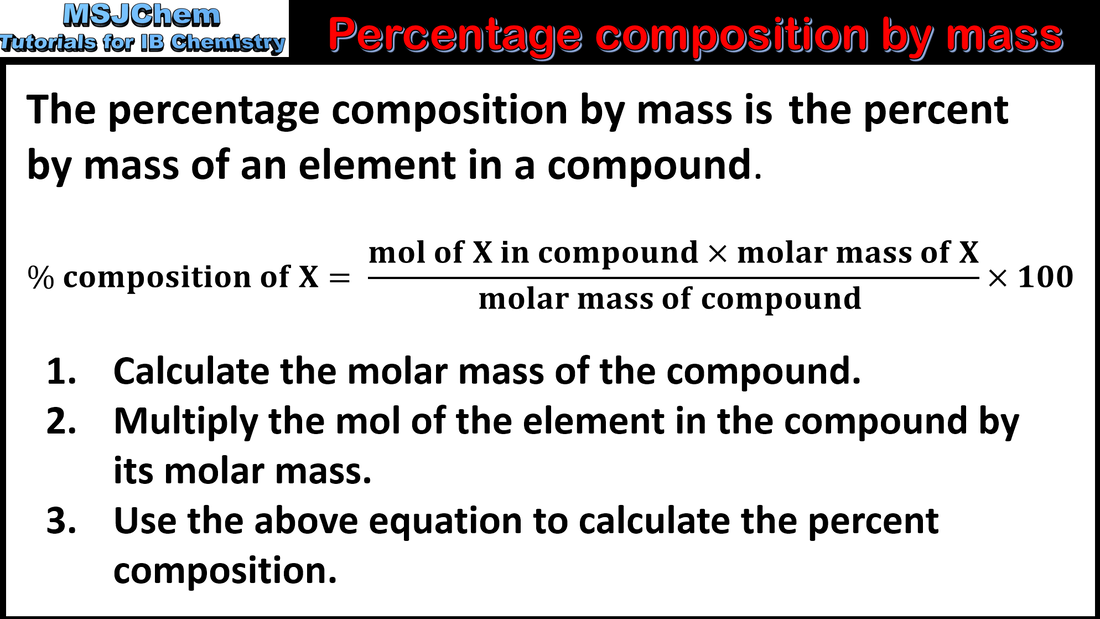
- Interconvert the percentage composition by mass and the empirical formula.
- Determine the molecular formula of a compound from its empirical formula and molar mass.
Structure 1.4.5
Understandings:
Understandings:
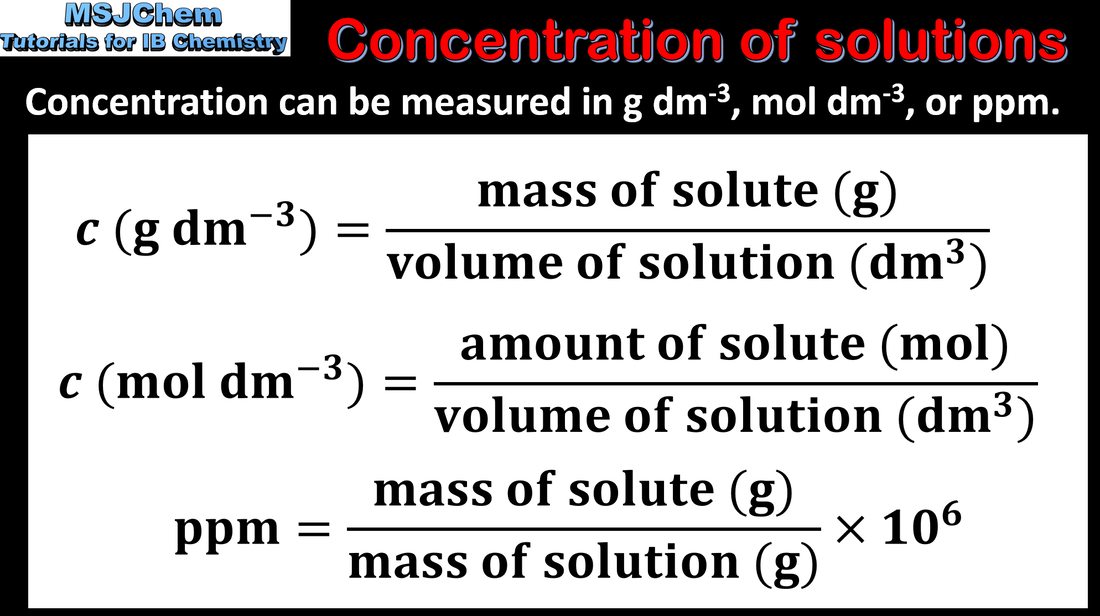
- The molar concentration is determined by the amount of solute and the volume of solution.
- Solve problems involving the molar concentration, amount of solute and volume of solution.
- The use of square brackets to represent molar concentration is required.
- Units of concentration should include g dm–3 and mol dm–3 and conversion between these.
- The relationship n = CV is given in the data booklet.
Structure 1.4.6
Understandings:
Understandings:
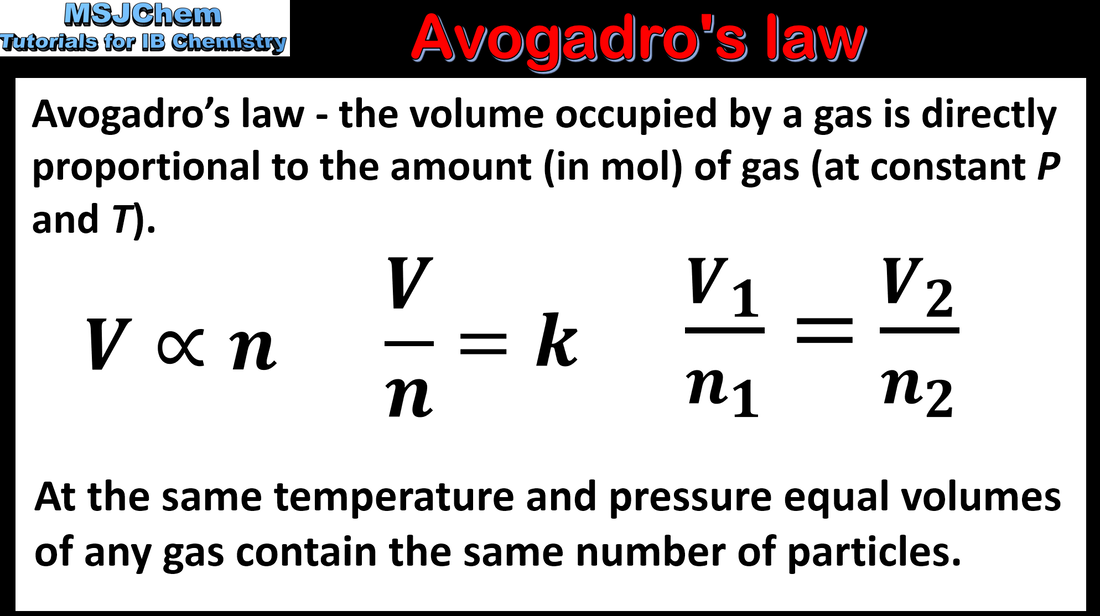
- Avogadro’s law states that equal volumes of all gases measured under the same conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules.
- Solve problems involving the mole ratio of reactants and/or products and the volume of gases.