Help support my work by joining the Member's Area or by becoming a Patron.
Topic 3 Periodicity
YouTube playlist
YouTube playlist
3.1 Groups and periods, metals and non-metals
|
Understandings:
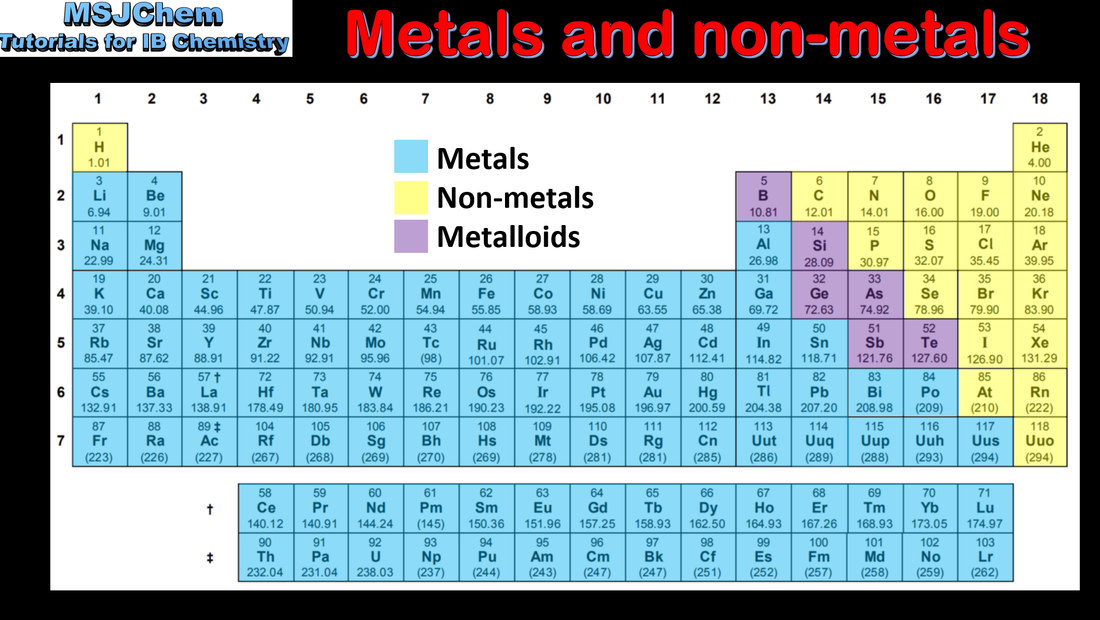
The periodic table consists of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows). The periodic table shows the positions of metals, non-metals and metalloids. The period number (n) is the outer energy level that is occupied by electrons. The number of the principal energy level and the number of the valence electrons in an atom can be deduced from its position on the periodic table. |
| new_syllabus_the_periodic_table.pdf |
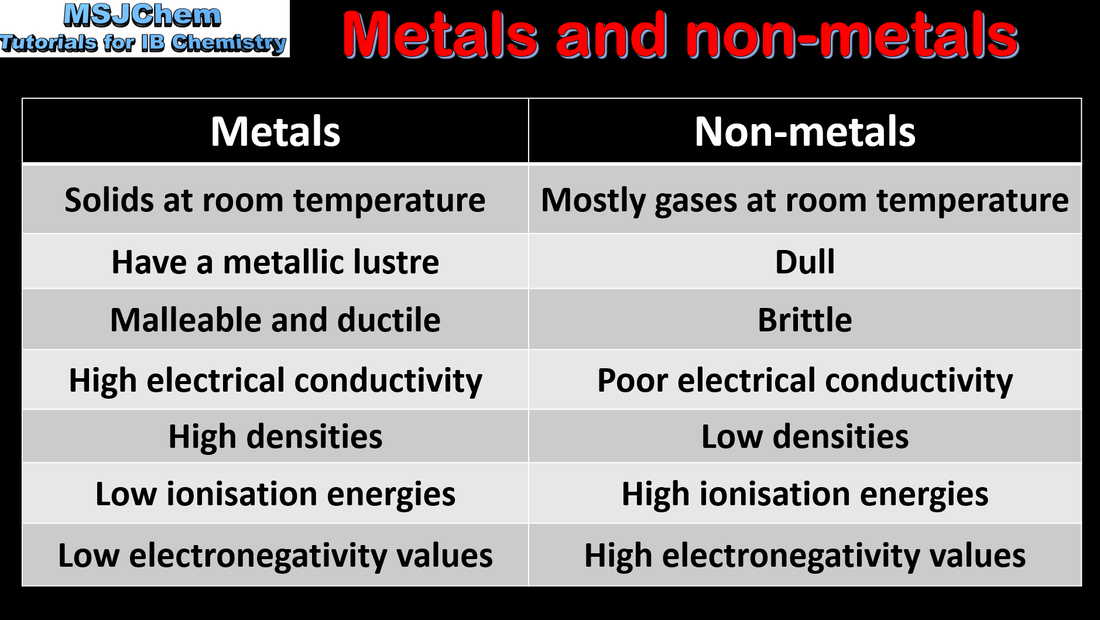
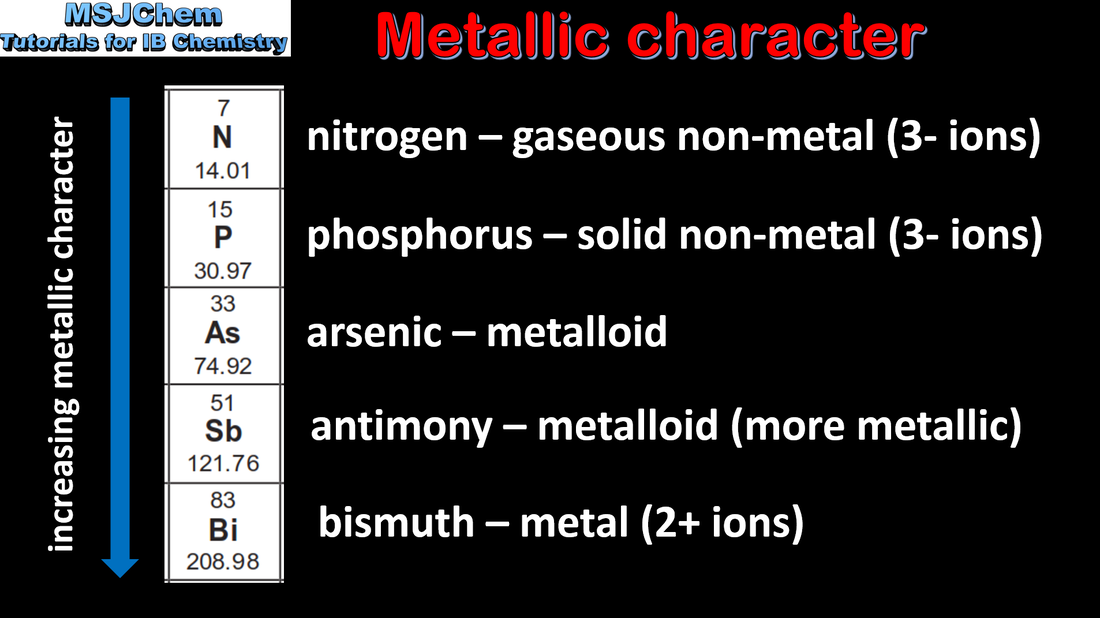
3.1 Properties of metals and non-metals
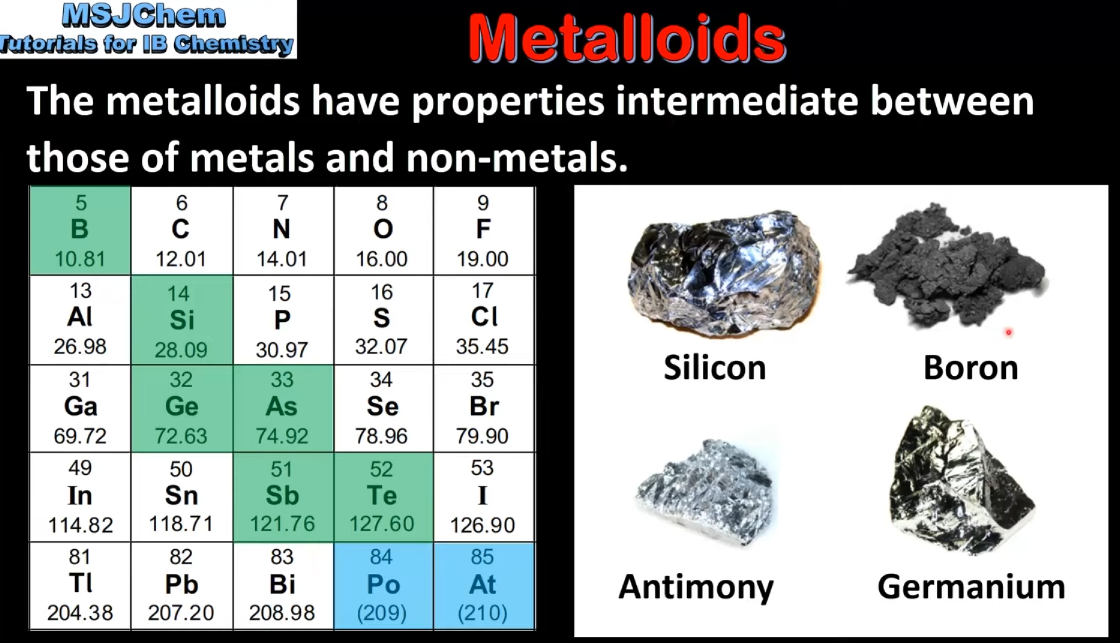
3.1 The metalloids
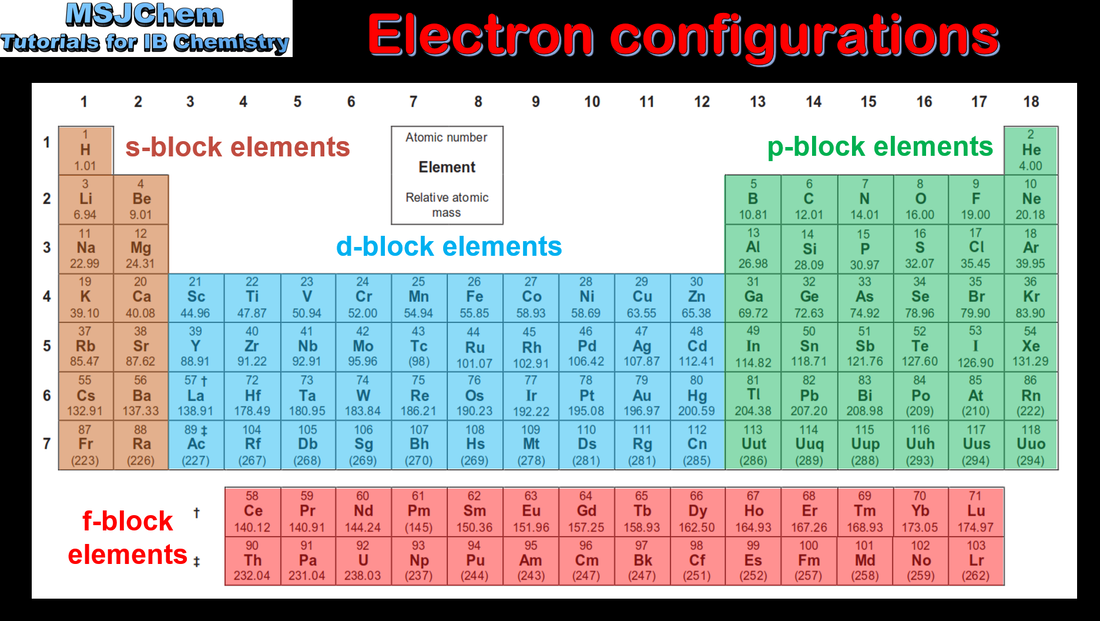
3.1 Electron configurations and the periodic table
| electronic_configurations_and_the_periodic_table.pdf |
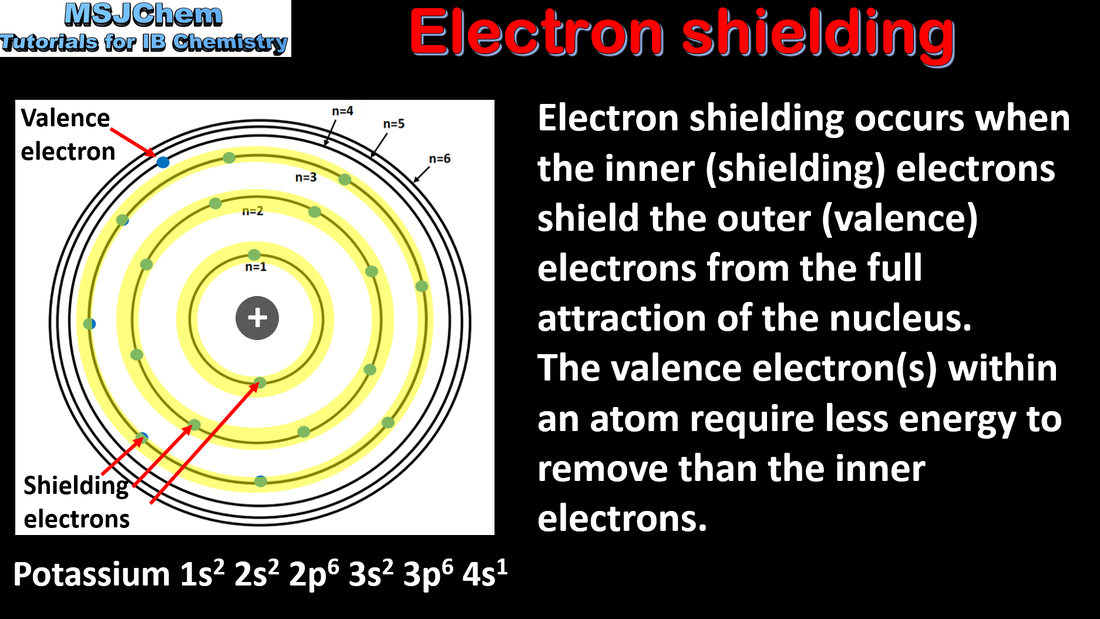
3.2 Electron shielding and effective nuclear charge
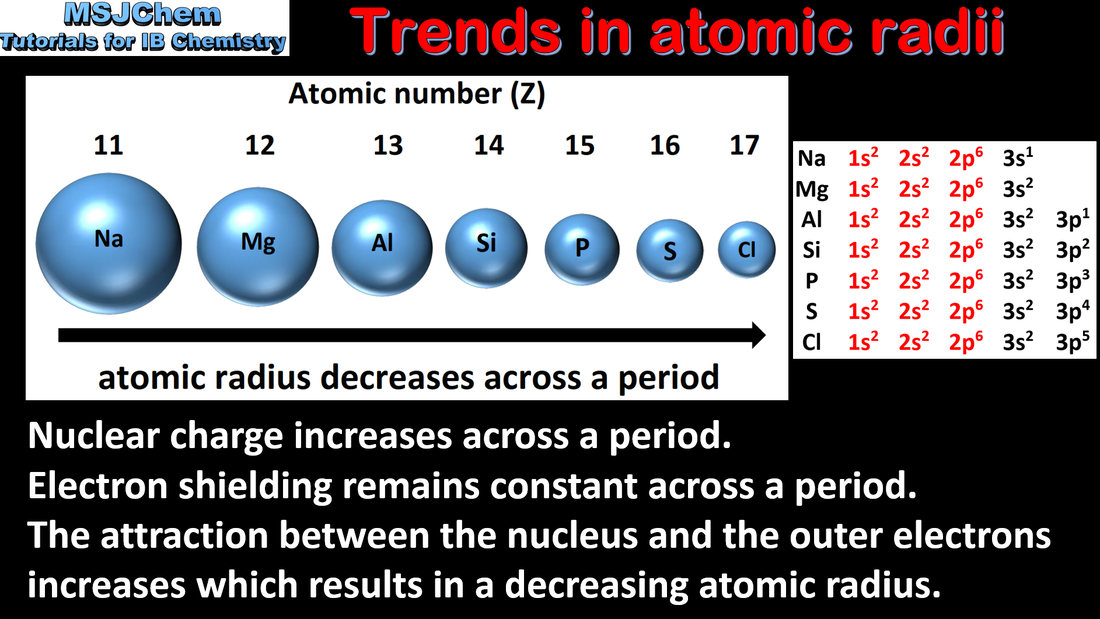
3.2 Trends in atomic radii
| trends_in_atomic_and_ionic_radius.pdf |
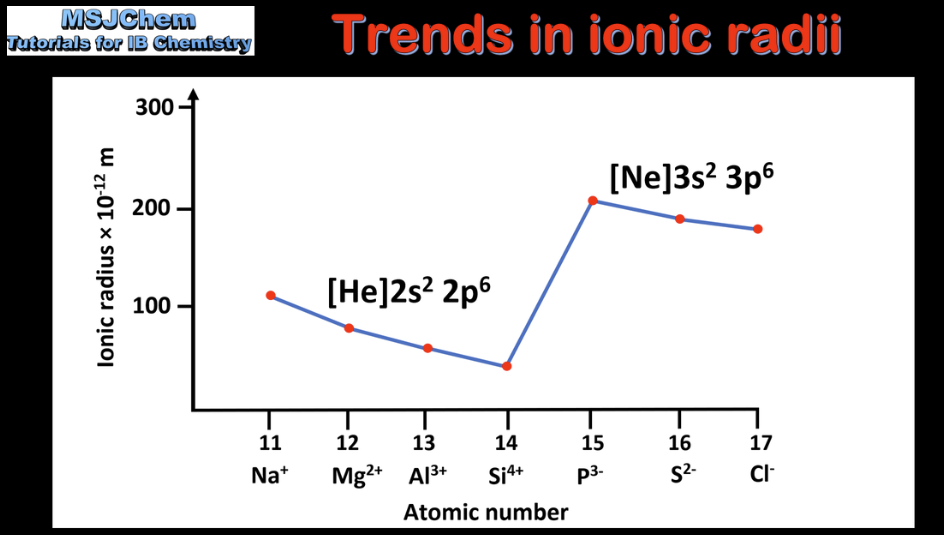
3.2 Trends in ionic radii
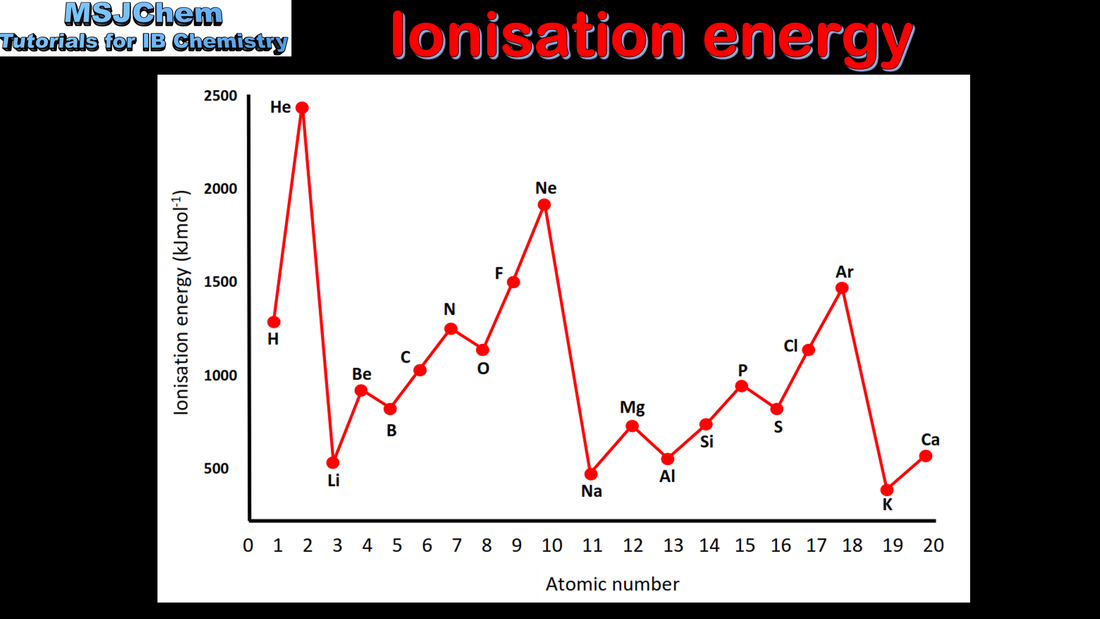
3.2 Trends in ionisation energy
This video covers the discontinuities in first ionisation energy
|
|
Guidance:
For ionization energy the discontinuities in the increase across a period should be covered. This video covers the exceptions to the trend in ionisation energy across a period. |
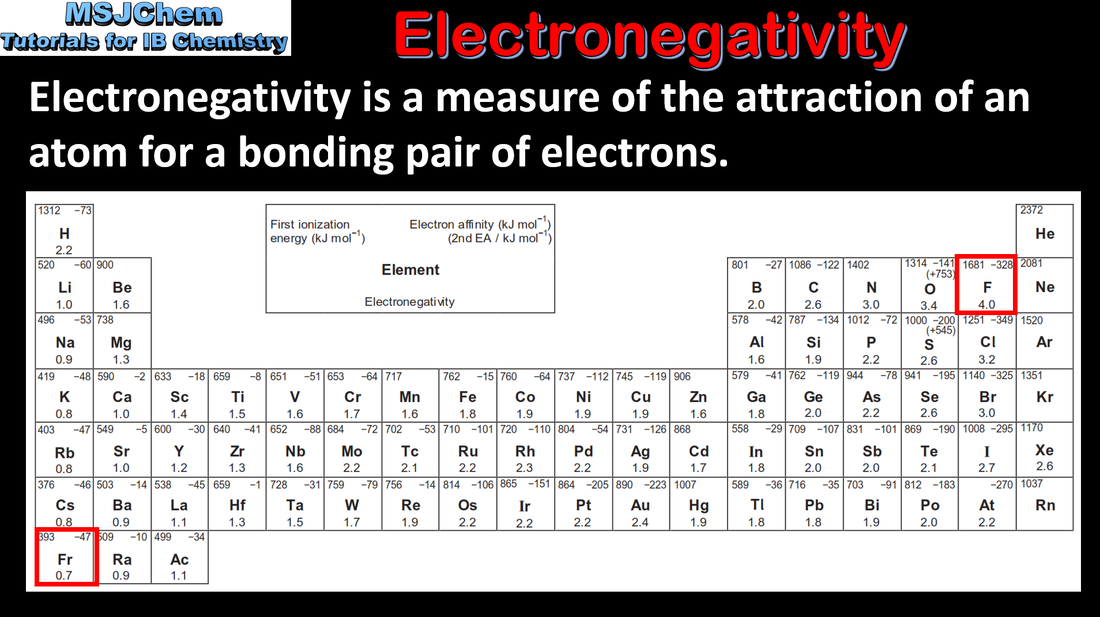
3.2 Trends in electronegativity
| topic_3_trends_in_electronegativity_and_electron_affinity.pdf |
3.2 Trends in electron affinity
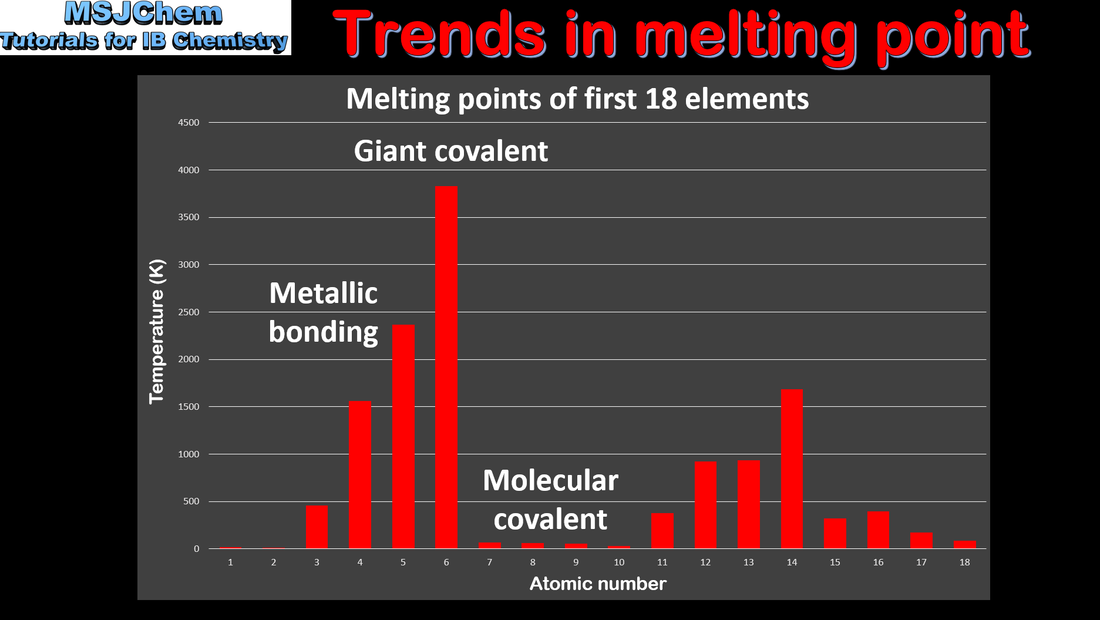
3.2 Trends in melting points
| topic_3_trends_in_melting_point.pdf |
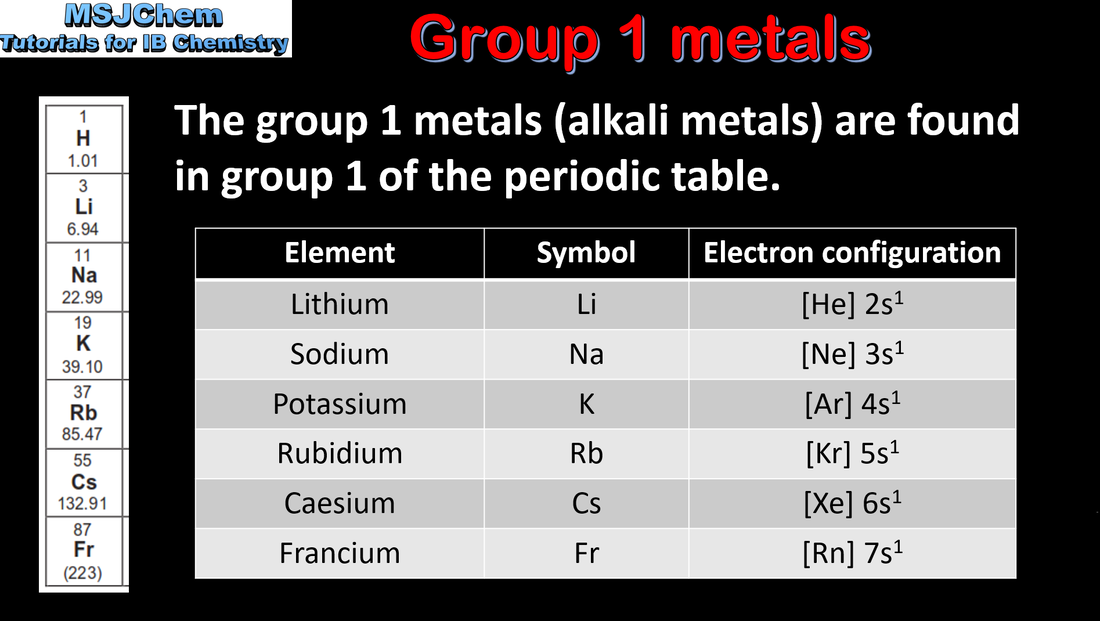
3.2 Group 1 elements - the alkali metals
|
Applications and skills:
Discussion of the similarities and differences in the properties of elements in the same group, with reference to alkali metals (group 1) and halogens (group 17). A note about Francium - it is a radioactive element with a very short half-life. More information can be found here. |
| topic_3_group_1_alkali_metals.pdf |
3.2 Group 17 elements - the halogens
| topic_3_group_17_elements.pdf |
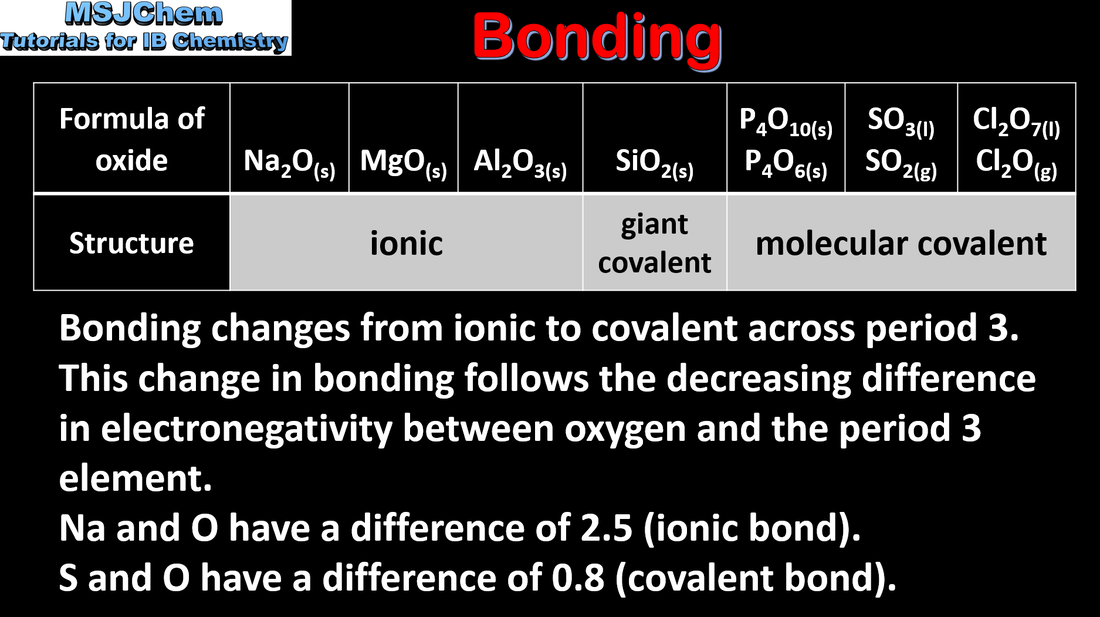
3.2 Bonding and acid-base properties of the period 3 oxides
| topic_3_bonding_of_the_period_3_oxides.pdf |